Ancient Manipur facts for kids
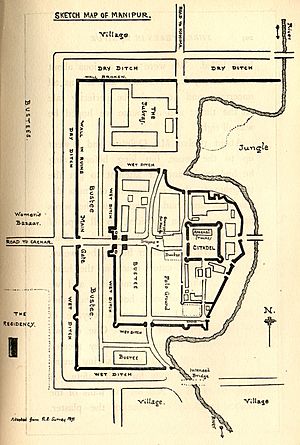
Ancient Manipur, also known as Kangleipak, was an old civilization. It was located in the central plains of what is now Manipur, India. The city of Kangla was the capital of Ancient Manipur (Kangleipak). It served as the main city from very ancient times until the late 1800s. The first signs of kings ruling (a monarchy) go back to the 15th century BC. This was during the time of Emperor Tangja Leela Pakhangba (1445 BC-1405 BC).
Contents
History of Ancient Manipur
The history of kings ruling in Ancient Manipur began in 1445 BC. This was with the reign of King Tangja Leela Pakhangba.
The game of polo (called sagol kangjei) was invented during the time of King Kangba. He ruled from 1405 BC to 1359 BC. King Kangba was the ruler after Tangja Leela Pakhangba. This amazing invention was written about in many old books. These books include the Kangbalon and the Kangjeirol.
Geography of Manipur
The land of Manipur (Kangleipak) is mostly mountainous. Because of this, ancient Manipur had many smaller regions. Each region had its own way of speaking (dialect). They also had special cultural traditions and their own identity.
Language of Ancient Manipur
The old Manipuri language, also known as Meitei language, had many important writings. These writings were called Puya. They covered many different topics. These texts were written using the old Meitei script.
One of the oldest writings is the "Wakoklon Heelel Thilen Salai Amailon Pukok Puya". It was written in 1398 BC. This date has been checked and confirmed by the National Archives of India in New Delhi.
Culture in Ancient Manipur
Daily Life
Most people in ancient Manipur were farmers. They worked on their lands. Their homes were usually just for their immediate family members.
Architecture
The old building designs for common houses were very smart. They were thought to be sustainable and good for the environment. They were also affordable. These houses helped keep people cool during hot summers. They also kept people warm during cold winters.
Religious Beliefs
The ancient religion of the local people in the hills and plains was Sanamahism. In this belief, the idea of space and time together is the ultimate God. This God is seen as the creator of the whole universe.
Beliefs in gods and in life after death were a big part of ancient Manipur. These ideas were there from the very beginning of the civilization. The ancient rulers believed they had a special right to rule from the gods.
Military System
Lallup System
The Lal-lup system was a very important way of life in ancient Manipur. The word Lal means war. The word lup means a club, an association, or an organization.
Under this system, every man from the local groups who was over 16 years old had to be a member. This meant they were part of the system.
Images for kids
-
The Kangla Uttra Sang at the Kangla Fort. This was once where the Manipur kings lived. The two Kangla-Sa Pakhangba dragons at the gate were destroyed after the Anglo-Manipur War in 1891. But they have been rebuilt in recent years.
-
Pakhangba, a dragon symbol used in heraldry by the Meetei people. It is an important symbol for the state of Manipur.
-
The Manipuri dance was once supported by the royal family of Manipur.
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |