Battle of Belleau Wood facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Belleau Wood |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of World War I | |||||||
 Painting by Frank Schoonover "Wheat Field" charge of 6th Marines—around Belleau Wood—to town of Bouresches. 250 started 19 finished |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 2 U.S. Army divisions (including 1 brigade of United States Marines) French 6th Army (elements) British IX Corps (elements) |
5 German divisions (elements) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1,811 killed 7,966 wounded |
10,000+ casualties
|
||||||
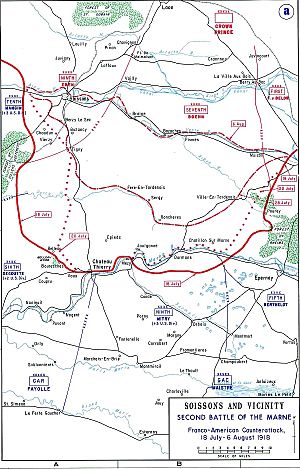
The Battle of Belleau Wood was a big battle during World War I. It happened from June 1 to June 26, 1918, near the Marne River in France. American, French, and British forces fought against German units. This battle is very important in the history of the United States Marine Corps.
Contents
Why the Battle Happened
In March 1918, Germany had many more soldiers available. This was because Russia had left the war on the Eastern Front. The German Army started a series of strong attacks on the Western Front. They hoped to win the war before more U.S. troops could arrive and join the fight.
In May, the Germans launched a third big attack against the French. They pushed forward quickly and reached the Marne River, about 95 kilometers (59 miles) from Paris. On May 31, American soldiers helped stop the German advance in a town called Château-Thierry. The Germans then turned towards Belleau Wood.
By June 1, German troops had moved into Belleau Wood. The U.S. 2nd Infantry Division, which included a group of U.S. Marines, arrived to help. They took up positions along the main highway.
The Battle Begins
On the evening of June 1, German forces broke through the French lines next to where the Marines were. American reserve troops, including Marines, marched over 10 kilometers (6 miles) to fill this gap. They got there by dawn. By the night of June 2, U.S. forces held a 20-kilometer (12-mile) front line. This line ran through fields and woods.
Stopping the German Advance
German commanders wanted to push through Belleau Wood as part of a larger attack. They planned to cross the Marne River. However, the commander of the Marine Brigade, General James Harbord, told his Marines to "hold where they stand." This was different from a French order to retreat. The Marines quickly dug shallow holes to fight from.
On the afternoon of June 3, German soldiers attacked the Marine positions. The Marines waited until the Germans were very close, about 100 yards away. Then, they opened fire with their rifles. This stopped many German soldiers, forcing the rest to retreat into the woods.
The Germans had lost many soldiers. They dug in along a defensive line that went through Belleau Wood. French forces who were retreating told the Marines to turn back. But Marine Captain Lloyd W. Williams famously replied, "Retreat, hell! We just got here."
On June 4, Major General Bundy took command of the American part of the front line. For the next two days, the Marines fought off continuous German attacks.
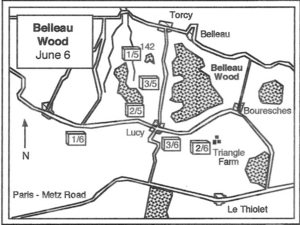
Attack on Hill 142
At 3:45 AM on June 6, the Allied forces launched an attack. The French attacked on the left side of the American line. The Marines attacked Hill 142 to stop Germans from attacking the French from the side. The plan was also for the 2nd Division to capture a ridge and Belleau Wood itself. However, the Marines didn't check the woods carefully. They didn't realize a German regiment was dug in there with many machine guns.
At dawn, the 1st Battalion, 5th Marines, attacked Hill 142. They advanced in waves across an open wheat field. German machine guns and artillery fired heavily, and many Marines were killed. Captain Crowther was killed almost right away. Captain Hamilton and his company fought from tree to tree, pushing back the Germans. Hamilton lost all his junior officers, and his company had only one officer left.
During a German counter-attack, Gunnery Sergeant Ernest A. Janson stopped 12 German soldiers by himself. He killed two with his bayonet, and the others ran away. For this brave action, he became the first Marine to receive the Medal of Honor in World War I. Another brave Marine, Henry Hulbert, also received a medal for his actions.
By the afternoon, the Marines had captured Hill 142. But it came at a high cost, with many officers and men lost.
Marines Attack Belleau Wood
On the night of June 4, a Marine officer named Lieutenant William A. Eddy and two men went behind German lines. They gathered important information. They found out that the Germans were setting up more machine guns and bringing in artillery. This showed the Germans were getting stronger and could try to break through to Paris.
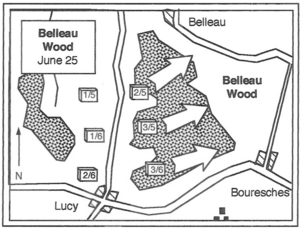
At 5:00 PM on June 6, two Marine battalions attacked Belleau Wood from the west. Again, the Marines had to advance through a wheat field while being shot at by machine guns.
The first groups of Marines were killed in large numbers. Major Berry was wounded. On the right, Major Sibley's Marines entered the southern part of Belleau Wood. They faced heavy machine gun fire, snipers, and barbed wire. Marines and German soldiers soon fought hand-to-hand. This day saw the most casualties the Marine Corps had ever suffered up to that point. About 31 officers and 1,056 men from the Marine brigade were killed or wounded. But the Marines had gained a small part of Belleau Wood.
Fighting Inside Belleau Wood
The battle became a stalemate, meaning neither side could gain much ground. On June 7-8, a German attack was stopped, and an American counter-attack also failed. On June 9, American and French artillery heavily bombed Belleau Wood. This turned the once beautiful forest into a mess of broken trees. The Germans fired back and strengthened their defenses inside the wood.
On the morning of June 10, Major Hughes' Marines attacked north into the wood. This attack also stopped because of heavy machine gun fire. The commander of the 6th Machine Gun Battalion was badly wounded and later died. The Germans also used a lot of mustard gas.
At 4:00 AM on June 11, Wise's men advanced through a thick morning mist towards Belleau Wood. They were met with heavy fire. Many groups of soldiers were cut off and destroyed by machine guns firing from different directions. They found out they had advanced in the wrong direction. However, they still broke through the German southern defense lines. One German soldier wrote that the Americans were "terribly reckless fellows."
The Marines attacked the woods a total of six times before they finally forced the Germans out. They fought against parts of five German divisions. Often, they had to fight hand-to-hand using only their bayonets or fists.
On June 26, the 3rd Battalion, 5th Marines, made a final attack on Belleau Wood. This attack finally cleared the forest of Germans. That day, Major Shearer sent a simple report saying, "Woods now U.S. Marine Corps entirely." This ended one of the toughest battles U.S. forces fought in the war.
After the Battle
The United States forces had 9,777 casualties, which included 1,811 killed. Many of them are buried in the nearby Aisne-Marne American Cemetery. We don't have clear numbers for German soldiers killed, but 1,600 were captured.
After the battle, the French renamed the wood Bois de la Brigade de Marine. This means 'Wood of the Marine Brigade'. It was to honor the Marines' toughness. The French government also gave special awards called the Croix de guerre to the 5th and 6th Marine Regiments and the 6th Machine Gun Battalion.
General John J. Pershing, who was the commander of the American forces, said, "The deadliest weapon in the world is a United States Marine and his rifle." He also said that the Battle of Belleau Wood was the biggest battle for the U.S. since the American Civil War.
There's a story that the Germans called the Marines Teufelshunde, which means 'devil dogs'. This hasn't been fully confirmed, but a German officer later wrote that the Marines' "fiery advance and great tenacity were well recognized by their opponents."
What We Remember
Marines who serve in the Fifth and Sixth Marine regiments today are allowed to wear a special braided cord called a fourragère on their uniform. This is to remember the bravery of the Marines who fought at Belleau Wood.
In June 1923, the Marine Band played a new march called "Belleau Wood" for the first time. It was dedicated to Major General James Harbord, who led the Marines during the battle.
In July 1923, Belleau Wood became an American battle monument. White crosses and Stars of David mark 2,289 graves there. The names of 1,060 missing men are on a memorial chapel wall. Visitors can also see a nearby German cemetery where 8,625 men are buried.
On November 18, 1955, a black marble monument was placed near the battle site. It shows a fighting Marine and is called The Marine Memorial. This memorial honors the 4th Marine Brigade for their bravery in June 1918. It is the only memorial in Europe dedicated only to the United States Marines.
Two U.S. Navy ships have been named for the battle. The first, USS Belleau Wood (CVL-24), was an aircraft carrier that fought in World War II. The second, USS Belleau Wood (LHA-3), was a large amphibious assault ship.
A shorter version of Captain Lloyd Williams' famous quote is now the motto for the 2nd Battalion, 5th Marines, his unit during the battle.
In April 2018, the French President Emmanuel Macron gave the United States a young oak tree from Belleau Wood. This was a symbol of friendship during his visit.
Images for kids
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |