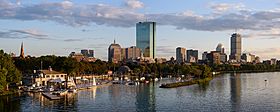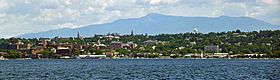New England facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
New England
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Left-right from top: Boston skyline, Portland Head Light in Cape Elizabeth, the Presidential Range, Burlington skyline, Aquinnah, the Connecticut River valley, skyline of Providence
|
||
|
||
| Motto(s):
None official. "An Appeal to Heaven" and "Nunquam libertas gratior extat" (Latin for 'Never does liberty appear in a more gracious form') are common de facto mottos.
|
||
Location of New England (red) in the United States
|
||
Location of New England (red) in North America
|
||
| Composition | ||
| Largest metropolitan area | ||
| Largest city | Boston | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 71,987.59 sq mi (186,447.0 km2) | |
| • Land | 62,688.4 sq mi (162,362 km2) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 15,116,205 | |
| • Density | 209.983485/sq mi (81.075077/km2) | |
| Demonym(s) | New Englander, Yankee, Novanglian, Novanglican (archaic) | |
| GDP | ||
| • Total | $1.41 trillion (2023) | |
| Dialects | New England English, New England French | |
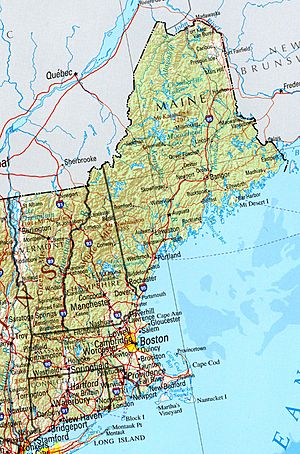
New England is a special region in the Northeastern United States. It includes six states: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. To the west, it borders New York. To the north, it meets the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec. The Atlantic Ocean is to its east and south.
Boston is New England's biggest city and the capital of Massachusetts. The area around Boston, called Greater Boston, is the largest metropolitan area. About one-third of all New Englanders live there. This area also includes Worcester, Massachusetts, the second-largest city in New England. Other important cities are Manchester, New Hampshire (New Hampshire's largest city) and Providence, Rhode Island (Rhode Island's capital and largest city).
In 1620, a group called the Pilgrims started Plymouth Colony. This was the second successful English settlement in North America. Ten years later, another group called the Puritans founded Massachusetts Bay Colony. For over a century, colonists fought in wars against the French and their Native American allies. The English and their Iroquois friends eventually won.
In the late 1700s, New England leaders began to resist Britain's unfair taxes. People in Rhode Island burned a British ship. Boston residents famously threw British tea into the harbor. Britain reacted with harsh laws, which colonists called the "Intolerable Acts". These events led to the first battles of the American Revolutionary War in 1775. British rule ended in the region by spring 1776. New England also played a big part in ending slavery in the U.S. It was the first U.S. region to experience the Industrial Revolution, with factories growing along rivers.
New England's land is very diverse. The southeastern part has a narrow coastal plain. The western and northern areas have rolling hills and old mountains. The Appalachian Mountains run through these parts. Many cities used water power from rivers like the Connecticut River. This river cuts through the region from north to south.
Each state is divided into small areas called towns. Many towns are run by town meetings, where citizens make decisions. New England is unique because it has very few areas without local government. It is the only U.S. region with clear and consistent borders across multiple states. New England has a strong cultural identity. It blends old traditions with new ideas, and rural life with industry and immigration.
History
Early Inhabitants: Native Americans
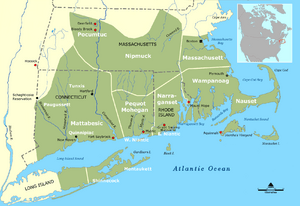
The first known people in New England were American Indians. They spoke different Eastern Algonquian languages. Important tribes included the Abenakis, Mi'kmaq, Penobscot, Pequots, Mohegans, Narragansetts, Nipmucs, Pocumtucks, and Wampanoags.
Before Europeans arrived, the Western Abenakis lived in what is now New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont. They also lived in parts of Quebec and western Maine. Their main town was Norridgewock in Maine. The Penobscots lived along the Penobscot River in Maine. The Narragansetts lived in Rhode Island, west of Narragansett Bay. This included Block Island.
The Wampanoags lived in southeastern Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and the islands of Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket. The Pocumtucks lived in Western Massachusetts. The Mohegan and Pequot tribes lived in Connecticut. The Connecticut River Valley connected many tribes through their culture, language, and politics.
Around 1600, traders from France, the Netherlands, and England explored the New World. They traded metal, glass, and cloth for beaver furs.
Colonial Period: Settling New England

On April 10, 1606, King James I of England gave a special paper to the Virginia Company. This company had two parts: the London Company and the Plymouth Company. These groups were funded by private money. Their goal was to claim land for England, trade, and make a profit.
In 1620, the Pilgrims arrived on the ship Mayflower. They started Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts. This was the beginning of permanent European settlements in New England. In 1616, English explorer John Smith had already named the region "New England". This name became official on November 3, 1620. The Plymouth Company was replaced by the Plymouth Council for New England. This new company was set up to colonize and govern the area.
Before leaving their ship, the Pilgrims wrote and signed the Mayflower Compact. This became their first governing document. The Massachusetts Bay Colony was founded by royal charter in 1629. Its main town and port, Boston, was established in 1630. This colony grew to be very powerful in the area.
Massachusetts Puritans began settling in Connecticut by 1633. Roger Williams was asked to leave Massachusetts for his religious beliefs. He led a group south and founded Providence Plantations in 1636. This later became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations. At this time, Vermont was not settled by Europeans. Massachusetts claimed and governed the areas of New Hampshire and Maine. As the region grew, many immigrants came from Europe. They were drawn by religious tolerance and a growing economy.
Conflicts and Growth: French and Indian Wars
Relationships between colonists and Native American tribes were sometimes peaceful, sometimes violent. The bloodiest conflict was the Pequot War in 1637. It ended with the terrible Mystic massacre. On May 19, 1643, the colonies of Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, New Haven, and Connecticut formed the New England Confederation. This group helped them work together for defense.
The confederation became important during King Philip's War. This war, from 1675 to 1678, involved colonists and their Native American allies fighting a widespread Native American uprising. There were killings and massacres on both sides. After these conflicts, hundreds of Native Americans were sold into slavery. Until 1700, Native Americans made up most of the non-white workers in colonial New England.
Over the next 74 years, there were six colonial wars. These wars were mainly between New England and New France (French colonies). New England was allied with the Iroquois Confederacy. New France was allied with the Wabanaki Confederacy. The British eventually defeated the French in 1763. This opened the Connecticut River Valley for British settlement into western New Hampshire and Vermont.
New England Colonies were mostly settled by farmers. They grew enough food to support themselves. Later, New England's economy shifted to crafts and trade. This was helped by the Puritan work ethic. In contrast, the Southern colonies focused on farming and bought finished goods from England.
The American Revolution and a New Nation
By 1686, King James II of England was worried about the colonies becoming too independent. He created the Dominion of New England. This was a single government for all New England colonies. In 1688, New York and New Jersey were added. This union was forced on the colonies and was very unpopular. It went against their tradition of self-government.
The Dominion changed the colonies' charters. Royal governors were appointed to almost all of them. There was tension between these governors and the elected local officials. Governors wanted full power, but local governments often resisted. Most town governments kept running as they had before.
After the Glorious Revolution in 1689, Bostonians overthrew the royal governor, Sir Edmund Andros. This was a peaceful uprising. These tensions eventually led to the American Revolution. The first battles of the War of American Independence were fought in Lexington and Concord, Massachusetts, in 1775. This led to the Siege of Boston. In March 1776, British forces had to leave Boston.
After the Dominion of New England ended, the New England colonies stopped being a single political unit. However, they kept a strong shared culture. There were often arguments over land borders.
By 1784, all New England states had started to end slavery. Vermont and Massachusetts completely abolished it in 1777 and 1783. The nickname "Yankeeland" was sometimes used for New England. Vermont became a state in 1791. Maine, which was part of Massachusetts, became a state on March 15, 1820. This was part of the Missouri Compromise. Today, New England includes Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
New England's economy relied on trade with the British Empire. The region's merchants did not like trade restrictions. During the War of 1812 between the U.S. and the UK, New England Federalists met at the Hartford Convention in 1814. They discussed their complaints about the war. They also suggested changes to the United States Constitution to protect their interests. Some delegates wanted the region to leave the U.S., but most did not.
Politically, the region often disagreed with the rest of the country. New England became a strong base for the new Whig Party in the 1830s. The Whigs were usually strong in New England, except in Maine and New Hampshire, which were more Democratic.
Industrial Revolution: Factories and Progress
New England was very important for the industrial revolution in the United States. The Blackstone Valley in Massachusetts and Rhode Island is called the birthplace of America's industrial revolution. In 1787, the first cotton mill in America opened in Beverly, Massachusetts. It was called the Beverly Cotton Manufactory. This factory was the largest cotton mill of its time.
New inventions from this factory led to more advanced cotton mills. One example is Slater Mill in Pawtucket, Rhode Island. Towns like Lawrence, Massachusetts, Lowell, Massachusetts, Woonsocket, Rhode Island, and Lewiston, Maine became big centers for making textiles (cloth).
The Connecticut River Valley became a place for new industrial ideas. The Springfield Armory led the way in things like interchangeable parts and the assembly line. These ideas changed manufacturing worldwide. From the early 1800s to the mid-1900s, the area around Springfield, Massachusetts and Hartford, Connecticut was a major center for advanced manufacturing. It attracted skilled workers from all over the world.
The fast growth of textile factories from 1815 to 1860 created a need for workers. Recruiters brought young women and children from farms to work in the factories. Thousands of farm girls moved to mills like the Lowell Mill Girls. As the textile industry grew, so did immigration. By the 1850s, immigrants, especially French Canadians and Irish, began working in the mills.
New England was the most industrialized part of the U.S. By 1850, it produced over a quarter of all manufactured goods in the country. It also had over a third of the industrial workers. It was also the most educated region.
During this time, New England was the center of strong movements against slavery. Abolitionists like William Lloyd Garrison demanded immediate freedom for enslaved people. Anti-slavery politicians wanted to stop slavery from spreading. The Republican Party, which was against slavery, formed in the 1850s. All of New England became strongly Republican. This lasted until Catholics began supporting Democrats, especially in 1928. This change led New England to become a Democratic stronghold in national elections.
20th Century and Beyond: Modern New England

Immigrants continued to arrive steadily from the 1840s until World War I. The largest groups were from Ireland and Britain before 1890. After that, many came from Quebec, Italy, and Southern Europe. These immigrants became factory workers, craftspeople, and laborers. The Irish played a bigger role in the Democratic Party in cities. Rural areas stayed Republican.
The Great Depression in the United States in the 1930s hit the region hard. Industrial cities had high unemployment. During World War II, huge spending on weapons, ships, and electronics brought prosperity to all parts of the economy.
After World War II, New England's economy changed a lot. Factories mostly disappeared. Many textile mills closed from the 1920s to the 1970s. For example, the Crompton Company went out of business in 1984 after 178 years. This cost 2,450 jobs in five states. Reasons included cheap imports and a failure to adapt. The shoe industry also left the region.

What remains is high-tech manufacturing. This includes jet engines, nuclear submarines, and medical devices. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) helped create many software and hardware companies. By the 21st century, New England became known for its leadership in education, medicine, research, high-technology, finance, and tourism.
Some industrial areas struggled to adapt to the new service economy. In 2000, Providence, Rhode Island, and Hartford, Connecticut, were among the poorest cities in the U.S. However, by 2010, they were no longer in the bottom ten. Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire are still among the ten wealthiest states in the U.S.
Geography
Land and Size
The New England states cover about 186,447 square kilometers (71,987 square miles). This makes the region a bit larger than the state of Washington. Maine alone makes up almost half of New England's total area. Even so, it is only the 39th-largest state in the U.S. The other New England states are among the smallest. Rhode Island is the smallest state in the U.S.
The areas of the states (including water) are:
- Maine: 35,380 square miles
- Massachusetts: 10,554 square miles
- Vermont: 9,616 square miles
- New Hampshire: 9,349 square miles
- Connecticut: 5,543 square miles
- Rhode Island: 1,545 square miles
Mountains, Rivers, and Lakes
New England's rolling hills, mountains, and jagged coastline were formed by glaciers. These huge ice sheets retreated about 18,000 years ago. The Appalachian Mountains generally follow the border between New England and New York. The The Berkshires in Massachusetts and Connecticut, and the Green Mountains in Vermont, are part of these mountains.
The Appalachians continue north into New Hampshire as the White Mountains. Then they go into Maine and Canada. Mount Washington in New Hampshire is the highest peak in the Northeast. It is known for having some of the world's most severe weather.
The coast of New England has many lakes, hills, marshes, and sandy beaches. Important valleys include the Champlain Valley, the Connecticut River Valley, and the Merrimack Valley. The longest river is the Connecticut River. It flows for 655 kilometers (407 miles) from northeastern New Hampshire. It empties into Long Island Sound, dividing the region. Lake Champlain, on the border of Vermont and New York, is the largest lake. After that are Moosehead Lake in Maine and Lake Winnipesaukee in New Hampshire.
Climate and Weather
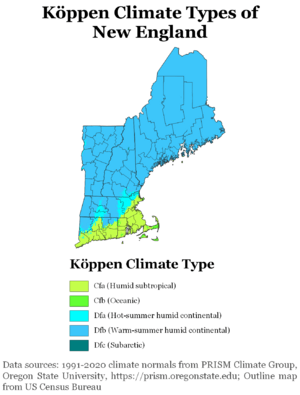
New England's climate changes a lot from northern Maine to southern Connecticut. Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and western Massachusetts have a humid continental climate. Winters here are long and cold, with heavy snow (60-120 inches annually). Summers are moderately warm but short. Rain falls throughout the year.
In central and eastern Massachusetts, northern Rhode Island, and northern Connecticut, the same climate exists. However, summers are warmer, winters are shorter, and there is less snow. This is especially true in coastal areas.
Southern and coastal Connecticut is a transition zone. It moves from the cold continental climates of the north to milder climates in the south. The frost-free season is longer than 180 days in far southern Connecticut, coastal Rhode Island, and the islands. Winters in southern Connecticut and Rhode Island are also much sunnier.
Regions of New England
New England is divided into many smaller regions, each with its own character. These include:
- Northwest Vermont/Champlain Valley
- Northeast Kingdom
- Central Vermont
- Southern Vermont
- Great North Woods Region
- White Mountains
- Lakes Region
- Dartmouth/Lake Sunapee Region
- Seacoast Region
- Merrimack Valley
- Monadnock Region
- Aroostook
- Maine Highlands
- Acadia/Down East
- Mid-Coast/Penobscot Bay
- Southern Maine/South Coast
- Mountain and Lakes Region
- Kennebec Valley
- North Shore
- Metro Boston
- South Shore
- Cape Cod and Islands
- South Coast
- Southeastern Massachusetts
- Blackstone River Valley
- Metrowest/Greater Boston
- Central Massachusetts
- Pioneer Valley
- The Berkshires
- South County
- East Bay
- Quiet Corner
- Greater Hartford
- Central Naugatuck Valley
- Northwest Hills
- Southeastern Connecticut/Greater New London
- Western Connecticut
- Connecticut Shoreline
Biodiversity: Plants and Animals
New England has many forests with different kinds of animals. Changes in how land was used, like clearing forests for farms, greatly changed the environment. This led to some animals disappearing from certain areas.
The number of different tree species increases from north to south. Taller trees are linked to more tree diversity. The red maple is becoming very common. It is outcompeting other maples, like the sugar maple. This is partly due to more nitrogen in the soil from climate change.
Largest Cities and Metropolitan Areas
New England has several large cities. The most populated cities in 2020 were:
 Boston, Massachusetts: 675,647 people (metropolitan area: 4,941,632)
Boston, Massachusetts: 675,647 people (metropolitan area: 4,941,632) Worcester, Massachusetts: 206,518 people (metropolitan area: 923,672)
Worcester, Massachusetts: 206,518 people (metropolitan area: 923,672) Providence, Rhode Island: 190,934 people (metropolitan area: 1,604,291)
Providence, Rhode Island: 190,934 people (metropolitan area: 1,604,291) Springfield, Massachusetts: 155,929 people (metropolitan area: 699,162)
Springfield, Massachusetts: 155,929 people (metropolitan area: 699,162) Bridgeport, Connecticut: 148,654 people (metropolitan area: 939,904)
Bridgeport, Connecticut: 148,654 people (metropolitan area: 939,904) Stamford, Connecticut: 135,470 people (part of Greater Bridgeport)
Stamford, Connecticut: 135,470 people (part of Greater Bridgeport) New Haven, Connecticut: 134,023 people (metropolitan area: 862,477)
New Haven, Connecticut: 134,023 people (metropolitan area: 862,477) Hartford, Connecticut: 121,054 people (metropolitan area: 1,214,295)
Hartford, Connecticut: 121,054 people (metropolitan area: 1,214,295) Cambridge, Massachusetts: 118,403 people (part of Greater Boston)
Cambridge, Massachusetts: 118,403 people (part of Greater Boston) Manchester, New Hampshire: 115,644 people (metropolitan area: 406,678)
Manchester, New Hampshire: 115,644 people (metropolitan area: 406,678)
Western Connecticut is strongly influenced by New York City. The U.S. Census Bureau groups Fairfield, New Haven, and Litchfield counties with New York City.
- Major cities of New England
Metropolitan Areas
Here are the largest metropolitan areas in New England:
| Rank | Metropolitan area | State(s) | Population (2020) | Encompassing CSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Boston | 4,941,632 | Boston | |
| 2 | Providence | 1,676,579 | Boston | |
| 3 | Hartford | 1,213,531 | Hartford | |
| 4 | Worcester | 978,529 | Boston | |
| 5 | Bridgeport | 957,419 | New York | |
| 6 | New Haven | 864,835 | Hartford | |
| 7 | Springfield | 699,162 | Springfield | |
| 8 | Portland | 551,740 | Portland | |
| 9 | Manchester-Nashua | 422,937 | Boston | |
| 10 | Norwich-New London | 268,555 | Hartford | |
| 11 | Barnstable | 228,996 | Boston | |
| 12 | Burlington | 225,562 | Burlington | |
| 13 | Bangor | 152,199 | N/A | |
| 14 | Pittsfield | 129,026 | N/A | |
| 15 | Lewiston-Auburn | 111,139 | Portland |
State Capitals
Each New England state has its own capital city:
- Hartford, Connecticut
- Augusta, Maine
- Boston, Massachusetts
- Concord, New Hampshire
- Providence, Rhode Island
- Montpelier, Vermont
People and Culture
Population and Diversity
In 2020, New England had over 15 million people. This was a 4.6% growth from 2010. Massachusetts is the most populated state. Vermont has the fewest residents. Boston is by far the region's largest city and metropolitan area.
New England is much more densely populated than the U.S. average. Three-quarters of its people live in southern New England. This includes Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island. Northern New England (Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont) has fewer people per square mile.
In 2006–2008, about 48.7% of New Englanders were male and 51.3% were female. About 22.4% of the population was under 18 years old. About 13.5% were over 65. The six New England states have the lowest birth rate in the U.S.
White Americans make up most of New England's population (73.4%). Hispanic and Latino Americans are the largest minority group. In 2014, they made up 10.2% of the population. Connecticut had the highest percentage (13.9%). Vermont had the lowest (1.3%). There were almost 1.5 million Hispanic and Latino people in New England in 2014.
Puerto Ricans were the largest Hispanic subgroup. Over 660,000 Puerto Ricans lived in New England in 2014. They formed 4.5% of the population. The Dominican population was over 200,000. Mexican and Guatemalan populations were each over 100,000.
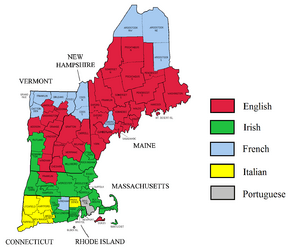
The top ten largest European ancestries reported in 2014 were:
- Irish: 19.2% (2.8 million people)
- English: 16.7% (2.4 million people)
- Italian: 13.6% (2.0 million people)
- French and French Canadian: 13.1% (1.9 million people)
- German: 7.4% (1.1 million people)
- Polish: 4.9% (about 715,000 people)
- Portuguese: 3.2% (467,000 people)
- Scottish: 2.5% (370,000 people)
- Russian: 1.4% (206,000 people)
- Greek: 1.0% (152,000 people)
English is the most common language spoken at home. About 81.3% of residents over five years old spoke only English. About 7.8% spoke Spanish at home. About 7.0% spoke other European languages. Over 2.9% spoke an Asian or Pacific Island language. About 1% spoke French at home, but this is over 20% in northern New England near Quebec.
As of 2014, about 87% of New Englanders were born in the U.S. Over 12% were born in other countries. Most foreign-born residents came from Latin America (35.8%), Asia (28.6%), or Europe (22.9%).
Southern New England is part of the BosWash megalopolis. This is a huge urban area from Boston to Washington, D.C. The region includes three of the four most densely populated states in the U.S.. Only New Jersey is more crowded than Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Connecticut.
Greater Boston has about 4.8 million people. Over half of New England's population lives within Boston's larger statistical area of over 8.2 million.
Religion and Beliefs
Today, New England is the least religious region in the U.S. In 2009, less than half of people in Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont said religion was important in their daily lives. Connecticut and Rhode Island are also among the least religious states. About 34% of Vermonters said they had no religion. Almost one in four New Englanders identifies as having no religion.
New England used to have one of the highest percentages of Catholics in the U.S. This number dropped from 50% in 1990 to 36% in 2008.
Cultural Traditions

Many early European colonists in New England were involved in whaling and fishing. They also farmed. New England has developed its own unique food, accent, architecture, and government style. New England food is known for seafood and dairy. Clam chowder, lobster, and other sea products are very popular.
New England has kept much of its regional character. This is especially true in its historic places. The region has become more diverse over time. Many immigrants have come from Ireland, Quebec, Italy, Portugal, Germany, Poland, Asia, Latin America, and Africa.
The lasting European influence can be seen in many ways. These include traffic rotaries (traffic circles). Northern Vermont, Maine, and New Hampshire have towns where both French and English are spoken. The traditional coastal accent is unique, often not pronouncing the "R" sound. Many towns and counties are named after places in England. For example, North Yarmouth, Maine, was named after Yarmouth, Massachusetts. This was named after Great Yarmouth in England. Every New England state has a town named Warren. Most have towns named Franklin and Washington.
Food and Drink
New England has its own special food culture. Early foods were influenced by Native American and English cooking. Colonists often changed their recipes to use local foods. New England staples show a mix of American Indian and Pilgrim cooking. Examples include johnnycakes, succotash, cornbread, and various seafood dishes.
New England also has unique food words. For example, "grinders" are submarine sandwiches. "Frappes" are thick milkshakes, called "Cabinets" in Rhode Island. Other local foods include steak tips (marinated beef), bulkie rolls, maple syrup, cranberry recipes, and clam chowder.
A type of beer called New England India Pale Ale (NEIPA) was created in Vermont in the 2010s. Other regional drinks include Moxie. This was one of the first mass-produced soft drinks in the U.S., started in Lowell, Massachusetts, in 1876. It is still popular in New England, especially in Maine. Coffee milk is the official state drink of Rhode Island.
Portuguese cuisine is important in the annual Feast of the Blessed Sacrament in New Bedford, Massachusetts. This is the largest ethnic festival in New England.
Accents and Dialects
Several American English accents are spoken in New England. The most famous is the Boston accent. This accent is heard in the northeastern coastal parts of New England. Its main features, like the "broad A" and dropping the final "R", are thought to come from England. Another source was the speech of 17th-century settlers from East Anglia and Lincolnshire. The Boston accent is now mostly linked with working-class people. You can hear it in movies like Good Will Hunting. This accent is common in eastern Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Maine.
Some Rhode Islanders speak with an accent that does not pronounce the "R" sound. Many compare it to a "Brooklyn" accent. It is like a mix of New York and Boston accents. For example, "water" sounds like "wata." This accent came from early settlers from eastern England.
Arts and Entertainment
Acadian and Québécois culture influence music and dance in rural New England. This is especially true in Maine. Contra dancing and country square dancing are popular. They are usually accompanied by live Irish, Acadian, or other folk music. Fife and drum corps are common, especially in southern New England and Connecticut. Their music is often Celtic, English, or local.
New England leads the U.S. in how much ice cream people eat. Candlepin bowling was invented in New England in the 1800s. It is mostly played there.
New England was an important center for American classical music. The First New England School of composers was active from 1770 to 1820. The Second New England School was active about a century later. Famous modern composers like Charles Ives and John Adams are from the region. Boston is home to the New England Conservatory and the Boston Symphony Orchestra.
In popular music, New England has produced many famous artists. These include Donna Summer, New Edition, Aerosmith, Phish, and the Dropkick Murphys. Quincy, Massachusetts, native Dick Dale helped make surf rock popular.
Media and Comedy
The main U.S. cable TV sports channel, ESPN, is in Bristol, Connecticut. New England has regional cable networks like New England Cable News (NECN) and the New England Sports Network (NESN). NECN is the largest regional 24-hour news network in the U.S. It broadcasts to over 3.2 million homes in New England.
NESN broadcasts Boston Red Sox baseball and Boston Bruins hockey games. NBC Sports Boston broadcasts games for the Boston Celtics and New England Revolution.
Most New England cities have daily newspapers. The Boston Globe and The New York Times are widely read. Other major newspapers include The Providence Journal and Hartford Courant. The Hartford Courant is the oldest continuously published newspaper in the U.S.
New Englanders are well-known in American comedy. Many writers for The Simpsons and late-night TV shows came from The Harvard Lampoon. Several Saturday Night Live (SNL) cast members are from New England, like Adam Sandler and Amy Poehler. Seth MacFarlane, creator of Family Guy, is from Connecticut. The show is set in a fictional Rhode Island town.
Late-night hosts Jay Leno and Conan O'Brien are from the Boston area. Famous stand-up comedians like Bill Burr and Sarah Silverman are also from the region.
Literature and Film

New Englanders have made big contributions to literature. The first printing press in America was set up in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in the 1600s. Writers in New England produced many works on religion and later on Enlightenment ideas. New England literature has greatly influenced American literature. It often explores themes like religion, society, and nature.
In the 1800s, New England was a center for progressive ideas. Many writings against slavery and supporting transcendentalist ideas were produced. Leading transcendentalists like Henry David Thoreau and Ralph Waldo Emerson were from New England. Harriet Beecher Stowe, from Hartford, Connecticut, wrote Uncle Tom's Cabin. This book was very important in spreading anti-slavery ideas. Other famous New England writers include Edgar Allan Poe, Louisa May Alcott, Stephen King, and Nathaniel Hawthorne.
Boston was once the center of American publishing. It was home to many local writers. The Atlantic Monthly literary magazine was also based there for a long time. Merriam-Webster dictionary is in Springfield, Massachusetts. Yankee is a magazine for New Englanders.
Many New England poets have been very important in American poetry. These include Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Emily Dickinson, and Robert Frost. Robert Frost often wrote about rural New England life.

New England has a rich history in filmmaking. It is sometimes called Hollywood East. Early films like The Scarlet Letter were set in New England. The region continued to produce many films throughout the 1900s. These included hits like Jaws, Good Will Hunting, and The Departed. These films often featured themes like small-town life, sea stories, and family secrets. The diverse landscapes and architecture of New England provide great backdrops for movies.
Since 2000, many films and TV shows have been made in New England. This is partly due to tax incentives from local governments. Famous actors from New England include Ben Affleck, Matt Damon, Chris Evans, and Amy Poehler.
Museums and Libraries
New England has many museums, especially around Greater Boston. These include private and public museums. Some famous ones are the Museum of Fine Arts, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, and the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum. The oldest public museum in the U.S. is the Pilgrim Hall Museum in Plymouth, Massachusetts, opened in 1824.
