Red spruce facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Red spruce |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Picea |
| Species: |
P. rubens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Picea rubens |
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
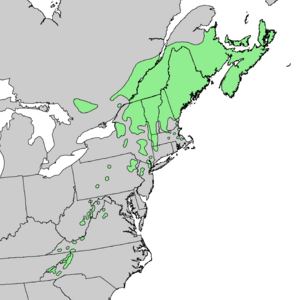
The red spruce (scientific name: Picea rubens) is a type of spruce tree. It grows naturally in eastern North America. You can find it from eastern Quebec and Nova Scotia in Canada, west to the Adirondack Mountains, and south through New England along the Appalachian Mountains to western North Carolina. People sometimes call it yellow spruce, West Virginia spruce, eastern spruce, or he-balsam.
Contents
What Does a Red Spruce Look Like?
The red spruce is a coniferous tree. This means it has needles instead of broad leaves and produces cones. It can live for many years and likes shady spots when it's young.
Under good conditions, these trees usually grow about 18 to 40 meters (60 to 130 feet) tall. Their trunks can be around 60 centimeters (2 feet) wide. Some very old trees can even reach 46 meters (150 feet) tall and 100 centimeters (3.3 feet) wide!
Red spruce trees have a narrow, cone-shaped top. Their leaves are like needles, about 12 to 15 millimeters (0.5 inches) long. They are yellowish-green, have four sides, and are slightly curved with a sharp tip. These needles stick out from all sides of the small branches.
The bark on the outside is gray-brown, but it's reddish-brown on the inside. It is thin and has small scales. The wood of the red spruce is light and soft. It has thin growth rings and a slight red color.
The tree's cones are shaped like cylinders. They are about 3 to 5 centimeters (1 to 2 inches) long. The cones are shiny, reddish-brown, and have stiff scales. They hang down from the branches.
Where Do Red Spruce Trees Live?
Red spruce trees grow slowly to moderately fast. They can live for a very long time, often 250 to over 450 years! Young red spruce trees can handle a lot of shade.
You often find red spruce growing in groups by themselves. They also grow in forests mixed with other trees. These include eastern white pine, balsam fir, or black spruce.
In the highest parts of the Southern Appalachian Mountains, red spruce is a main tree. It grows with Fraser fir in a special forest called the Southern Appalachian spruce–fir forest. This type of forest is only found in these high places.
Red spruce likes moist soil that drains well, often in high mountain areas. Strong winds can easily damage these trees. Also, acid rain can hurt them.
You can see famous red spruce forests in places like Gaudineer Scenic Area in West Virginia. Other spots include Canaan Valley, Roaring Plains West Wilderness, Dolly Sods Wilderness, Spruce Mountain, and Spruce Knob. Many of these areas are now seeing the red spruce forests grow back well.
Related Trees
The red spruce is very similar to the black spruce. When their growing areas meet, they often create hybrid trees. This means they mix their genes. Scientists think the red spruce became a separate species from the black spruce a long time ago. This happened during the Pleistocene Ice Age because of glaciation (when glaciers covered parts of the Earth).
How People Use Red Spruce
Red spruce trees are used in many ways:
- They are popular as Christmas trees.
- Their wood is very important for making paper pulp.
- The wood is also excellent for making musical instruments. It's called a "tonewood." You can find it in many high-quality acoustic guitars and violins.
- The sap from the tree can be used to make spruce gum.
- People boil the leafy twigs with sugar to make spruce beer.
- You can even make spruce pudding!
- The wood is also used for building materials, like millwork and crates.
The red spruce is the official provincial tree of Nova Scotia, Canada.
What Harms Red Spruce Trees?
Like most trees, red spruce can be attacked by insects. The spruce budworm is one insect enemy. However, it causes more problems for white spruce and balsam fir.
Two other big issues harming red spruce are acid rain and climate change.
Acid rain makes the soil less healthy for trees. It reduces important nutrients like calcium and increases harmful substances like aluminum. This happens because acid rain changes the balance of nutrients in the forest soil.
Calcium is very important for red spruce trees. It helps them breathe, resist cold, fight diseases, and build strong cells. But too much aluminum in the soil can be poisonous. It can also stop the tree's roots from taking in calcium and other nutrients. Studies have shown that red spruce trees die more often when there is too much aluminum in the soil.
In the 1980s, more acid rain led to many red spruce trees dying in high mountain areas. This was because calcium was washed out of the soil, making the trees less able to handle freezing temperatures. The shape of spruce needles also collects more acid rain, which makes the soil even more acidic.
Good news! Recently, there has been less acid rain. This has helped red spruce trees grow back in some mountain areas in the northeastern United States. This growth is linked to rain becoming less acidic. This shows that efforts to reduce air pollution have been working.
Protecting Red Spruce
Many groups are working together to bring back red spruce forests. The Central Appalachian Spruce Restoration Initiative (CASRI) is one such group. They want to restore these important forests across the high mountains of the central Appalachians. Many different partners are part of this effort, including government agencies and conservation groups.
A long time ago, in the late 1800s, West Virginia had about 600,000 hectares (1.5 million acres) of red spruce forests. But then, a lot of logging happened. The number of red spruce trees dropped to only 12,000 hectares (30,000 acres). Now, people are using special forestry methods to help the red spruce population grow back.
In western North Carolina, there have been big efforts to increase red spruce trees. Molly Tartt, a resident, found a forgotten red spruce forest. This forest of 50,000 trees was planted in 1940 as a memorial. Tartt helped to locate and identify this important forest.
See also
 In Spanish: Pícea roja para niños
In Spanish: Pícea roja para niños





