Uapaca kirkiana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Uapaca kirkiana |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Malpighiales |
| Family: | Phyllanthaceae |
| Genus: | Uapaca |
| Species: |
U. kirkiana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Uapaca kirkiana Müll. Arg.
|
|
 |
|
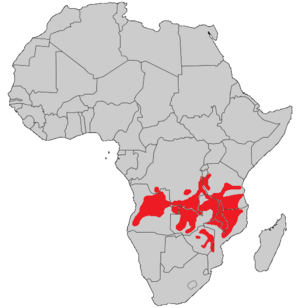
| approximate range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Uapaca kirkiana, also known as the sugar plum or mahobohobo, is a special kind of plant. It belongs to the Phyllanthaceae family. This plant grows naturally in the southern parts of Africa, in areas called miombo woodlands where there is enough water.
The sugar plum fruit is one of the most liked wild fruits in these regions. People don't often grow it on farms. Instead, when land is cleared, these trees are usually left standing. This fruit is a traditional food in Africa. Even though it's not very well-known globally, it can help people get more nutrients. It also helps with food security and supports local communities.
In the Shona language, the fruit is called mazhanje. In Chichewa, it's known as masuku.
Contents
Where Does the Sugar Plum Grow?
This tree is found in the miombo woodlands. You can find it in countries like Angola, the DRCongo, Zambia, southern Burundi, Tanzania, Malawi, central and northern Mozambique, and Zimbabwe.
How the Sugar Plum Tree Grows
The sugar plum tree is a dioecious plant. This means it has separate male and female trees. Male trees have flowers that produce pollen, and female trees have flowers that grow into fruit.
These trees can grow quite tall, usually between 5 and 13 meters (about 16 to 43 feet). Their trunks can be 15 to 25 centimeters (about 6 to 10 inches) wide. The leaves are dark green and shiny, measuring 12 to 36 cm long and 8 to 24 cm wide.
Sugar plum trees are strong and don't often get attacked by pests. They need more than 600mm of rain each year to grow well. They prefer sandy or gravelly soils that drain water easily and don't have much organic material. If you see these trees growing, it often means the soil isn't great for farming other crops.
The Delicious Sugar Plum Fruit
Female sugar plum trees start to produce fruit when they are about 9 to 10 years old from a seed. The fruit is round, about 2 to 4 centimeters (about 1 to 1.5 inches) across. It starts green and turns yellow or brown when it's ripe.
When the fruit is ready to eat, it has a thin, hard shell, only about 1.5mm thick. Inside, there's yellow, sweet flesh. Many people say it tastes like a pear or a plum! Each fruit usually has 3 or 4 seeds inside, but sometimes it can have 5. The fruits can weigh from 5 to 50 grams each, with the edible part being 0.2 to 30 grams. Wild animals, like monkeys, also love to eat these fruits.
How Sugar Plum Trees Reproduce
Most sugar plum trees grow from seeds. The seeds sprout easily, and about 90% of fresh seeds will grow into new plants within 6 weeks.
It's also possible to grow these trees using other methods:
- Grafting: This is when a part of one tree is joined to another. About 80% of these attempts have been successful.
- Air Layering: This method involves making a part of a branch grow roots while still attached to the parent tree. However, trees grown this way don't always do well because they don't have a strong main root.
The tree can also spread naturally underground. It sends out new shoots from its roots, forming groups of trees.
Developing New Varieties
Not much work has been done to create new types of sugar plum trees, though some special varieties do exist. Since 1996, scientists have been working in Malawi, Tanzania, Zambia, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. They are trying to find and grow the best sugar plum seedlings. This work is part of the Southern Africa Regional Programme.
Who is the Sugar Plum Named After?
The Uapaca kirkiana species is named in honor of Sir John Kirk. He was a famous explorer and naturalist who lived from 1832 to 1922.
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |

