2003 San Simeon earthquake facts for kids

The earthquake caused significant damage to Pan Jewelers upon collapse of the Acorn Building
|
|
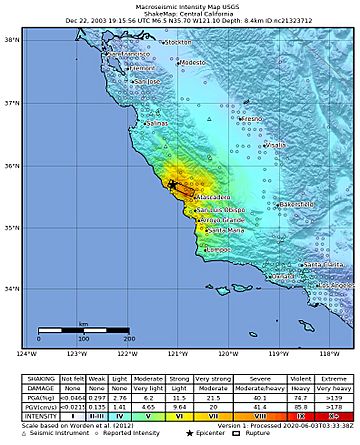
ShakeMap made by the United States Geological Survey for the earthquake
|
|
| UTC time | 2003-12-22 19:15:56 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 7215050 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | December 22, 2003 |
| Local time | 11:15 |
| Magnitude | 6.6 Mw |
| Depth | 10 mi (16 km) |
| Epicenter | 35°37′N 121°04′W / 35.62°N 121.07°W |
| Type | Blind thrust |
| Areas affected | Central Coast (California) United States |
| Total damage | $250–300 million |
| Max. intensity | VIII (Severe) |
| Casualties | 2 killed 40 injured |
The 2003 San Simeon earthquake was a strong earthquake that hit the Central Coast of California on December 22, 2003. It happened at 11:15 AM PST. The earthquake's center was about 7 miles (11 km) northeast of San Simeon.
This earthquake was caused by a thrust fault. This is when one block of Earth's crust pushes up and over another. The shaking was strongest within 50 miles (80 km) of where the earthquake started. People felt the earthquake as far away as Los Angeles. With a moment magnitude of 6.6, it was a very powerful quake.
Contents
Understanding the Earthquake
What is a Fault?
The Earth's outer layer, called the crust, is made of huge pieces called tectonic plates. These plates are always moving slowly. A fault is a crack in the Earth's crust where these plates slide past each other. When they get stuck and then suddenly slip, it causes an earthquake.
The San Simeon earthquake happened in an area with many faults. It was likely caused by movement in the Oceanic Fault zone. This area is within the Santa Lucia Mountains.
How Strong Was It?
The earthquake had a magnitude of 6.6. This number tells us how much energy the earthquake released. A 6.6 magnitude earthquake is considered strong. It was the most damaging earthquake in the United States since the Northridge earthquake of 1994.
Damage Caused by the Quake
The area closest to the earthquake's center did not have many people living there. So, the worst damage happened in Paso Robles, which was about 24 miles (39 km) away.
Buildings Collapsed
Sadly, two women died in Paso Robles when the Acorn Building collapsed. This building was very old, built in 1892, and was made of unreinforced masonry. This means it did not have extra support to help it stand during an earthquake. Many other old buildings made of the same material were also badly damaged.
However, buildings that had even some earthquake-proofing did not collapse. This shows how important it is to make buildings safer for earthquakes.
Hot Springs Erupt
Something unusual happened in Paso Robles after the earthquake. Two hot springs erupted! One was under a parking lot near the city hall. Hot water and mud shot out, creating a large sinkhole. This put the building in danger. It took many years to fix this damage and fill the hole. Another hot spring flowed out near U.S. Route 101.
Other Damage
Many other old buildings in Paso Robles' historic downtown were also damaged. Buildings as far as 40 miles (64 km) away in San Luis Obispo had minor damage, like ceiling tiles falling.
- Water tanks in Paso Robles, Templeton, and Los Osos were damaged.
- Most homes, which were usually one or two stories and made of wood, had little to no damage.
- The City Hall building in Atascadero was damaged and closed. It reopened in 2013 after many repairs.
- Some wineries near the earthquake's center reported damage. Barrels of wine fell over and broke.
- The historic Mission San Miguel Arcángel suffered about $15 million worth of damage.
- George H. Flamson Middle School's main building was so damaged it had to be torn down. A new building opened in 2010.
- Bethel Lutheran Church in Templeton also had major damage, and part of it had to be rebuilt.
After the Earthquake
After the earthquake, California passed a new law called Jenna's Bill. This law was named after Jennifer Myrick, one of the people who died in the quake. The law requires that certain old buildings that have not been made safer for earthquakes must put up a sign. This sign warns people about the possible earthquake danger.
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |

