Native elm facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Native elm |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
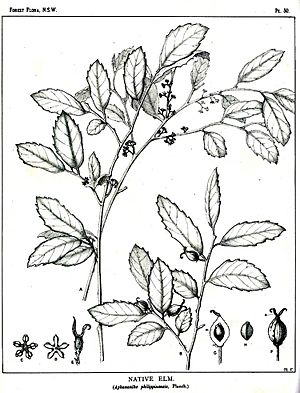
| Drawing by Margaret Flockton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Aphananthe
|
| Species: |
philippinensis
|
| Synonyms | |
The native elm (scientific name: Aphananthe philippinensis) is a common tree found in rainforests. It belongs to the Cannabaceae family, which might surprise you because this family also includes the hemp plant!
This tree grows in Australia, stretching from the Manning River in New South Wales all the way up to Herberton in tropical Queensland. It was first discovered and described on the island of Luzon in the Philippines, which is why its scientific name includes "philippinensis." The name Aphananthe means "insignificant flowers," referring to its small blooms. You can also find this tree in the Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea.
While it can grow in dry rainforests, the native elm prefers to be near streams where the soil is moist and rich. People in Australia call it by many names, like grey handlewood, axe handle wood, rough-leaved hickory, and even asbestos tree.
What Does It Look Like?
The native elm can grow quite tall, up to 35 metres (about 115 feet), and its trunk can be 85 centimetres (about 33 inches) wide. However, you often see it as a smaller tree. The trunk isn't perfectly round; it has grooves and bumps, especially at the bottom where it spreads out to support the tree.
The bark is brown and peels off in patches, making it look a bit bumpy and uneven. The smaller branches are grey and have long cracks along them.
Leaves
The leaves of the native elm grow one after another along the stem. They feel hard and dry, almost like sandpaper, but they are also quite brittle and can snap easily. Each leaf has sharp, prickly teeth along its edges and a pointed tip.
The leaves are shaped like a spearhead, usually 4 to 6 centimetres (about 1.5 to 2.5 inches) long and 1.5 to 3 centimetres (about 0.6 to 1.2 inches) wide. They are green on both sides, but a bit lighter underneath. You can see the veins clearly on both sides of the leaf. The main vein is slightly sunken on the top but sticks out on the underside, where it looks pale.

Flowers and Fruit
The native elm has both male and female flowers on the same tree. The male flowers grow in small clusters called cymes. The female flowers usually grow alone, or sometimes two together, on a short stalk about 5 millimetres long. Both male and female flowers are small, around 5 millimetres long, and they appear from September to November.
After the flowers, the tree produces fruit. The fruit is a black, egg-shaped drupe, which is a type of fruit with a hard pit inside, like a cherry or peach. It's about 6 millimetres long and contains a single seed. The seed itself is about 5 millimetres long and has a somewhat triangular shape. The fruit ripens between February and June.
Who Eats It?
The native elm is an important food source for many animals. Its leaves are eaten by the caterpillars of butterflies like the common aeroplane and the rounded six-line blue.
The fruit of the native elm is a favourite snack for many different birds, including:

