Vigna subterranea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Vigna subterranea |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Vigna |
| Species: |
V. subterranea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
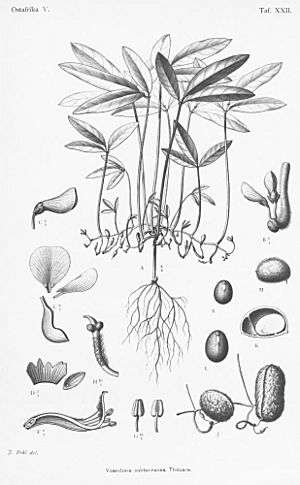
The Bambara groundnut (also called Bambara nut or earth pea) is a special plant from the Fabaceae family, which includes beans and peas. It first grew in West Africa. Just like peanuts, its pods grow and ripen underground! People can eat Bambara groundnuts fresh, or boil them after they've been dried. You can even grind them into a powder to make tasty puddings.
Contents
Where Bambara Groundnuts Grow
The Bambara groundnut started in West Africa. Today, it grows mostly in the warm, tropical parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. It thrives wherever peanuts grow, so you'll find lots of it in northern Nigeria and northern Ghana.
Why This Plant is Important
Bambara groundnut is the third most important bean-like crop in dry parts of Africa. It can handle hot weather and grows well in poor soils where other crops might struggle. This makes it a very helpful plant for farmers.
Bambara groundnuts are super nutritious! They are packed with carbohydrates (about 58% to 62%) and protein (about 24% to 25%). This makes them a great food source. Some studies also show that parts of the plant can help fight off certain germs like Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus.
How People Use Bambara Groundnuts
Cooking and Eating Them
People use the seeds of Bambara groundnuts for food and drinks because they have so much protein. The whole plant is also good for the soil because it helps add nitrogen.
In West Africa, people often eat the nuts as a snack. They might roast them with salt, or make them into cakes. They can also be boiled like other beans to make a meal.
In South Eastern Nigeria, especially in Enugu, dried Bambara beans are ground into a fine powder. This powder is then mixed with palm oil, water, and pumpkin leaves. This mixture is wrapped in banana leaves or plastic bags and boiled to make a popular breakfast food called okpa. During the rainy season in central Nigeria, fresh Bambara beans are cooked with their shells still on and eaten as a snack.
What the Plant Needs to Grow Well
Soil Requirements
Bambara groundnuts grow best in sandy soils. This helps prevent too much water from sitting around the roots. The soil should be about 50 to 100 centimeters deep and have a light texture. It doesn't need very rich soil. The best soil pH for it is between 5 and 6.5.
Climate Requirements
This plant loves tropical and subtropical climates. The best temperatures for growing Bambara groundnuts are between 19°C and 30°C. They don't do well in temperatures below 16°C or above 38°C.
Bambara groundnuts are very good at surviving dry periods. They need at least 300 millimeters of rain each year, but ideally between 750 and 1400 millimeters. They shouldn't get more than 3000 millimeters of rain.
How Farmers Grow Them
Farmers can grow Bambara groundnuts by themselves or mix them with other crops. This is called intercropping. Some good crops to grow with Bambara groundnuts include sorghum, millet, maize, peanuts, yams, and cassava.
When grown with other crops, farmers usually plant between 6 and 29 Bambara groundnut plants in every square meter. In places like Côte d'Ivoire, planting about 25 plants per square meter gives the best harvest.
World Production
The amount of Bambara groundnuts grown around the world has increased a lot. In 1972, about 29,800 tonnes were produced, and by 2015, this went up to 79,155 tonnes.
| Production Year 2013 (Source FAOSTAT) | Area Harvested (Ha) | Yield (kg/ha) | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120,000 | 9,498 | 113,981 | |
| 68,000 | 4,412 | 30,000 | |
| 55,000 | 8,909 | 49,000 | |
| 43,392 | 8,444 | 36,639 | |
| 4,828 | 750 | 14,000 | |
| World | 315,392 | 7,724 | 243,620 |
Bambara Groundnut Life Cycle
Growth and Development
The Bambara groundnut plant takes about 90 to 170 days to grow from a seed to mature pods. In perfect conditions, this cycle is around 120 to 150 days. The flowers usually appear about 40 to 60 days after the plant is put in the ground. About 30 days after a flower is pollinated, the pod becomes fully grown. Then, it takes another 55 days for the seeds inside the pod to fully develop. New pods are produced every 30 days.
How They Reproduce
Bambara groundnuts reproduce by self-fertilization. This means they can pollinate themselves without needing another plant or an insect to carry pollen. They are also self-pollinating, which means their flowers can pollinate themselves even without opening.
Images for kids
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |




