Wind turbine facts for kids
A wind turbine is a big machine that spins around. It uses the power of the wind to make energy. Think of it like a giant fan, but instead of using electricity to spin, it uses the wind to make electricity!
When the wind makes the turbine's blades spin, it creates mechanical energy. If this energy is used directly, like to pump water or grind grain, it's called a windmill. But if the mechanical energy is changed into electricity, then it's called a wind turbine generator or wind energy converter. These machines help us get clean energy from the wind.
Contents
How Wind Turbines Make Electricity
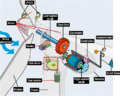
Wind turbines work by catching the wind with their large blades. When the wind pushes the blades, they start to spin. This spinning motion turns a long rod inside the turbine, called a shaft.
From Slow Spin to Fast Power
The shaft turns quite slowly, usually about 10 to 20 times per minute. But it has a lot of turning force, called torque. This slow-turning shaft goes into a special part called a gearbox. The gearbox is like the gears on a bicycle; it makes things spin faster. It takes the slow spin of the shaft and speeds it up a lot, usually about 50 times faster! So, the gearbox makes another shaft spin around 1000 times per minute.
Generating the Electricity
This faster-spinning shaft is connected to an electric generator. The generator is the part that actually makes the electricity. It works by using magnets and coils of wire to create an electric current when it spins.
Sending Power to Homes
Once the electricity is made, it's often combined with electricity from other wind turbines in the same area. This group of turbines is called a wind farm. The combined electricity can be used nearby, or it can be sent to the main power grid. The power grid is like a huge network of wires that carries electricity to homes and businesses everywhere.
Small Turbines for Homes

Small wind turbines are useful for many things. They can power homes (whether connected to the grid or not), cell phone towers, offshore platforms, rural schools, and other places far from the main power lines. Some are as small as 50-watt generators for boats or RVs. You might see hybrid solar- and wind-powered units on traffic signs in rural areas, as they don't need long cables. The U.S. Department of Energy considers small wind turbines to be those 100 kilowatts or less. These smaller units often have simple generators, make direct current (DC) electricity, and use a wind vane to point into the wind.
Wind Power: Good and Bad Points
Why Wind Power is Great
Wind turbines are one of the cheapest ways to get renewable energy, along with solar panels. As the technology gets better, the prices keep going down. Wind is a free natural resource, so there's no cost for the "fuel." The main cost for small turbines is buying and installing them, which usually pays off over time with the energy they produce.
Wind turbines provide clean energy. They use very little water and don't release greenhouse gases or waste products while they are running. Using a one-megawatt turbine instead of a fossil fuel power plant can prevent over 1,500 tons of carbon dioxide from entering the air each year!
Challenges of Wind Power
Wind turbines can be very large. Some are over 260 meters (853 feet) tall with blades 110 meters (361 feet) long. Some people don't like how they look in the landscape.
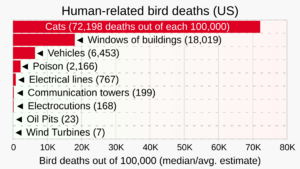
Wind turbines can affect wildlife, especially birds and bats. However, if wind farms are planned carefully, these effects can be reduced. Studies show that wind turbines cause far fewer bird deaths than other human activities, like cats or cars. For example, wind farms cause about 0.3 to 0.4 bird deaths per gigawatt-hour of electricity, while fossil fuel power plants cause about 5.2 deaths per gigawatt-hour. A study from 2000 to 2020 found that wind turbines did not significantly affect bird populations in the United States.
The amount of energy from wind turbines can change because the wind doesn't always blow. This means wind power isn't always available exactly when electricity is needed. However, wind energy can be part of a mix of different power sources. New technologies are also being developed to store extra wind energy for later use.
Wind turbines have blinking lights to warn aircraft. Some people living near wind farms find these lights annoying. New systems are being developed that only turn on the lights when an aircraft is detected nearby by radar.
Amazing Wind Turbine Records
See also List of most powerful wind turbines
| Record | Model/Name | Location | Constructor/Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Largest and most powerful | MYSE18.X-20MW | Hainan, China | Mingyang Wind Power |
| Largest vertical-axis | Éole | Cap-Chat, Québec, Canada | NRC, Hydro-Québec |
| Largest 1-blade turbine | Monopteros M50 | Jade Wind Park | MBB Messerschmitt |
| Largest 2-blade turbine | SCD6.5 | Longyuan Wind Farm | Mingyang Wind Power |
| Most rotors | Four-in-One | Maasvlakte, Netherlands | Lagerwey |
| Highest-situated | 2.5 | Pastoruri Glaicer | WindAid |
| Largest offshore | MySE18.X-20MW | Hainan, China | Mingyang Wind Power |
| Tallest | Schipkau GICON Wind Turbine | Schipkau, Germany | Vensys, GICON |
Interesting facts about wind turbines
- A study from 2009 even found that wind power had the "lowest greenhouse gas emissions" and was good for the environment compared to other energy sources.
- Wind power arrived in Europe during the Middle Ages. Records show them being used in England in the 11th and 12th centuries.
- Over time, a turbine's efficiency might drop a little. This can happen if dust or insects build up on the blades, changing their shape.
- Turbines work best in steady, constant wind. This is why choosing the right location is so important. Places near the shore or on mountain ridges often have stronger, more consistent winds.
- The higher a turbine is, the faster the wind usually blows.
- Offshore wind turbines today can be up to 8 MW and have blades up to 80 meters (262 feet) long. Even larger designs, like a 15 MW+ prototype with 118-meter (387-foot) blades, are being developed.
- The average height of the center of a horizontal turbine is about 90 meters (295 feet).
- In 2021, the longest blade measured 115.5 meters (379 feet) and could help produce 15 MW of power.
- Blades usually last about 20 years, which is the typical lifespan of a wind turbine.
- The Bahrain World Trade Center is the first skyscraper to have wind turbines built right into its design!
- When turbines are taken out of use, about 85% of their materials can be reused or recycled. The blades, made of a composite material, are harder to recycle. However, companies and researchers are finding new ways to reuse or recycle them.
Images for kids
-
The rotor of a gearless wind turbine being set up.
-
A Nordex wind turbine manufacturing plant in Jonesboro, Arkansas, United States
-
The Nordex N50 wind turbine and visitor centre of Lamma Winds in Hong Kong, China
-
A small Quietrevolution QR5 Gorlov type vertical axis wind turbine in Bristol, England.
-
Fuhrländer Wind Turbine Laasow, in Brandenburg, Germany, one of the world's tallest wind turbines
See also
 In Spanish: Turbina eólica para niños
In Spanish: Turbina eólica para niños
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |