American ginseng facts for kids
Quick facts for kids American ginseng |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Panax quinquefolius | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: |
Aralioideae
|
| Genus: |
Panax
|
| Species: |
P. quinquefolius
|
| Binomial name | |
| Panax quinquefolius |
|
American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) is a special plant. It is a perennial plant, which means it lives for more than two years. This plant belongs to the ivy family. People often use it as an herb in traditional medicine, including traditional Chinese Medicine.
American ginseng grows naturally in eastern North America. However, it is also grown in China. For a long time, since the 1700s, American ginseng has been sent to Asia. There, it is highly valued for its calming and cooling effects in medicine. It is thought to have "yin" qualities, which are cooling. Asian ginseng, on the other hand, is seen as having "yang" qualities, which are warming.
Contents
What is American Ginseng?
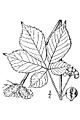
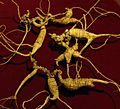
The root of American ginseng smells nice and looks a bit like a small parsnip. As the plant gets older, its root can split into two parts. The plant usually grows about 6 to 18 inches (15 to 45 cm) tall. It typically has three leaves, and each leaf has three to five smaller leaflets. These leaflets are usually 2 to 5 inches (5 to 13 cm) long.
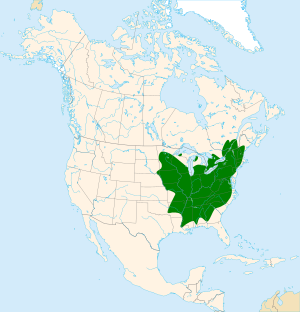
You can find American ginseng in many parts of the eastern and central United States. It also grows in some areas of southeastern Canada. It mostly lives in deciduous forests in places like the Appalachian Mountains and The Ozarks. These forests have trees that lose their leaves in the fall. American ginseng needs full shade to grow well.
Because it needs a very specific environment and is so popular, it is becoming rare in some places. Some states in the U.S. list American ginseng as endangered or vulnerable. For example, Maine and Rhode Island say it is endangered. New York and Pennsylvania consider it vulnerable. In Canada, it is listed as endangered across the country and in Ontario. It is threatened in Quebec.
How is it Used in Traditional Medicine?
Long ago, Native American people used the root and leaves of this plant in their traditional medicines. Since the 1700s, people called "sang hunters" have collected the roots. They sell them to traders, often from China or Hong Kong. Very old wild roots can be worth a lot of money.
When American ginseng first arrived in China, it came through a warm seaport called Guangzhou. Because it came from a warm area, Chinese doctors thought it must be good for "yin" (cooling) qualities. They didn't know that the plant actually grows in cooler, temperate places. Still, it is truly considered more "yin" because it helps the body create fluids.
Some people use American ginseng to help with the common cold. However, there is not strong scientific proof that it works against colds. Some studies suggest it might make a cold shorter if you use it before you get sick.
Things to Know About Using Ginseng
If someone is taking medicines to stop blood clots, like warfarin, they should not use ginseng. It is also not suggested for people with liver or kidney problems. Pregnant or breastfeeding people should avoid it too.
Sometimes, ginseng can cause side effects. These can include headaches, feeling anxious, trouble sleeping, or an upset stomach.
Some studies have looked at how American ginseng is grown. They found that sometimes, the plants can have small amounts of mold, pesticides, or metals. While these amounts are usually not very high, it is still important to be careful. It means you should always get ginseng from trusted sources.
How is American Ginseng Produced?
American ginseng used to be very common in the Appalachian Mountains and The Ozarks. It also grew in nearby forested areas like Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario. But because it is so popular and needs special places to grow, wild plants have been overharvested. This means too many plants were collected. Also, its natural homes have been destroyed. So, it is now rare in most parts of the United States and Canada.
Other things that harm ginseng include deer eating the plants, cities growing bigger, and forests being broken up into smaller pieces.
People can grow ginseng on farms. They can grow it under artificial shade, in forests, or by making it seem like it's growing wild. It usually takes three to four years to harvest. If it's grown to seem wild, it can take up to 10 years before it's ready.
Ontario, Canada is the biggest producer of North American ginseng in the world. In the United States, Marathon County, Wisconsin, grows about 95% of it. Some programs in states like Vermont, Maine, and Tennessee are encouraging people to plant ginseng. This helps bring back its natural habitats and protects the wild ginseng that is left.
What are its Names?
The name "ginseng" comes from the Chinese word jen-shen. In Chinese, it has other names too. One is huaqishen (simplified Chinese: 花旗参; traditional Chinese: 花旗參; pinyin: huāqíshēn; Cantonese Yale: fākèihsām; literally "Flower Flag ginseng"). Another is xiyangshen (simplified Chinese: 西洋参; traditional Chinese: 西洋參; pinyin: xīyángshēn; Cantonese Yale: sāiyèuhngsām; literally "west ocean ginseng").
Is it Protected?
Yes, American ginseng is listed in Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species. This helps control how it is traded around the world to protect it.
Gallery
See also
 In Spanish: Ginseng americano para niños
In Spanish: Ginseng americano para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |