Appalachian Plateau facts for kids
The Appalachian Plateau is a large area of high, flat land with many hills and valleys. It is found on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. These mountains stretch from Nova Scotia in Canada all the way to Alabama in the United States.
The Appalachian Plateau is the northwestern part of a larger natural land area called the Appalachian Highlands. It reaches from New York state down to Alabama. This plateau covers parts of many states. These include New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia.
Contents
What is the Appalachian Plateau like?
The Appalachian Plateau started to form a very long time ago, during the Paleozoic Era. During this time, the whole area slowly lifted up. But the land's surface stayed mostly the same.
The eastern side of the plateau looks like a mountain range. This is because of a very steep slope called the Allegheny Front. This eastern edge is the highest part of the plateau. In Pennsylvania, the land is about 1,750 to 3,000 feet high. It gets even higher in West Virginia, reaching around 4,800 feet. Further south, in Tennessee, it lowers to 3,000 feet. Then it slopes down to 1,000 feet in Alabama.
On the western side, the plateau is about 900 feet high in Ohio. It rises to about 2,000 feet in Kentucky. From Kentucky, it drops to 500 feet in northwestern Alabama. The plateau gently slopes towards the northwest. This means it is higher on its eastern side.
A big part of the plateau has lots of coal. This coal formed about 320 million years ago. This was during a time called the Pennsylvanian Age.
How was the land shaped?
Some parts of the plateau were covered by ice during the Pleistocene ice age. Because of this, these areas are flatter than the rest of the plateau. You can still see signs of the ice age here. These include bogs, lakes, and small hills made of sand and gravel.
Most of the plateau's rugged shape comes from streams cutting through the land. This has created a landscape with many narrow valleys. These valleys are surrounded by steep ridges.
In Kentucky, this region is known as the Eastern Kentucky Coalfield. It covers about 30% of Kentucky's land. Important parts include the Allegheny Plateau, the Cumberland Plateau, and the Cumberland Mountains. The highest points are in the Cumberland Mountains.
What are physiographic regions?
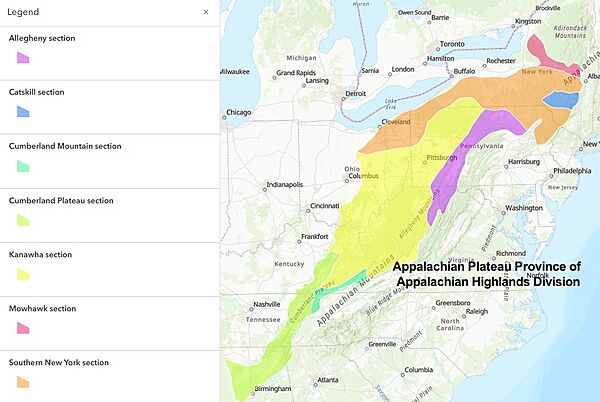
A physiographic region is a large area of land. It is grouped by similar geology, land shape (called topography), and types of plants and animals. The United States has eight main physiographic regions. These are divided into smaller areas called provinces. The Appalachian Plateau is one of these provinces. It belongs to the Appalachian Highlands region.
The Appalachian Plateau province is divided into seven sections. These are the Mohawk, Catskill, Southern New York, Allegheny Mountains, Kanawha, Cumberland Plateau, and the Cumberland Mountains. Each section shares similar features.
What is the geology of the plateau?
The rocks under the Appalachian Plateau have a base of very old Precambrian rock. On top of this are layers of sedimentary rock from the Paleozoic Era. There is a thick layer, about 20,000 feet deep, of different rocks. These include shale, siltstone, and sandstone.
When the Appalachian Mountains formed, the plateau was also lifted up. Many ridges and valleys that are part of the mountains continue under the plateau. There are also many valleys throughout the plateau itself. In these valleys, you can see exposed areas of limestone and shale.
History of the Appalachian Plateau
Early Native Americans
Scientists have found proof that Native Americans in the United States lived in the Appalachian region over 12,000 years ago. It is hard to know exactly when people first lived there. Human tools found near the Meadowcroft Rockshelter in southern Pennsylvania are at least 16,000 years old.
Early Native Americans were hunter-gatherers. They moved around to find food. This means they left few traces behind. This makes it hard for researchers to know exactly when they settled in this area.
During this time, North America was recovering from its last glacial period (ice age). The climate was much colder. It was like a tundra, with many conifer trees and large animals. These animals included mammoths and saber-toothed tigers.
Later, the climate became warmer. The large animals disappeared. The plants we see more often today began to grow. These changes made life easier for Native Americans. They kept inventing new tools and improving farming. This continued until Europeans arrived in North America.
European settlement
Europeans began to settle in North America in the 1600s. In 1749, Jacob Martin and Steven Sewell were the first Europeans known to settle in the Appalachian Plateau. They settled in what is now Pocahontas County, West Virginia.
When Europeans came, they competed with Native Americans for land. Many Native Americans died from new diseases. There were also more deaths and problems due to fighting. After the Native Americans were pushed out, European American settlers developed much of this land for farming.
From 1861 to 1865, the Appalachian Plateau was affected by the American Civil War. However, not much damage was done compared to other parts of the country. Union forces took control of most of the plateau during the war. This control was not challenged afterward. Only three major battles happened in the plateau region.
After the war, the coal industry grew very quickly. Many counties in the Appalachian Plateau, like McDowell County, West Virginia, became focused on coal mining. Mining towns were built. Many immigrants came to the region for work. Mining helped the economy, but it was very dangerous. Many miners died in accidents. One terrible event was the Monongah mining disaster in 1907.
Protecting the land
Protecting the Appalachian Region from human damage has become very important. People who care about nature have worked to save the wildlife in the Appalachia region. The plants and animals here can recover well if they are cared for.
However, around 1890, the forests of the Appalachian region were being destroyed. This was due to railroads, sawmills, and clear-cutting of trees. This caused big floods and wildfires. It also destroyed important animal and plant species.
The government realized this destruction was a big problem. So, in 1911, they passed the Weeks Act. This law allowed the government to buy private land. The goal was to protect rivers and watersheds in the eastern United States. The first land bought under this act was the Pisgah National Forest.
Later, the Wilderness Act of 1964 protected millions of acres of federal land. Examples include Shining Rock and Linville Gorge. The Eastern Wilderness Act of 1975 created more protected areas. These were in North Carolina, Virginia, and Tennessee. Today, about 21% of the region is protected.
Groups like the Southern Appalachian Forest Coalition work to preserve the Appalachian Plateau. Experts say the best way to keep protecting the region is to teach people about conservation. This helps everyone understand why saving these lands is important.
Wildlife of the Appalachian Plateau

The Appalachian region has many different plants and animals. This is because it has a wide range of climates and conditions. This gives the Appalachian Plateau great biodiversity.
Plants
In the northern parts of the plateau, you can find many conifer trees. These include red spruce and balsam fir. At lower elevations in the north, you will see northern hardwoods. Examples are sugar maple and white oak. In the southern Appalachia, sycamore, walnut, and hickory trees are common.
It is thought that there are about 2,000 types of plants in the Appalachia region. Flowers change depending on the elevation and climate. Different flowers grow in the northern and southern sections. Flowers like rhododendron, azalea, and mountain laurel are found in southern areas. Up north, trees will have serviceberry, redbud, sourwood, and many others.
Animals
Animals like bison and wolves used to live in the Appalachian region but are now gone. Elk have been brought back to some areas. They had died out because of too much hunting and loss of their homes.
Across the Appalachian Plateau, you can find many foxes, raccoons, wild boars, black bears, white-tailed deer, and beavers. Researchers have also found over 200 types of birds. These include wild turkeys, herons, geese, hawks, and ducks.
Fungi are also common in the Appalachia region. You can find many mushrooms and lichen. Some examples are chanterelle, oyster mushroom, and rock tripe.
Natural resources
The Appalachian Plateau has many natural resources. In its valleys, there is a lot of limestone. This limestone is still mined for cement and other building materials. Over time, some limestone areas have been used up. But some still have plenty.
Ironstone and coal are also common natural resources. In different parts of the plateau, dead plants built up to form peat. When this peat was buried, pressed, and heated, it turned into the coal found in the Appalachian coalfields. Because of all this coal, coal mining has been a very important industry here.
Iron ore was once very common. But because the iron layer was thin, most of it was used up over time. The land and soil of the Appalachian Plateau are also very valuable. The soil is rich and good for farming.
Within the limestone, many fossils of old plants can be found. This might help explain why the plateau also has a lot of natural gas and petroleum.
Landmarks and state parks

The Appalachian Plateau has many famous places and public parks. You can go camping, hiking, and sightseeing there.
Some notable state parks include Allegany State Park in New York. There is also Ohiopyle State Park in Pennsylvania. In Ohio, you can visit Hocking Hills State Park. Cooper's Rock State Forest is in West Virginia. Cloudland Canyon State Park is in Georgia. There are many more state parks and forests throughout the region. The Wayne National Forest and Allegheny National Forest are also on the Appalachian Plateau.
See also
 In Spanish: Meseta de los Apalaches para niños
In Spanish: Meseta de los Apalaches para niños