The Boston Public Library is the largest public library in the region. It has over 8 million items. The largest academic research library in the world is the Harvard Library in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The W. E. B. Du Bois Library at the University of Massachusetts Amherst is the tallest academic library in the world.
There are also many historical societies. Historic New England runs museums and historic sites to preserve history. The Massachusetts Historical Society, founded in 1791, is the oldest operating historical society in the U.S.
Sports and Recreation
New England has a strong sports history. Many popular sports were invented here. These include basketball, volleyball, and American football.
Football is the most popular sport. It was developed by Walter Camp in New Haven, Connecticut, in the 1870s and 1880s. The New England Patriots are based in Foxborough, Massachusetts. They are the most popular professional sports team in New England. The Patriots have won six Super Bowl championships. They are one of the most successful teams in the National Football League.
There are also old college and high school football rivalries in New England. Many games are played on Thanksgiving Day. The rivalry between Wellesley High School and Needham High School in Massachusetts started in 1882. It is considered the nation's oldest football rivalry.
Before modern baseball rules, a different form called the Massachusetts Game was played. This version was popular throughout New England. In 1869, there were 59 teams playing by Massachusetts rules. The New York rules eventually became more popular. Professional teams like the Boston Red Sox grew famous. Fenway Park was built in 1912. It is the oldest ballpark still used in Major League Baseball.
Basketball was invented in Springfield, Massachusetts, by James Naismith in 1891. Naismith wanted an indoor game for athletes during New England winters. The Boston Celtics were founded in 1946. They are the most successful NBA team, with 18 titles. The Basketball Hall of Fame is in Springfield, Massachusetts.
Winter sports are very popular. These include alpine skiing, snowboarding, and Nordic skiing. Ice hockey is also popular. The Boston Bruins were founded in 1924. They have a historic rivalry with the Montreal Canadiens. College hockey is also popular, with Boston's annual Beanpot tournament.
Volleyball was invented in Holyoke, Massachusetts, in 1895 by William G. Morgan. He was a YMCA instructor. He wanted an indoor game for his athletes. The international Volleyball Hall of Fame is in Holyoke.
Rowing, sailing, and yacht racing are also popular. The Head of the Charles race is held on the Charles River every October. It attracts over 10,000 athletes and 200,000 spectators. Sailing races include the Newport Bermuda Race.
The Boston Marathon is run every Patriots' Day. It started in 1897. It is one of the world's most famous marathons. It is New England's largest sporting event, with almost 500,000 spectators.
New England has a professional soccer team, the New England Revolution. They play in Major League Soccer.
-
Bill Russell and Red Auerbach of the Boston Celtics.
-
The New England Patriots are the most popular professional sports team in New England.
-
The Middlebury College rowing team in the 2007 Head of the Charles Regatta.
Economy

New England's economy is special for several reasons. It is far from the center of the country. It is a small but densely populated region. Historically, it was a major center for industry and manufacturing. It also provided natural resources like granite, lobster, and codfish. The service industry is now very important. This includes tourism, education, finance, and insurance. The U.S. Department of Commerce calls New England's economy a small version of the entire U.S. economy.
The region lost many factories in the first half of the 20th century. Textile and furniture manufacturing moved to the South. In the late 20th century, the economy shifted. It now includes high technology, military defense, finance, and health services. In 2018, New England's total economic output was $1.1 trillion.
New England exports food products like fish, lobster, cranberries, potatoes, and maple syrup. About half of the region's exports are industrial machines. This includes computers and electronic equipment. Granite is quarried in Barre, Vermont. Guns are made in Springfield, Massachusetts, and Saco, Maine. Submarines are built in Groton, Connecticut.
Major Economic Centers

In 2017, Boston was ranked as the ninth most competitive financial center in the world. It was fourth in the United States. Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped make mutual funds popular in the 1980s. This made Boston a top financial center. The city is home to Santander Bank and many venture capital firms. State Street Corporation, a big asset management company, is also based there.
Boston is also a center for printing and publishing. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt is headquartered there. The city has large convention centers.
General Electric Corporation moved its global headquarters to Boston in 2016. They chose Boston because of its excellent universities. The city also has headquarters for major athletic and footwear companies. These include Converse, New Balance, and Reebok.
Hartford is a historic center for the insurance industry. Companies like Aetna and The Hartford are based there. It is also home to United Technologies.
Fairfield County, Connecticut, has many investment management firms. These include Bridgewater Associates, one of the world's largest hedge fund companies. Many international banks also have their North American headquarters in Fairfield County.
Agriculture and Energy

Farming is limited in New England. This is due to rocky soil, a cool climate, and small land area. However, some New England states are highly ranked for certain products. Maine is ninth for aquaculture (fish farming). It also has many potato fields in its northeast. Vermont is fifteenth for dairy products. Connecticut and Massachusetts are seventh and eleventh for tobacco. Cranberries are grown in Massachusetts. Blueberries are grown in Maine.
New England is mostly energy-efficient compared to the rest of the U.S. Every state except Maine is among the ten most energy-efficient states. However, electricity prices are very high in all New England states. Wind power, especially from offshore sources, is expected to grow in the 2020s.
Employment and Taxes
| Employment area | October 2010 | October 2011 | October 2012 | October 2013 | December 2014 | December 2015 | December 2016 | Net change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 9.7 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 7.2 | 5.6 | 5.0 | 4.7 | −5.0 |
| New England | 8.3 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.1 | 5.4 | 4.3 | 3.5 | −4.7 |
| Connecticut | 9.1 | 8.7 | 9.0 | 7.6 | 6.4 | 5.2 | 4.4 | −4.7 |
| Maine | 7.6 | 7.3 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 4.0 | 3.8 | −3.8 |
| Massachusetts | 8.3 | 7.3 | 6.6 | 7.2 | 5.5 | 4.7 | 2.8 | −5.5 |
| New Hampshire | 5.7 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 3.1 | 2.6 | −3.1 |
| Rhode Island | 11.5 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 5.1 | 5.0 | −6.5 |
| Vermont | 5.9 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 3.1 | −2.8 |
As of January 2017, employment was stronger in New England than in the rest of the United States. During the Great Recession, unemployment rates rose. However, they steadily declined afterward. New Hampshire and Massachusetts had some of the lowest unemployment rates in the country. Rhode Island saw its rate drop by over 6% in six years.
In December 2016, the area with the lowest unemployment rate was Burlington-South Burlington, Vermont (2.1%). The area with the highest rate was Waterbury, Connecticut (4.9%).
In 2023, three New England states were among the top ten states for taxes paid per taxpayer. These were Maine (#3), Vermont (#4), and Connecticut (#5). New Hampshire was among the bottom five (#48). All six states have very high property taxes. Five of them are in the nationwide top 10.
Education
Colleges and Universities

New England has some of the oldest and most famous universities in the U.S. and the world. Harvard College was the first. It was founded in 1636 in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was started to train preachers. Yale University was founded in Saybrook, Connecticut, in 1701. It moved to New Haven, Connecticut, in 1718. Yale gave the nation's first doctoral degree in 1861.
Brown University was the first college to accept students of all religions. It is the seventh oldest U.S. university. It was founded in Providence, Rhode Island, in 1764. Dartmouth College was founded five years later in Hanover, New Hampshire. Its goal was to educate local American Indian people and English youth. The University of Vermont, the fifth oldest university in New England, was founded in 1791.
Besides four of the eight Ivy League schools, New England has the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It also has many schools known as the "Little Ivies". Four of the original Seven Sisters colleges are here. The main state universities are the University of Maine, the University of New Hampshire, the University of Connecticut, the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, the University of Rhode Island, and the University of Vermont.
Private and Public Schools
For students before college, New England has many independent schools (also called private schools). The idea of the elite "New England prep school" is a well-known part of the region's image.
New England has some of the oldest public schools in the nation. It was the first U.S. region to require all children to attend school. Boston Latin School is the oldest public school in America. Several signers of the Declaration of Independence went there. Hartford Public High School is the second oldest operating high school in the U.S.
As of 2005, Connecticut had the highest-paid teachers in the country. Massachusetts and Rhode Island ranked eighth and ninth. New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont work together on a common test. This helps them compare student scores.
Transportation

Each New England state has its own Department of Transportation. These departments plan and develop transport systems. However, some transportation groups work across state and city lines. The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) manages public transport in the Greater Boston area. It is the largest agency of its kind. It operates in eastern Massachusetts and into Rhode Island. The MBTA runs the oldest subway system in the U.S. (the Tremont Street subway).
Coastal Connecticut uses the Metropolitan Transportation Authority of New York. This is because the region is connected to New York's economy. The MTA operates the Metro-North Railroad with the Connecticut Department of Transportation. CTrail operates the Shore Line East along Connecticut's southern coast. It also runs the Hartford Line from New Haven to Springfield, Massachusetts.
Amtrak provides train service between states throughout New England. Boston is the northern end of the Northeast Corridor. The Vermonter connects Vermont to Massachusetts and Connecticut. The Downeaster links Maine to Boston. The Lake Shore Limited train also serves Boston.
Bus transportation is available in most cities. It is managed by regional and local groups. South Station in Boston is a major center for buses and trains.
Major highways in the region include I-95, I-93, I-91, I-89, I-84, and I-90 (the Massachusetts Turnpike). Logan Airport in Boston is the busiest transportation hub in the region. It is the 16th busiest airport in the United States. Other airports include Patrick Leahy Burlington International Airport, Bradley International Airport, and Rhode Island T. F. Green International Airport.
See also
 In Spanish: Nueva Inglaterra para niños
In Spanish: Nueva Inglaterra para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |