Dartmouth College facts for kids
 |
|
| Latin: Collegii Dartmuthensis | |
| Motto | Vox clamantis in deserto (Latin – A quotation from the Book of Isaiah in the Old Testament) |
|---|---|
|
Motto in English
|
"A voice crying out in the wilderness" |
| Type | Private research university |
| Established | December 13, 1769 |
| Accreditation | NECHE |
|
Academic affiliations
|
|
| Endowment | $8.3 billion (2024) |
| Budget | $1.5 billion (2024) |
| President | Sian Beilock |
| Provost | Santiago Schnell |
|
Academic staff
|
943 (fall 2018) |
|
Administrative staff
|
2,938 full time, 328 part time (Fall 2018) |
| Students | 6,746 (fall 2023) |
| Undergraduates | 4,447 (fall 2023) |
| Postgraduates | 2,299 (fall 2023) |
| Location |
,
,
United States
43°42′12″N 72°17′18″W / 43.70333°N 72.28833°W |
| Campus | Remote town, 31,869 acres (128.97 km2) (total) |
| Newspaper | The Dartmouth |
| Colors | Dartmouth Green and White |
| Nickname | Big Green |
|
Sporting affiliations
|
|
Dartmouth College is a private university in Hanover, New Hampshire, United States. It is part of the Ivy League, a group of eight famous universities in the Northeastern U.S.
Eleazar Wheelock started Dartmouth in 1769. It was one of nine colleges created before the American Revolution. Dartmouth was first meant to teach Native Americans about Christianity and American life. Over time, it became a university that trains students in many subjects.
Today, Dartmouth is known for its strong focus on undergraduate education. It offers many different subjects in the humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, and engineering. Dartmouth also has four special schools for advanced studies: the Geisel School of Medicine, the Thayer School of Engineering, the Tuck School of Business, and the Guarini School.
Dartmouth is the smallest university in the Ivy League, with about 6,700 students. Getting into Dartmouth is very competitive. The main campus is in a rural area of New England. The university uses a "quarter system," meaning it has four ten-week terms throughout the year. Dartmouth is also famous for its Greek culture and many campus traditions. Its sports teams, called the Big Green, compete in the Ivy League. Many famous people have graduated from Dartmouth, including leaders, writers, and athletes.
Contents
History of Dartmouth College

Dartmouth College was founded by Eleazar Wheelock, a minister from Connecticut. He wanted to create a school to train Native Americans as Christian missionaries. This was one of the first colleges established in America.
Wheelock started a school called Moor's Indian Charity School in 1755. He needed more money to keep it going. Samson Occom, a Mohegan Indian who studied with Wheelock, traveled to England to raise funds. These funds helped Wheelock establish a trust. The trust was led by William Legge, 2nd Earl of Dartmouth.
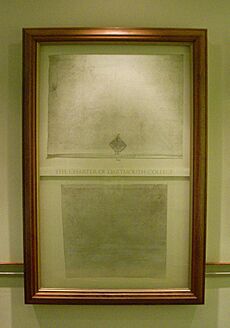
Wheelock decided to move his school to Hanover, New Hampshire. The Royal Governor of New Hampshire, John Wentworth, gave the land for the college. On December 13, 1769, King George III officially approved the college's creation. The college was named after William Legge, 2nd Earl of Dartmouth. Dartmouth was the ninth oldest college in the nation. It gave out its first degrees in 1771.
Even though the college was meant to help Native Americans, Wheelock mostly focused on educating white students. Samson Occom was disappointed by this. He went on to create his own community for Native Americans.
In 1819, Dartmouth College was part of a very important court case called Dartmouth College v. Woodward. The state of New Hampshire tried to change Dartmouth into a public university. Daniel Webster, a Dartmouth graduate, argued the college's case in the Supreme Court. The Court decided that the state could not change Dartmouth's original charter. This ruling helped keep Dartmouth as a private college.
Dartmouth started admitting its first African-American students in 1775. By the end of the American Civil War, many black men had attended the college. Dartmouth was known as a place where men of color could get an education.
In 1866, a new college for agriculture was started in Hanover, connected to Dartmouth. This college later moved and became the University of New Hampshire.
Dartmouth became more well-known in the early 1900s. Under President William Jewett Tucker, the college improved its buildings and grew its student body and faculty. Many people say Tucker "refounded Dartmouth" and made it a nationally recognized school.
Later presidents continued to improve the campus and made admissions more selective. During World War II, Dartmouth was one of many colleges that helped train students for the navy.
In 1956, a special meeting called the Dartmouth workshop happened at the college. This event is seen as the start of artificial intelligence as a field of study.
In 1970, John George Kemeny became president. He made big changes, including admitting women as full-time students in 1972. This was a major step for the college. Around the same time, Dartmouth started its "Dartmouth Plan" for academic scheduling. This plan allowed more students to attend without needing bigger buildings.
In 1988, the words of Dartmouth's school song changed from "Men of Dartmouth" to "Dear old Dartmouth" to include women.
In 2010, Dartmouth joined the Matariki Network of Universities, a group of universities from around the world.
In 2022, Dartmouth College returned important historical papers of Samson Occom to the Mohegan Tribe. Occom had helped Wheelock get money for the college.
On June 12, 2023, Sian Beilock became the first female president of Dartmouth.
In September 2023, Dartmouth hosted an event about the future of mental health. It included seven former U.S. Surgeons General. In 2024, the college hired a chief wellness officer to help students with mental health.
In April 2024, Dartmouth announced the Dartmouth Climate Collaboration. It pledged $500 million to remove carbon emissions from campus by 2050. This plan includes installing special heat pumps and a geoexchange system. It is the biggest change in the college's history.
Academics at Dartmouth
Dartmouth offers a four-year Bachelor of Arts degree and an engineering degree. The college has 39 departments with 56 different major programs. Students can also create their own special majors. Popular majors include economics, government, computer science, engineering, and history.
To graduate, students must complete 35 courses. This includes courses for their major and ten "distributive requirements" in different subjects. Students also need to be good at a foreign language and take writing classes. Many departments offer special programs for students who want to do advanced research and write a thesis. Dartmouth also has 57 different programs where students can study off-campus.
Dartmouth also offers advanced degrees like doctorates and master's degrees. It has three professional schools: the Geisel School of Medicine (started in 1797), Thayer School of Engineering (1867), and Tuck School of Business (1900). Even with these advanced schools, Dartmouth keeps the name "Dartmouth College" to show its focus on undergraduate education.
Dartmouth has many talented teachers. It has the highest number of female tenured professors among the Ivy League schools.
Research at Dartmouth
Dartmouth College is a major research institution. It is known for having "very high research activity." In 2019, Dartmouth College joined the Association of American Universities (AAU). This group includes 69 top research universities.
Dartmouth professors have made important discoveries. These include the Dartmouth Workshop (which helped start artificial intelligence), the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System, and the BASIC computer language. In 2005, Dartmouth faculty received $169 million for their research projects.
In 2017, Eric Fossum, an engineering professor, won the Queen Elizabeth Prize for his work on imaging sensors. The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, approved in 2021, was based on discoveries made in a science lab at Dartmouth. In 2024, Dartmouth researchers received a $31.3 million grant to study prostate cancer. In 2025, Dartmouth received about $97 million in funding from the National Institutes of Health.
College Rankings
| ARWU World | 301–400 |
|---|---|
| THES World | 168 (tie) |
| USNWR National University | 15 (tie) |
| Washington Monthly National University | 32 |
| Forbes | 16 |
| Business | 6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering | 55 | |
| Medicine | Primary Care | 46 |
| Research | 48 | |
| Biological Sciences | 33 |
|---|---|
| Chemistry | 67 |
| Computer Science | 43 |
| Earth Sciences | 54 |
| Mathematics | 53 |
| Physics | 61 |
| Psychology | 53 |
| Public Health | 41 |
U.S. News & World Report ranked Dartmouth 12th among national universities in 2022. It also ranked Dartmouth 3rd best for veterans and 5th best for undergraduate teaching. For five years in a row (2009–2013), U.S. News ranked Dartmouth's undergraduate teaching as 1st. Dartmouth College is officially approved by the New England Commission of Higher Education.
In Forbes magazine's 2019 rankings, Dartmouth was 10th overall among 650 universities. In 2018, Forbes ranked Dartmouth first for "grateful graduates" for the second year in a row.
The 2021 Academic Ranking of World Universities placed Dartmouth among the top universities in the nation.
How to Get Into Dartmouth
| Admissions statistics | |
|---|---|
|
2023 (Fall) entering
class for admissions and GPA; 2020 (Fall) entering class for SAT/ACT, the most recent time it was required |
|
| Admit rate | Overall: 6.23% ED: 19.9% RD: 4.6% |
| Test scores middle 50% | |
| SAT EBRW | 710–770 |
| SAT Math | 730–790 |
| ACT Composite | 32–35 |
| High school GPA† | |
| Top 10% | 94.5% |
| Top 25% | 98.3% |
| Top 50% | 99.8% |
|
|
Getting into Dartmouth College is very competitive. For the class entering in Fall 2023, Dartmouth received over 28,000 applications. Only about 6.2% of these students were accepted. Most of the accepted students were ranked at the top of their high school classes. The average SAT score for admitted students was 1501, and the average ACT score was 33.
Dartmouth helps students pay for college by meeting 100% of their financial need. This means they admit students, including international students, without looking at their ability to pay.
In 2020, Dartmouth made it optional for students to submit their SAT scores because of the Covid-19 pandemic. In 2024, Dartmouth became the first Ivy League school to require test scores again.
Financial Aid for Students
Dartmouth promises to meet all the financial needs of every admitted student who applies for aid. Dartmouth is one of only seven American universities that does "international need-blind admissions." This means they admit students based on their qualifications, not on whether they can pay, even for international students.
Students from families with incomes of $125,000 or less usually get free tuition. Dartmouth has also stopped giving out student loans to undergraduates. Instead, they offer more scholarship grants. In 2015, Dartmouth gave out $88.8 million in scholarships.
In March 2024, the family of Glenn Britt gave over $150 million to Dartmouth. This gift helps students from middle-income families attend the college for free.
The Dartmouth Plan

Dartmouth uses a "quarter system" for its academic year. This means it has four ten-week terms. The Dartmouth Plan, or "D-Plan," lets students customize their academic year.
All freshmen must live on campus and study during the fall, winter, and spring terms. They also must study during the summer term of their sophomore year and two terms of their senior year. For other terms, students can choose to study on campus, join an off-campus program, or take a term off. Students might use their time off for vacation, internships, or research. Most students take three classes per term.
The D-Plan started in the early 1970s when Dartmouth began admitting women. It was designed to allow more students to enroll without building more dorms. Even though new dorms have been built, the D-Plan is still used today.
How Dartmouth is Governed
Dartmouth is managed by a group called the Board of Trustees. This board includes the college president, the governor of New Hampshire, and 21 other trustees. Some trustees are chosen by the board itself, and others are nominated by alumni (former students).
Working with Other Universities
Dartmouth is an active member of the University of the Arctic (UArctic). UArctic is a group of over 200 universities and colleges. They work together to promote education and research in the Arctic region.
Dartmouth Campus
Dartmouth College is in the town of Hanover, New Hampshire. It is located in the Upper Valley region of New England. The main campus is 269 acres and is built around a 5-acre "Green" area. Dartmouth owns a lot of land in Hanover. It also owns 4,500 acres of Mount Moosilauke and a 27,000-acre forest called the Second College Grant.
Dartmouth's buildings are old and new. Some, like Wentworth and Thornton Halls, are from the 1820s. Newer buildings were finished in 2006. Most buildings are in the Georgian colonial style. The college works hard to reduce its carbon emissions and energy use.
The campus has many trees, including about 200 American elms. It also has the largest Kentucky coffeetree in New Hampshire.
Even though Dartmouth is in a rural area, it's connected to major cities by bus. Students can easily travel to Boston and New York City for weekends or vacations.
Academic Buildings

The Hopkins Center for the Arts (called "the Hop") is where students can study drama, music, film, and art. It has workshops for wood, pottery, and jewelry. The Hop was designed by famous architect Wallace Harrison. It has two theaters and a large auditorium. The Hop is connected to the Hood Museum of Art, which is one of the oldest museums in North America.
Dartmouth has three graduate schools. The Geisel School of Medicine has labs, classrooms, and a library. The Dartmouth–Hitchcock Medical Center is a teaching hospital for the Medical School. The Thayer School of Engineering and the Tuck School of Business are located near the Connecticut River. They share a library. In 2018, Dartmouth started building a new Center for Engineering and Computer Science. This center was finished by Spring 2022.
Dartmouth's libraries are all part of the Dartmouth College Library. They have over 2.48 million books and 6 million other resources. The main library is Baker-Berry Library. Its tall tower is a famous symbol of the college.
Sports Facilities
Dartmouth's main sports area is in the southeast part of campus. The Alumni Gymnasium has pools, a fitness center, and an indoor track. The Berry Sports Center, attached to the gym, has basketball and volleyball courts. Behind the gym is Memorial Field, a large stadium for football and track. The Thompson Arena is the ice rink, designed by an Italian engineer. The Nathaniel Leverone Fieldhouse is home to the indoor track. A new softball field was built in 2012.
Dartmouth also has boathouses along the Connecticut River for rowing. The Hanover Country Club is Dartmouth's oldest sports facility, started in 1899. The college also has the Dartmouth Skiway, a skiing area in Lyme Center, New Hampshire. It's where the Dartmouth Ski Team practices.
Student Housing and Life
Starting in 2016, Dartmouth placed all undergraduate students into one of six House communities. These are like smaller neighborhoods within the college. The houses are Allen House, East Wheelock House, North Park House, School House, South House, and West House. Dartmouth guarantees housing for freshmen and sophomores. More than 3,000 students live in college housing.
In November 2022, Dartmouth Hall was reopened after a $42 million renovation. This project was supported by many female alumni to celebrate 50 years of women attending Dartmouth.
Dartmouth Dining Services runs 11 places to eat on campus. The Class of 1953 Commons, or "Foco," is the main dining hall. There are also cafes and a convenience store.
The Collis Center is the main hub for student life. It has a cafe, study areas, and offices for student groups. Robinson Hall, next door, also houses many student organizations.
House Communities
| Name | Founded | Total capacity | Main location capacity | Main location buildings | Freshman buildings | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allen House | 2016 | 426 | 257 | Gile Hall, Streeter Hall, Lord Hall | Bissell Hall, Cohen Hall | Red |
| East Wheelock House | 2016 | 327 | 327 | Andres Hall, Zimmerman Hall, Morton Hall, McCulloch Hall | Orange | |
| North Park House | 2016 | 214 | 137 | Thomas Hall, Goldstein Hall, Byrne II Hall, Rauner Hall, Bildner Hall, Berry Hall | Dark Blue | |
| School House | 2016 | 561 | 333 | North, Mid- and South Massachusetts Halls, Hitchcock Hall | Brown Hall, Little Hall, Wheeler Hall | Light Blue |
| South House | 2016 | 592 | 366 | Topliff Hall, New Hampshire Hall, The Lodge | North, Mid- and South Fayerweather Halls, Richardson Hall | Black |
| West House | 2016 | 520 | 335 | Russell Sage Hall, Butterfield Hall, Fahey Hall, McLane Hall | French Hall, Judge Hall | Purple |
Student Life at Dartmouth
| Race and ethnicity | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| White | 49% |
|
|
| Asian | 15% |
|
|
| Foreign national | 11% |
|
|
| Hispanic | 10% |
|
|
| Other | 8% |
|
|
| Black | 6% |
|
|
| Native American | 1% |
|
|
| Economic diversity | |||
| Low-income | 15% |
|
|
| Affluent | 85% |
|
|
Dartmouth Student Government represents students on campus issues. Students elect a president and other leaders each year. In 2006, The Princeton Review ranked Dartmouth high for "Quality of Life" and "Happiest Students." Sports and Greek organizations are very popular. Dartmouth has over 350 student groups, teams, and sports. The school also has many old traditions and a strong network of alumni.
Student Groups and Clubs
Dartmouth has over 200 student organizations and clubs. These groups cover many interests, like academics, culture, and performing arts. Some famous groups include the Dartmouth Outing Club, which is the largest and oldest college outdoors club in the nation. There's also The Dartmouth Aires, the oldest a cappella group on campus. The Dartmouth is the college's daily newspaper, and it's one of the oldest university newspapers in the country.
Because Dartmouth is in a rural area, the Greek system is a very popular way for students to socialize. Dartmouth has 32 recognized Greek houses. About 70% of eligible students belong to a Greek organization. Students can join Greek groups starting in their sophomore year. Dartmouth was one of the first colleges to allow different races in fraternity houses in the 1950s. It also helped create coeducational Greek houses in the 1970s.
Dartmouth also has secret societies. These groups are led by students and alumni. They often work to preserve the college's history and do service projects. The Sphinx society is one of the most well-known.
Sports at Dartmouth
About 20% of students play a varsity sport. Nearly 80% of students participate in some kind of club, varsity, or intramural sport. In 2021, Dartmouth College had 33 varsity teams. These teams compete in the NCAA Division I Ivy League conference. Dartmouth does not offer sports scholarships, which is a rule for Ivy League schools. Besides common sports like football and basketball, Dartmouth also competes in track and field, softball, squash, sailing, tennis, rowing, and skiing.
The college also offers 26 club and intramural sports. These include fencing, rugby, water polo, and ultimate frisbee. The Dartmouth Fencing Team won a national championship in 2014. The Dartmouth Men's Rugby Team has been ranked among the best college teams. The figure skating team won national championships five times in a row. To graduate, every student must pass a 50-yard swim test and complete three terms of physical education.
Native American Students at Dartmouth
Dartmouth College's original charter from 1769 stated that the school was created to educate "Youth of the Indian Tribes in this Land." However, in its first 200 years, only 19 Native Americans graduated.
In 1970, Dartmouth started new programs to increase Native American enrollment. Since then, Dartmouth has graduated over 700 Native American students from more than 200 different tribes. This is more than all the other seven Ivy League universities combined.
Dartmouth Traditions
Dartmouth is known for its strong school spirit and many traditions. The college has a "quarter system," and one weekend each term is a special celebration. These are called "big weekends" or "party weekends."
In the fall, Homecoming (also called Dartmouth Night) features a large bonfire built by the freshman class. In the winter, students celebrate Winter Carnival. This tradition started in 1911 to promote winter sports. It is the oldest winter carnival tradition in the United States. In the spring, Green Key is a weekend for campus parties and celebrations.
The summer term used to have an unofficial tradition called Tubestock, where students floated on the Connecticut River. This ended in 2006. The Class of 2008 replaced it with Fieldstock. This new celebration includes a barbecue, live music, and chariot races around the Green. Fieldstock is supported by the college.
Another long-standing tradition is the four-day, student-run First-Year Trips for new freshmen. These trips started in 1935. Each trip ends at the Moosilauke Ravine Lodge. In 2011, over 96% of freshmen participated.
Dartmouth's Symbols
Motto and Song
Dartmouth's motto is Vox clamantis in deserto. This Latin phrase means "A voice crying out in the wilderness." It refers to the college's location, which was once a frontier area. Richard Hovey's "Men of Dartmouth" became the school's official song in 1926. In the 1980s, the song was renamed "Alma Mater" and its lyrics were changed to include women.
College Seal
Dartmouth's original charter from 1769 required a seal for official documents. The founder, Eleazar Wheelock, designed the seal. It looks similar to the seal of a missionary group. The seal was ready by 1773.
The seal shows a pine grove and Native Americans walking towards a building. It also has the motto "vox clamantis in deserto." The seal is supported by figures representing Religion and Justice. The date on the seal was changed from "1770" to "1769" in 1957 to match the college's charter date.
College Shield
In 1926, the trustees approved a "Dartmouth College Shield" for general use. This shield was designed based on the shield in the center of the original seal. In 1944, Canadian artist Thoreau MacDonald designed another coat of arms based on the seal's shield. This design is widely used today. Like the seal, its date was changed to "1769" around 1958.
Nickname and Mascot
Dartmouth has never had an official mascot. Its nickname, "The Big Green," started in the 1860s. It comes from the "Dartmouth Green" color chosen as the school's official color in 1866.
From the 1920s to the early 1970s, Dartmouth's sports teams were unofficially called "the Indians." In 1974, the college decided that using the Indian symbol was not right for its goals of Native American education. Some alumni and students have tried to bring the symbol back, but they have not succeeded.
Students have tried to adopt new mascots. One idea from a college humor magazine was Keggy the Keg, an anthropomorphic beer keg. Another idea was the "Dartmoose." Neither has become official.
Famous Dartmouth Alumni
Dartmouth's alumni are known for often donating money to their college.
By 2008, Dartmouth had over 60,000 living alumni. Many graduates work in finance, consulting, and technology. Top employers include Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, McKinsey & Company, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google.
Nelson Rockefeller, who was the 41st Vice President of the United States, graduated from Dartmouth in 1930. Over 164 Dartmouth graduates have served in the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives. These include Daniel Webster. Many Dartmouth alumni have served in the U.S. Cabinet, such as Henry Paulson and Timothy Geithner. C. Everett Koop was the Surgeon General of the United States. Two Dartmouth alumni, Salmon P. Chase and Levi Woodbury, served as justices on the Supreme Court of the United States.
In literature and journalism, Dartmouth has produced 13 Pulitzer Prize winners. Robert Frost, a famous poet, attended Dartmouth but did not graduate. He is the only person to receive two honorary degrees from Dartmouth.
Other famous authors and media personalities include CNN journalist Jake Tapper, novelist Heidi Julavits, and children's author Dr. Seuss. Norman Maclean, author of A River Runs Through It and Other Stories, graduated in 1924. Tom Ryan, CEO of Paramount Streaming, graduated in 1991.
In religion, alumni include ministers like Jonathan Clarkson Gibbs and rabbis like Marshall Meyer. Hyrum Smith, brother of Mormon Prophet Joseph Smith, also attended the college.
Dartmouth alumni in academics include Stuart Kauffman and Jeffrey Weeks, who both received "genius grants." Dartmouth has also graduated three Nobel Prize winners: Owen Chamberlain (Physics, 1959), K. Barry Sharpless (Chemistry, 2001 and 2022), and George Davis Snell (Physiology or Medicine, 1980). Nine of Dartmouth's seventeen presidents were alumni.
Many Dartmouth alumni are CEOs or executives at major companies. These include John Donahoe (Nike, Inc.), Louis V. Gerstner, Jr. (IBM), Jeffrey R. Immelt (General Electric), and Gail Koziara Boudreaux (United Health Care).
In film, entertainment, and television, Dartmouth is represented by David Benioff, co-creator of Game of Thrones; Shonda Rhimes, creator of Grey's Anatomy; and Budd Schulberg, who won an Academy Award for writing On the Waterfront. Other notable figures include Rachel Dratch from Saturday Night Live, Mindy Kaling from The Office, and Fred Rogers from Mister Rogers' Neighborhood.
Many Dartmouth alumni have found success in professional sports. Baseball players include Brad Ausmus and Kyle Hendricks. Football players include Jay Fiedler and Nick Lowery.
Dartmouth has also produced many Olympic athletes. Adam Nelson won silver and gold medals in shot put. Kristin King and Sarah Parsons won bronze medals in ice hockey for the United States. Cherie Piper, Gillian Apps, and Katie Weatherston won gold medals in ice hockey for Canada. At the 2024 Olympics, Ariana Ramsey won a bronze medal in rugby sevens for the United States.
Dick Durrance and Tim Caldwell competed in skiing in the Olympics. Dominic Seiterle won a gold medal in rowing for Canada at the 2008 Summer Olympics.
Images for kids
-
Robert Frost, poet
-
Dr. Seuss, writer and illustrator
-
Henry Paulson, former CEO of Goldman Sachs and United States Secretary of the Treasury
-
Daniel Webster, former Secretary of State
-
Robert Reich, former United States Secretary of Labor, political commentator, professor, and author
-
Sarah Wayne Callies, actress
-
Mindy Kaling, actress and comedian
-
Connie Britton, actress, singer and producer
-
Shonda Rhimes, television producer and writer
-
Brad Ausmus, baseball player
-
Jake Tapper, journalist, author, and commentator
-
David Benioff, screenwriter and television producer, writer, and director
-
Fred Rogers, television personality
(did not graduate) -
Rachel Dratch, comedian
See also
 In Spanish: Dartmouth College para niños
In Spanish: Dartmouth College para niños