Almond moth facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Almond moth |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
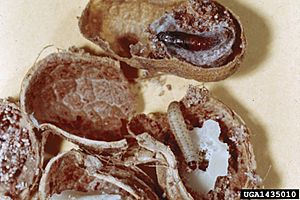
| Caterpillar and moth | |
 |
|
| Caterpillar (below) and pupa (above) in peanut husks | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Family: | Pyralidae |
| Genus: | Cadra |
| Species: |
C. cautella
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cadra cautella (Walker, 1863)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Numerous, see text |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The almond moth or tropical warehouse moth (Cadra cautella) is a small moth that often lives in places where food is stored, like warehouses. It's known as a pest because its young (called larvae or caterpillars) can eat and spoil many dry foods. These include flour, bran, oats, other grains, and even dried fruits.
This moth is part of a large group of moths called snout moths. The almond moth is found all over the world. This is because it often travels accidentally with food products. Adult almond moths live for about 10 days and do not eat.
Contents
What Does the Almond Moth Look Like?
Adult almond moths are mostly light brown. Their back wings are usually gray. When their wings are spread out, they measure about 14 to 22 millimeters wide. The edges of their wings have a short, fuzzy fringe.
The young almond moths, called larvae or caterpillars, are mostly gray with darker heads. They grow to be about 12–15 millimeters long. You can often tell them apart by the pattern of spots on their backs.
Where Do Almond Moths Live?
Almond moths are found all around the world. They like warm, tropical climates the best. However, they have spread to many other places. This happens because they infest dry foods that are shipped internationally. For example, they have traveled across Polynesia with shipments of copra (dried coconut meat).
What Do Almond Moths Eat?
Larvae Food
Almond moth larvae hatch on many different dry food products. These foods then become their main source of food. While they can infest various foods, the larvae grow fastest on products made from wheat. They also prefer cracked or ground seeds and grains. This is because they cannot easily get through hard shells or hulls of whole seeds. Interestingly, these caterpillars can also be cannibalistic. This means they might eat other eggs or smaller larvae if food is scarce.
Adult Food
Adult almond moths do not eat during their short lives. However, they will drink water if it is available to them.
How Do Almond Moths Grow?
Life Cycle
The almond moth grows best in warm and humid places. The perfect temperature for them to develop is around 30–32 degrees Celsius (86–90 degrees Fahrenheit). The best humidity is 70-80%.
In these ideal conditions:
- Eggs hatch in about three and a half days.
- The larvae go through five growth stages (called instars). This takes about 17 to 37 days.
- The pupal stage, where they transform into adults, lasts about seven days.
- Adult female moths live for about ten days on average.
- Adult male moths live for about six to seven days.
Laying Eggs
Female almond moths usually lay around 200 eggs at a time. The number of eggs and when they are laid can change. This depends on things like temperature, humidity, if water is available, and the type of food source. Lower temperatures can delay egg-laying. Low humidity or no water can reduce the number of eggs laid. Females usually lay their eggs at night.
Who Are the Almond Moth's Enemies?
Predators
Some insects like to eat almond moths. For example, a type of beetle called Xylocoris flavipes prefers to eat the eggs and young larvae of the almond moth. Also, a kind of mite called Blattisocius tarsalis eats almond moth eggs throughout its life. Scientists have even thought about using these mites to help control almond moth infestations.
Parasites
Many types of wasps are parasites of the almond moth. This means they live on or in the moth and harm it.
- Tiny wasps from the genus Trichogramma (like T. evanescens and T. brassicae) are common parasites. They will sting almond moth eggs and lay their own young inside. These parasites then kill the moth larva inside the egg and later emerge from the egg themselves.
- Other wasps, such as Bracon hebetor and Venturia canescens, parasitize almond moth larvae when they are older.
Diseases
A type of bacteria called Wolbachia can infect almond moths. This bacteria lives in the moth's ovaries and is passed from a mother moth to her offspring. Wolbachia does not directly kill the infected moth. Instead, it spreads when the moth reproduces. This means only moths that live to adulthood can spread the bacteria further.
How Do Almond Moths Interact with Humans?
The almond moth is often seen as a pest because it can spoil many dry food products. These include dried fruits, wheat products, flours, nuts, and seeds. People have looked for different ways to control these moths.
While pesticides and other chemicals can reduce infestations, they can also harm the environment and the people who eat the food. Because of this, scientists are exploring natural enemies of the almond moth, like predators and parasites, as safer ways to control them.
Synonyms
Because of its wide distribution and accidental introductions, it has become known under a number of junior synonyms:
- Cadra defectella Walker, 1864
- Cryptoblabes formosella Wileman & South, 1918
- Ephestia cautella (Walker, 1863)
- Ephestia irakella Amsel, 1959
- Ephestia passulella Barrett, 1875
- Ephestia pelopis Turner, 1947
- Ephestia rotundatella Turati, 1930
- Nephopteryx desuetella Walker, 1866
- Nephopterix passulella (Barret, 1875)
- Pempelia cautella Walker, 1863
See also
 In Spanish: Cadra cautella para niños
In Spanish: Cadra cautella para niños


