Electric power facts for kids
Electric power is about how fast electrical energy is used or produced. Think of it as the speed at which electricity does work. It's a very important part of our daily lives.
When electricity flows through a path called a circuit, it can be slowed down by something called resistance. This resistance helps devices change the electricity into useful things. For example, it can create heat, light, movement, or sound.
The standard unit for measuring electric power is the watt. You might see this on light bulbs or appliances. Other units related to power are the joule for energy, the second for time, and the ampere for electric current.
Contents
What is Electric Power?
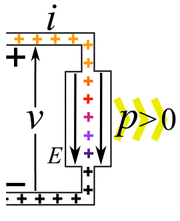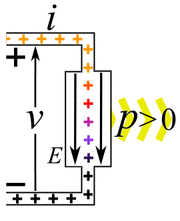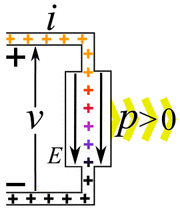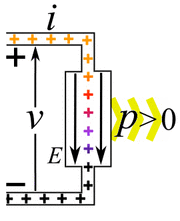
Electric power is simply the rate at which work is done by electricity. It tells us how much energy is being used or created each second. We measure electric power in watts. The letter P often stands for power in science. Sometimes people use the word wattage to mean the amount of electric power in watts.
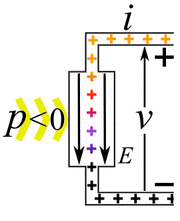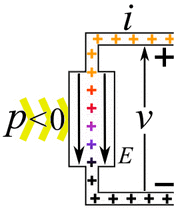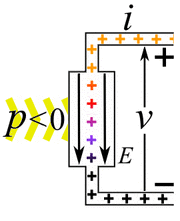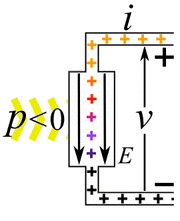
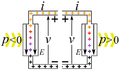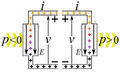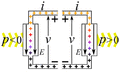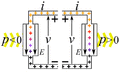
Imagine you have an electric current flowing. This current is made of tiny electric charges moving. If these charges move through a difference in electric potential (which we call voltage), they do work. The amount of power depends on how much current is flowing and the voltage difference.
How Electricity Works in Devices
Electric power changes into other forms of energy when electric charges move through a voltage difference. This happens inside electrical parts in circuits. We can put these parts into two main groups:
- Passive devices or loads: These devices use electric power. When electric charges move from a higher voltage to a lower voltage, the device uses that energy. It turns the electrical energy into something else. This could be mechanical work, heat, or light. Examples include light bulbs, electric motors, and electric heaters. They "consume" electricity.
- Active devices or power sources: These devices create electric power. Here, an outside force pushes charges from a lower voltage to a higher voltage. This process changes other types of energy, like mechanical energy or chemical energy, into electrical energy. Examples are electric generators and batteries. They "provide" electricity.
Some devices can act as both! For instance, a rechargeable battery gives power when you use it. But when you charge it, it acts like a load, taking in power.
How Electricity is Made
A scientist named Michael Faraday discovered the main ideas behind making electricity in the 1820s and 1830s. His basic idea is still used today. It involves moving a wire or a copper disc between the ends of a magnet. This movement creates electricity.
Most electricity is made at a power station. Large generators spin to create it. These generators are often powered by heat engines. These engines get their heat from burning fuels, geothermal power (heat from the Earth), or nuclear fission (splitting atoms). Other generators use the kinetic energy of flowing water (like in a dam) or wind (like in a wind turbine). There are also solar panels that turn sunlight directly into electricity.
A battery is another way to get electric power. It uses electrochemical cells to change stored chemical energy into electrical energy. The first battery was invented in 1800 by Alessandro Volta. Batteries are now used in many homes and industries. There are two main types:
- Primary batteries (disposable batteries): You use these once and then throw them away.
- Secondary batteries (rechargeable batteries): You can charge these many times and use them again.
Batteries come in all sizes, from tiny ones for hearing aids to huge ones that power large computer centers.
The Electric Power Industry
The electric power industry is in charge of making and delivering electricity. They make sure there's enough power for everyone who needs it. This power is sent through a grid connection. The grid is like a huge network of wires and stations that brings electricity to homes and businesses.
This industry is often seen as a public utility. This means it provides an essential service to the public.
Why We Use Electric Power
Most homes and businesses, especially in developed nations, need electric power. We rely on it for almost everything!
Electricity powers our home appliances like refrigerators and washing machines. It runs office equipment and industrial machinery. It also provides energy for lighting, heating, and cooking. Because electricity is so important for daily life, the electric power industry is a key part of a country's infrastructure.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Potencia eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Potencia eléctrica para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |