Barrow Strait facts for kids
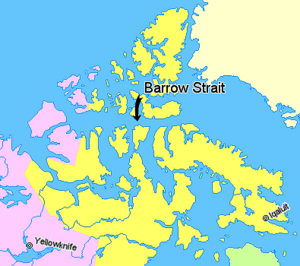
The Barrow Strait is an important shipping route in Nunavut, a territory in Northern Canada. It is part of the larger Parry Channel. This strait acts like a big watery highway, separating several large islands. To the north, you'll find Cornwallis Island and Devon Island. To the south are Prince of Wales Island, Somerset Island, and Prince Leopold Island.
Where is Barrow Strait?
The eastern part of the strait, for about 30 miles (48 km), has no islands. This area usually stays unfrozen until late November and doesn't fully freeze solid until late December.
There are several smaller islands within the strait. South of Bathurst Island, you can find Garrett Island, Lowther Island, Young Island, Hamilton Island, and Russell Island. Southwest of Cornwallis Island are Browne Island, Somerville Island, and Griffith Island. Beechey Island is located off the coast of Devon Island.
Size and Shape
The Barrow Strait stretches for about 170 miles (274 km). It goes from its eastern entrance at Lancaster Sound to its western end at Viscount Melville Sound.
The eastern entrance, between Prince Leopold Island and Cape Hurd on Devon Island, is about 28 miles (45 km) wide. The western entrance, near Cape Cockburn on southwestern Bathurst Island, is much wider at about 66 miles (106 km).
Wildlife and Importance
The Barrow Strait is home to many amazing Arctic animals. Along the edge of the ice, especially near Leopold Island, you can find Arctic foxes, various birds, polar bears, ringed seals, and whales.
When the ice in the central and western parts of the strait freezes solid, it creates a natural bridge. This ice bridge is used by caribou to cross between islands.
This strait is a very important waterway for large ships traveling through the Arctic. Because of its strategic location, the Strait was carefully mapped by the Soviet Navy during the Cold War, a time when different countries were very competitive.
See also
 In Spanish: Estrecho de Barrow para niños
In Spanish: Estrecho de Barrow para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |