Apatosaurus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids ApatosaurusTemporal range: Upper Jurassic
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
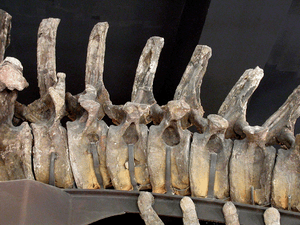
| A. louisae skeleton, Carnegie Museum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Infraorder: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Apatosaurus
Marsh, 1877
|
Apatosaurus is a huge, plant-eating dinosaur that lived during the Upper Jurassic period. This was about 150 million years ago! It belongs to a group of dinosaurs called sauropods, known for their long necks and tails. Apatosaurus is related to Diplodocus.
For a long time, people thought Brontosaurus was just another name for Apatosaurus. But now, scientists have found enough differences to say they are actually two separate types of dinosaurs.
Apatosaurus was truly enormous. It could grow up to 21 meters (about 69 feet) long. That's longer than two school buses! It stood about 4.5 meters (15 feet) tall at its hips. This giant weighed around 23 metric tons, which is like four large elephants. Its bones have been discovered in parts of the United States, including Wyoming, Colorado, Oklahoma, and Utah.
When Apatosaurus was first found, some scientists thought it might have lived partly in water. They believed it was too heavy to walk easily on dry land. But now, most scientists agree that Apatosaurus lived on land. It probably roamed in herds, just like elephants do today.
Contents
What did Apatosaurus look like?
Apatosaurus had a very long neck and a long, whip-like tail. Its neck bones were strong and solid. The bones in its legs were also very thick and sturdy. This suggests it was a very strong and powerful animal.
Scientists believe Apatosaurus held its tail off the ground when it walked. Like many other sauropods, it had a single large claw on each front foot. On its back feet, the first three toes also had claws.
Different Kinds of Apatosaurus
Scientists have found at least two main species of Apatosaurus:
- A. ajax: This species was discovered by a scientist named Othniel Charles Marsh in 1877.
- A. louisae: This one was found by William Holland in 1915.
- Another dinosaur found in 1994 was first called A. yahnahpin. But later, in 1998, it was given a new name: Eobrontosaurus yahnahpin.
How Apatosaurus Lived
For a long time, people thought huge dinosaurs like Apatosaurus were too heavy to live only on land. They imagined these giants spending most of their time in water, perhaps in swamps. However, newer discoveries don't support this idea. Scientists now think sauropods were fully terrestrial animals. This means they lived entirely on land.
Studies of their snouts and teeth suggest that Apatosaurus ate plants that grew close to the ground. It probably wasn't picky about its food. It might have munched on ferns, cycads, seed ferns, horsetails, and even algae.
Scientists are still trying to understand how these huge dinosaurs kept warm or cool. They also wonder how their bodies worked, like how they breathed. Some scientists have wondered if their hearts could pump enough blood all the way up to their brains. But others think that because their heads and necks were often held almost straight out, it might not have been a problem.
One scientist, James Farlow, calculated that a dinosaur the size of Apatosaurus would have had a lot of food being digested inside it. He suggested that the heat from this digestion might have helped keep these reptiles warm.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Apatosaurus para niños
In Spanish: Apatosaurus para niños