The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints facts for kids
Quick facts for kids The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints |
|
|---|---|

Official logo since 2020 featuring the Christus statue
|
|
| Classification | Restorationist |
| Orientation | Latter Day Saint movement |
| Scripture |
|
| Theology |
|
| Polity | Hierarchical |
| Region | Worldwide |
| Founder | Joseph Smith |
| Origin | April 6, 1830 (as Church of Christ) Fayette, New York, U.S. |
| Other name(s) |
|
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints is a Christian church also known by the nicknames LDS Church or Mormon Church. Members believe it is the same church that Jesus Christ started, but restored to the earth in modern times. It is the largest church within the Latter Day Saint movement. The church's main offices are in Salt Lake City, Utah. It has congregations and special buildings called temples all over the world.
The church was started by Joseph Smith in 1830. Members, who are called Latter-day Saints, believe that Joseph Smith was a modern prophet chosen by God. He translated a sacred book called the Book of Mormon. Along with the Bible, the Book of Mormon is one of the main books of scripture for the church.
Latter-day Saints believe that the president of the church is a modern-day prophet who receives guidance from God. Members try to follow Jesus Christ's teachings. They focus on the importance of families and helping others. The church has a large missionary program and is known for its humanitarian aid around the world.
Contents
History

How the Church Began
The church began with a young man named Joseph Smith. He said that when he was 14 years old, he had a vision where God the Father and Jesus Christ appeared to him. This is known as the First Vision. Later, he said an angel named Moroni guided him to a set of buried golden plates. Joseph Smith translated the writing on these plates, and the translation was published as the Book of Mormon.
On April 6, 1830, Joseph Smith officially organized the church in New York. The church grew quickly, but its members often faced conflict with their neighbors. Because of this, they moved several times, first to Ohio, then to Missouri, and finally to Illinois. In Illinois, they built a large city called Nauvoo.
On June 27, 1844, Joseph and his brother Hyrum were killed by a mob while they were in jail in Carthage, Illinois. After their deaths, the church members had to decide who would be their next leader. Most chose to follow Brigham Young, who was the senior apostle.
The Pioneer Journey West

After Joseph Smith's death, conflicts continued in Illinois. Brigham Young led his followers, known as the Mormon pioneers, on a long journey west. In 1847, they arrived in the Salt Lake Valley in what is now the state of Utah. At the time, this land was home to Native American tribes like the Ute, Goshute, and Shoshone.
The pioneers worked hard to build new communities in the desert. They built homes, farms, and eventually the Salt Lake Temple. From Utah, groups of Latter-day Saints spread out and settled in many areas of the western United States.
During this time, some church leaders practiced plural marriage, where a man could be married to more than one woman. This was a source of conflict with the U.S. government. In 1890, the church president, Wilford Woodruff, announced that the church would stop the practice. This helped improve relations with the government, and Utah became a U.S. state in 1896.
The Church in Modern Times
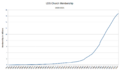
In the 20th and 21st centuries, the church has grown into a worldwide organization with millions of members. It has built temples in many countries and sends out tens of thousands of missionaries.
The church has also made some important changes. In 1978, the church announced that all worthy male members of any race could be ordained to the priesthood. Before this, men of Black African descent were not allowed to hold the priesthood.
Today, the church continues to emphasize the importance of family, missionary work, and serving others through its large humanitarian aid program.
What Latter-day Saints Believe

