Allegheny Plateau facts for kids
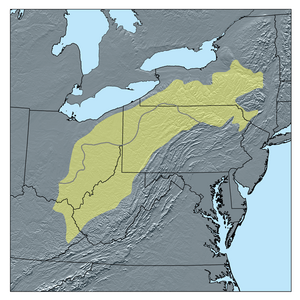
The Allegheny Plateau is a large, high area of land in the eastern United States. It stretches across parts of New York, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Ohio. Imagine a big, flat-topped mountain that has been carved up by rivers and streams over millions of years – that's a dissected plateau!
This huge plateau is split into two main parts: the glaciated Allegheny Plateau and the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau. The glaciated part was once covered by giant sheets of ice (glaciers) during the Ice Age. These glaciers smoothed out the land. The unglaciated part was not covered by ice, so it has more rugged hills and valleys.
The Allegheny Plateau also reaches south into Kentucky and Tennessee. In these states, it is known by a different name: the Cumberland Plateau.
To the east, the plateau ends at the Allegheny Mountains. These mountains are the highest ridges just west of a steep drop-off called the Allegheny Front. This "Front" runs from central Pennsylvania down through Maryland and into eastern West Virginia. To the west, the plateau meets flat plains in the north and the Bluegrass region in the south, near the Ohio River.
The height of the land on the Allegheny Plateau changes a lot. In the northern, glaciated areas, the hills might only be about 100 feet (30 meters) tall. But in the unglaciated parts of Ohio and West Virginia, the hills can be 200 to 400 feet (60 to 120 meters) high. The highest points in these areas are often between 900 and 1,500 feet (270 to 450 meters) above sea level. Near the Allegheny Front, the land gets much higher, reaching over 4,000 feet (1,200 meters) with steep drops of up to 2,000 feet (600 meters)!
What is the Allegheny Plateau?
The Allegheny Plateau is a special type of landform. It is part of a much larger area called the Appalachian Plateau province. This province is itself a big part of the Appalachian Mountains system. Think of it like a family tree: the Allegheny Plateau is a section of the Appalachian Plateau, which is a part of the greater Appalachian Mountains.
How Glaciers Shaped the Land
Millions of years ago, huge sheets of ice, called glaciers, moved across the northern parts of the Allegheny Plateau. These glaciers were like giant bulldozers. They scraped away rocks and soil, making the landscape smoother and less rugged. This is why the glaciated parts of the plateau have gentler hills and wider valleys.
In contrast, the southern parts of the plateau were never covered by these glaciers. Because of this, the rivers and streams there have had more time to carve deep valleys and steep hills. This gives the unglaciated areas a much more rugged and dramatic look.

See also
 In Spanish: Meseta de Allegheny para niños
In Spanish: Meseta de Allegheny para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |