Basketmaker culture facts for kids
The Basketmaker culture was a group of ancient people. They lived in the American Southwest a very long time ago. Their story began around 1500 BC and lasted until about AD 750. They were called "Basketmakers" because archaeologists found so many amazing baskets where they lived. These baskets are between 2,000 and 3,000 years old!
Contents
Who Were the Basketmakers?
Scientists have learned a lot about the Basketmakers. This is thanks to well-preserved mummies found in dry caves.
What They Looked Like
Basketmaker women were usually about 5 feet tall. Men were a bit taller, around 3 to 4 inches more. They had long, narrow faces. Their bodies were medium to strong. Their skin color ranged from light to dark brown. They had brown or black hair and eyes.
Their Clothes and Style
The Basketmakers wore sandals. These were made from woven yucca plant fibers or strips of leaves. They didn't wear much clothing. A few loincloths have been found. Women might have worn aprons for special events. For warmth, they used blankets. These blankets were made from yucca fibers and rabbit fur.
Both men and women liked to wear jewelry. They had necklaces, bracelets, and pendants. These were made from shells, stones, bones, and dried berries. Some shells, like abalone and olivella, came from the Pacific coast. This means they traded with other groups far away!
Life Through the Eras
The Basketmaker culture changed over time. It is divided into different periods or "eras."
Early Basketmaker II Era (Around 1500 BC to AD 50)
In this early time, people moved around a lot. They were semi-nomadic hunter-gatherers. This means they hunted animals and gathered plants for food. Then, they started to grow corn. This important change helped them settle down more. Some early Basketmakers lived in cave shelters. These were found near the San Juan River. When archaeologists dug there, they found many baskets. They also found corn and signs of human burials.
Late Basketmaker II Era (Around AD 50 to AD 500)
During this period, Basketmakers started living in permanent homes. These were simple pit-houses. They were built from brush, logs, and earth. Later in this era, they began making fired pottery. Pottery helped archaeologists learn more about where people lived. It also showed how their culture changed.
Basketmaker III Era (Around AD 500 to AD 750)
Hunting became much easier in this era. This was because the bow and arrow were invented! Before this, they used spears and a tool called an atlatl. The bow and arrow made hunting more efficient.
-
Basketmaker II "two rod and bundle" basket (around AD 1 to 700), found in Zion National Park
After the Basketmaker eras came the Pueblo Eras. During these times, people built multi-room homes above ground. These were made of stone. They also had better stone tools. Their clothes were made of cotton or turkey feathers. A special ceremonial room called a kiva also became important.
Their Home and Environment
Water was the most important thing for the Ancestral Puebloan people. The land they lived on had different climates. In lower areas, it was dry. There were juniper trees and sagebrush. Higher up, around 6,000 feet (1,829 meters), it was wetter. Pinyon trees grew there.
Other Ancient Groups
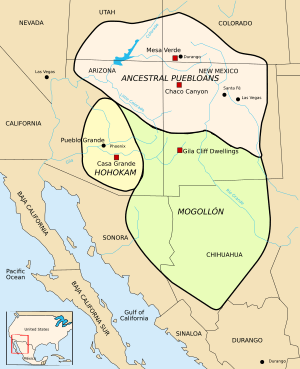
The Basketmaker culture was part of a larger picture. Other cultural groups lived in the same region during this time:
- Ancestral Puebloans – Found in southern Utah, southern Colorado, northern Arizona, and northern and central New Mexico.
- Hohokam – Lived in southern Arizona.
- Mogollon – Found in southeastern Arizona, southern New Mexico, and northern Mexico.
- Patayan – Lived in western Arizona, California, and Baja California.
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |