Apollonia–Arsuf facts for kids
|
Ἀπολλωνία
Σώζουσα אפולוניה أرْسُوف Arsur |
|

An aerial view of the Crusader castle and anchorage
|
|
| Alternative name | Arsur |
|---|---|
| Location | Tel Aviv District, Israel |
| Coordinates | 32°11′43″N 34°48′24″E / 32.19528°N 34.80667°E |
| Grid position | 132/178 PAL |
| Type | Lowland castle (for the city citadel) |
| History | |
| Abandoned | 1265 |
| Periods | Mainly Early Islamic and Crusader periods |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruin |
| Public access | Yes, national park |
| Website | Apollonia National Park – Israel Nature and Parks Authority |
Apollonia was an ancient city located on the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Israel. It was also known as Arsuf during the Early Islamic period and Arsur during the Crusader period. Today, archaeologists call it Tel Arshaf.
This city was first built by the Phoenicians around 500 BCE. People lived there continuously through the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine times. During the Byzantine era, its name changed to Sozusa.
Apollonia was located on a cliff overlooking the Mediterranean Sea, about 34 kilometers (21 miles) south of Caesarea.
In 640 CE, the city was taken over by Muslims and became known as Arsuf. It was an important stronghold, especially during the Third Crusade. The famous Battle of Arsuf was fought nearby in 1191. In 1265, the city and its castle were completely destroyed by the Mamluks.
Today, the site of Apollonia–Arsuf is part of the Herzliya municipality in Israel. It has been actively excavated since 1994. In 2002, the Apollonia National Park opened to the public, allowing visitors to explore the ancient ruins.
Contents
Understanding the City's Names
The city's first recorded name was Apollonia, given by the Greeks around the 4th century BCE. Many believe this name came from the Canaanite god Resheph, who was similar to the Greek god Apollo.
Later, during the Byzantine period, the city's name changed from Apollonia (meaning "city of Apollo") to Sozusa. Sozousa means "city of the Saviour". This change happened because Christianity became the main religion, and "Saviour" was a name for both Apollo and Jesus Christ.
When Muslims took over, the city became known as Arsuf. During the Crusader period, it was often called Arsur in documents. These different names show how the city's rulers and cultures changed over many centuries.
A Look at Apollonia's History
Ancient Times
Even though some very old remains have been found, there's no clear evidence of a large settlement before the Persian period, around 500 BCE. Apollonia grew into an important regional center and a main harbor in the southern Sharon Plain by the 4th century BCE.
Hellenistic and Roman Periods
During the Hellenistic period, Apollonia was a port town ruled by the Seleucids. Under Roman rule, the city became a busy center for trade and industry. In 113 CE, an earthquake damaged Apollonia, but it quickly recovered.
Ancient writers like Pliny the Elder and Ptolemy mentioned Apollonia. The Roman leader Aulus Gabinius rebuilt the city in 57 BCE after finding it in ruins. This shows how important it was as a coastal town between Caesarea and Jaffa.
Byzantine Era and Sozusa
In the late Roman period, the city was known as Sozusa in Palaestina. It was an important religious center with its own bishop. The name changed from Apollonia to Sozusa before 449 CE. This new name was used by Byzantine geographers.
The city was briefly held by the Sasanian Empire during a war in the early 7th century, but it returned to Byzantine control before the Muslim conquest.
Early Muslim Period
In 640 CE, the city fell to the Muslims and was renamed Arsuf. It became smaller, covering about 22 acres. To protect itself from attacks by Byzantine ships, the city built strong walls with buttresses.
At the time of the Muslim conquest, many Samaritans lived in Sozusa. However, in 809 CE, the Abbasids forced a large group of Samaritans to leave the city, and their synagogue was destroyed.
Crusader and Mamluk Periods
The Crusaders, led by Godfrey de Bouillon, tried to capture Arsuf but failed. Later, in 1102, King Baldwin I successfully took the city after a siege by land and sea. The Crusaders called it Arsur and rebuilt its walls.
In 1187, Muslims recaptured Arsuf. But on September 7, 1191, it was taken back by the Crusaders after the famous Battle of Arsuf, where Richard I of England defeated Saladin.
In 1241, new walls, a large castle, and a new harbor were built. In 1251, Louis IX of France helped rebuild its defenses. From 1261, the city was ruled by the Knights Hospitaller, a military order.
The Fall of Arsuf
In 1265, the Mamluk sultan Baibars besieged Arsuf for 40 days. He eventually captured the city. The people living there were either killed or sold as slaves, and the entire town was completely destroyed. The destruction was so thorough that the site was abandoned and never became a city again.
The Sidna Ali Mosque, just south of Arsuf, was built by Baibars to celebrate his victory.
Ottoman Period
In 1596, Ottoman records show Arsuf as a small village with 22 families, all Muslim. It was a quiet place during this time.
Modern Times in Israel
The site became part of the Herzliya municipality in 1924. A nearby village was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. In the 1950s, new housing for immigrants was built south of the site.
The settlement of Rishpon was established in 1936 northeast of the site. Today, there's also a modern community called Arsuf, built in 1995, named after the ancient city.
Archaeological Discoveries
The site of Apollonia–Arsuf has been actively excavated since the 1990s. In 2002, it opened to the public as the Apollonia National Park. Excavations continued as of 2015, revealing many secrets of the ancient city.
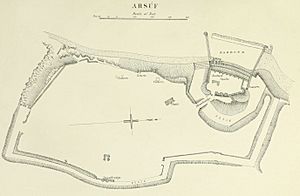
Before the excavations, visible remains included the medieval city wall and its moat. There was also a Crusader castle with a double-wall system and a port with built jetties.
Archaeologists found large amounts of pottery from the Byzantine and early Islamic periods. This shows that the city was much larger than its old walls during the 7th century. They also uncovered a large Roman-era villa maritima (a fancy seaside house) south of the main site.
See Also
 In Spanish: Arsuf para niños
In Spanish: Arsuf para niños
- List of ancient Greek cities
- Tel Michal
- Via Maris
- Crusader period:
- Vassals of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
- Lord of Arsuf
- Battle of Arsuf (1191)
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |