Stereographic projection facts for kids
A stereographic projection is a special way to draw a round, 3D shape, like a ball or the Earth, onto a flat, 2D surface, like a piece of paper. Imagine you have a clear ball and a flat sheet of paper. If you shine a light from one point on the ball, the shadow it casts on the paper is a stereographic projection. This method helps us see and work with round objects in a flat way.
This projection is used in many areas, including making maps, studying rocks in geology, and even in photography to create cool effects. Scientists and artists use it because spheres and flat surfaces appear often in mathematics and real-world problems. You can make these projections using a computer or by hand with a special kind of graph paper called a stereonet or Wulff net.

Contents
What is a Stereographic Projection?
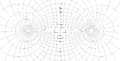
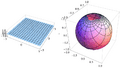
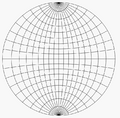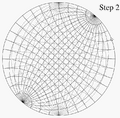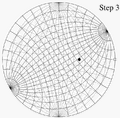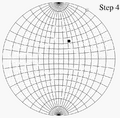
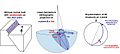
A stereographic projection is a type of function. It takes every point on a sphere (except for one special point) and maps it to a point on a flat plane. The special point that isn't mapped is called the projection point. It's like the spot where the light source is located when casting a shadow.
How Does It Work?
Imagine a sphere sitting on a flat surface. Pick a point on the sphere that will be your "light source" or projection point. This point is usually the very top or bottom of the sphere. To project any other point on the sphere, you draw a straight line from your projection point through that point on the sphere. Where this line hits the flat surface, that's where the point from the sphere is drawn on the plane.
The Projection Point
The projection point is super important. It's the only point on the sphere that doesn't get mapped to the flat plane. If you try to draw a line from the projection point through itself, it won't hit the plane. This is why the projection works for almost the entire sphere.
Where Do We Use Stereographic Projections?
Stereographic projections are very useful in different fields. They help us understand and work with 3D shapes in a 2D world.
Making Maps (Cartography)
One of the most common uses is in cartography, which is the science of making maps. The Earth is a sphere, but maps are flat. Stereographic projections are great for mapping areas near the North Pole or South Pole. They show shapes accurately in those areas, though they can stretch areas further away from the center.
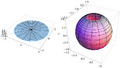
Studying Rocks (Geology)
In geology, scientists use stereographic projections to understand the orientation of rock layers, faults, and other features. Geologists can plot measurements from the field onto a stereonet. This helps them see patterns and relationships between different rock structures. It's like taking a 3D puzzle of rocks and laying it flat to see how the pieces fit.
Cool Photos (Photography)
You might have seen "tiny planet" photos. These are often created using a type of stereographic projection. A panoramic photo (a very wide picture) is wrapped onto a sphere. Then, it's projected onto a flat image, making it look like the scene is on a small planet.
Math and Science
In complex analysis, a part of advanced mathematics, the stereographic projection helps connect a sphere to a flat plane of numbers. This connection makes it easier to study certain mathematical problems. It's also used in other areas like crystallography, which is the study of crystals, to understand their 3D structures.
Images for kids
-
A "tiny planet" photo of a sculpture at Wikimania 2016.
See also
 In Spanish: Proyección estereográfica para niños
In Spanish: Proyección estereográfica para niños