God, Jesus Christ, and the Holy Ghost
Latter-day Saints believe in God the Father, his Son Jesus Christ, and the Holy Ghost. They believe these three are separate beings who are perfectly united in their purpose. This is different from the traditional Christian belief in the Trinity, which teaches that God is one being in three persons. They believe God the Father and Jesus Christ have perfect, glorified bodies of flesh and bone.
Members of the church worship Jesus Christ as the Son of God and the Savior of the world. They believe He is the head of the church and leads it today through revelation to a living prophet.
The Plan of Salvation
The church teaches a "plan of salvation," which is God's plan for his children. This plan includes:
- Premortal Life: We lived as spirits with God before we were born.
- Mortal Life: We came to Earth to get a physical body, learn, and make choices.
- Life After Death: After we die, our spirits go to the spirit world. After the resurrection, we will be judged and can return to live with God.
A key part of this plan is that families can be together forever. Through special ceremonies in temples, marriages and family relationships can be "sealed" to last for eternity.
Restoration of the Church
Latter-day Saints believe that after Jesus and his original apostles died, the true church and its authority were lost from the earth. They call this the "Great Apostasy." They believe that in the 1820s, God the Father and Jesus Christ appeared to Joseph Smith to begin the "Restoration" of the original church. This is why the church is called a "restorationist" faith.
Scriptures
The church uses four main books of scripture, called the "standard works":
- The Bible (the King James Version is most commonly used).
- The Book of Mormon, which they believe is another testament of Jesus Christ and a record of God's dealings with ancient peoples in the Americas.
- The Doctrine and Covenants, a collection of modern revelations from God to his prophets.
- The Pearl of Great Price, which contains other writings of Joseph Smith and ancient prophets.
Church Practices and Lifestyle
Worship Services
Church members meet on Sundays in buildings called meetinghouses. The main worship service is called "Sacrament meeting." During this meeting, members sing hymns, pray, and listen to talks from other members. They also partake of the sacrament (bread and water) to remember Jesus Christ's sacrifice. There are also Sunday School classes for different age groups.
Temples

Temples are the most sacred buildings for Latter-day Saints. They are considered the "House of the Lord." Unlike regular meetinghouses, temples are not open to the general public. Only members who live the church's standards can enter. Inside temples, members make sacred promises to God and participate in ceremonies like eternal marriage.
Missionary Work
The church is well-known for its missionary program. Many young men serve full-time missions for two years, and young women can serve for 18 months. They are sent to locations all over the world to teach others about the gospel of Jesus Christ. Older couples can also serve missions.
Word of Wisdom
Members follow a health law called the Word of Wisdom. This includes not drinking alcohol, coffee, or tea, and not using tobacco or harmful substances. The Word of Wisdom also encourages eating healthy foods like grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Tithing and Donations
Members are asked to give ten percent of their income to the church. This is called "tithing." These funds are used to build churches and temples, print scriptures, and run the church's programs. Members also donate to help the poor and needy through "fast offerings."
Family Life
Families are very important in the church. Members are encouraged to hold a "Family Home Evening" once a week, usually on Monday nights. This is a time for families to learn about the gospel, have fun together, and strengthen their relationships.
Church Organization
Leadership
The church is led by a president, who members believe is a "prophet, seer, and revelator." He is assisted by two counselors. Together, they form the First Presidency. The next governing body is the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles. When a president dies, the longest-serving apostle becomes the new president.
Local congregations are called "wards" or "branches." A ward is led by a volunteer leader called a "bishop." Several wards in an area make up a "stake," which is led by a "stake president."
Priesthood and Service
Worthy male members age 11 and older can be ordained to the priesthood, which is the authority to act in God's name. Women do not hold priesthood offices but serve in many important leadership and teaching roles in the church's organizations for women (Relief Society), youth (Young Women), and children (Primary). Nearly all positions in the church are filled by volunteer members who receive a "calling," or an assignment to serve.
Humanitarian Services
The church provides humanitarian aid to people in need around the world, regardless of their religion. It helps with disaster relief after events like earthquakes and hurricanes. It also runs long-term projects to provide clean water, food, vision care, and wheelchairs to communities in developing countries. These efforts are funded by donations from church members. In 2022, the church gave $32 million to the United Nations World Food Programme to help fight hunger.
Images for kids
-
Carthage Jail, where Joseph Smith was killed in 1844.
-
A 19th-century painting of Mormon pioneers crossing the plains of Nebraska.
-
A couple after their marriage in the Manti Utah Temple. The church teaches that marriages performed in temples can continue after death.
-
The inside of a typical Sunday sacrament meeting in Provo, Utah.
-
The campus of Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah, one of several schools run by the church.
-
Deseret Book Company headquarters in Salt Lake City.
-
Church president Thomas S. Monson (left) and apostle Dallin H. Oaks (right) meeting with U.S. president Barack Obama in 2009.
See also
 In Spanish: La Iglesia de Jesucristo de los Santos de los Últimos Días para niños
In Spanish: La Iglesia de Jesucristo de los Santos de los Últimos Días para niños
- Index of articles related to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- List of temples of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- List of missions of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- Christianity in the United States
- Anti-Mormonism
- List of attacks against Latter-day Saint churches
- Mormon (word)
- Mormonism and Islam
- Mormonism and Judaism
- List of new religious movements