Botany facts for kids
Botany is the exciting study of plants! It's a big part of biology, which is the study of all living things. You might also hear it called plant biology. Scientists who study plants are called botanists. They explore everything about plants, from how they grow to how they help our planet.
What Do Botanists Study?
Botany covers many different areas. Here are some of the main branches:
- Agronomy—This is about growing crops for food and other uses.
- Bryology—The study of tiny plants like mosses and liverworts.
- Forestry—Managing and caring for forests.
- Horticulture—Focuses on growing garden plants, fruits, and vegetables.
- Micropaleontology—Studying ancient pollen and spores found in rocks.
- Mycology—The study of fungi, like mushrooms.
- Paleobotany—Learning about plants from long ago by studying their fossils.
- Phycology—The study of algae, which are simple plant-like organisms.
- Phytochemistry—Looking at the chemicals inside plants and how they work.
- Phytopathology—Understanding and treating plant diseases.
- Plant anatomy—Examining the tiny parts of plants, like their cells and tissues.
- Plant ecology—How plants interact with their environment and other living things.
- Plant genetics—Studying how plants pass on traits from one generation to the next.
- Plant morphology—Learning about the shapes, structures, and life cycles of plants.
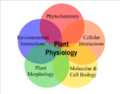
- Plant physiology—How plants perform their life functions, like making food.
- Plant systematics—Classifying and giving names to different types of plants.
Famous Plant Scientists
Many amazing people have helped us learn about plants. Here are a few notable botanists:
- Ibn al-Baitar (died 1248) was an Arab scientist from Spain. He wrote one of the biggest books about plants.
- Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707–1788) was a French naturalist. He managed the King's Garden and wrote many books about nature.
- Luther Burbank (1849–1926) was an American botanist. He was a pioneer in growing new types of plants for farming.
- Charles Darwin (1809–1882) is famous for his ideas on evolution. He also wrote eight important books about plants.
- Al-Dinawari (828–896) was a Kurdish scholar. He is known as the founder of Arabic botany.
- Conrad Gessner (1516–1565) was a Swiss naturalist. He was also a famous writer about books.
- Joseph Dalton Hooker (1817–1911) was an English botanist and explorer. He won the Darwin Medal for his work.
- Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) was a Swedish botanist. He created the system we use today to name plants and animals. He is called the father of modern taxonomy.
- Gregor Mendel (1822–1884) was a priest and scientist. He is often called the father of genetics. He studied how traits are passed down in pea plants.
- John Ray (1627–1705) was an English naturalist. He is known as the father of English natural history.
- G. Ledyard Stebbins (1906–2000) was an American botanist and geneticist. He was a leading expert in how living things change over time.
- Eduard Strasburger (1844–1912) was a Polish-German professor. He was one of the most famous botanists of his time.
- Nikolai Vavilov (1887–1943) was a Russian botanist. He studied how and where important crop plants like wheat and corn first grew.
Images for kids
-
The fruit of Myristica fragrans, from Indonesia, gives us two spices: mace and nutmeg.
-
An old drawing of cork cells from Robert Hooke's book Micrographia (1665).
-
Thale cress, Arabidopsis thaliana, was the first plant to have its entire genetic code mapped.
-
A cross-section of a fossil stem from an ancient plant called Rhynia gwynne-vaughani.
-
An old drawing showing the parts of a rice plant, Oryza sativa.
-
A botanist getting a plant ready to be stored in a herbarium (a collection of dried plants).
See also
 In Spanish: Botánica para niños
In Spanish: Botánica para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |