Nutmeg facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nutmeg |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Myristica fragrans | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Myristica
Gronov.
|
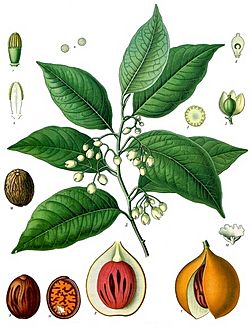
Nutmeg is a popular spice that comes from the seed of a special tree called Myristica fragrans. This tree is an evergreen plant, meaning it stays green all year round. People grow it for two main spices: nutmeg, which is the seed itself, and mace, which is a covering around the seed. This tree also provides an essential oil and a type of butter. There's another plant called California nutmeg, but it's not related to the true nutmeg tree and isn't used as a spice.
Contents
What is Nutmeg?
Nutmeg is a spice made by grinding the seed of the Myristica fragrans tree into a powder. It has a strong, sweet smell and a warm, slightly sweet taste. You can find nutmeg in many foods like baked goods, sweets, puddings, potatoes, meats, and drinks such as eggnog.
The seeds are dried slowly in the sun for about six to eight weeks. As they dry, the nutmeg seeds shrink inside their hard shells. When they are ready, you can hear the seeds rattle inside the shells if you shake them. Workers then break the shells with a wooden tool to get the nutmegs out. Dried nutmegs are oval-shaped and grayish-brown with lines on their surface. They are usually about 2 to 3 centimeters (about 1 inch) long and weigh around 5 to 10 grams.
What is Mace?
Mace is another spice that comes from the same nutmeg tree. It is made from the reddish covering (aril) that surrounds the nutmeg seed. Mace tastes similar to nutmeg but is a bit milder. It is often used to flavor baked goods, meats, fish, and vegetables. It's also used in preserving and pickling foods.
To prepare mace, the bright red covering is carefully removed from the nutmeg seed. It is then flattened and dried for 10 to 14 days. During this drying process, its color changes to a pale yellow, orange, or tan. Whole dried mace looks like flat, smooth, and brittle pieces, usually about 4 centimeters (1.6 inches) long.
Growing Nutmeg Trees
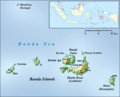
The most important nutmeg tree for spices is Myristica fragrans. This tree originally comes from the Banda Islands in Indonesia, which are also known as the Spice Islands. Today, nutmeg is also grown in Malaysia, the Caribbean (especially in Grenada), and in southern India. People in India learned about nutmeg from Indonesians a long time ago through trade.
Nutmeg trees can be grown from seeds or by taking parts of other trees (like grafting). Growing from seeds can be tricky because about half of the trees will be male, and male trees don't produce fruit. It's hard to tell if a tree is male or female until it flowers, which can take six to eight years! Because of this, farmers often use grafting. Grafting means joining a part of one nutmeg tree to another, which helps ensure they grow fruit-producing trees.
The first nutmeg harvest usually happens seven to nine years after planting. The trees reach their full production after about twenty years.
How Nutmeg is Used
As a Spice
Nutmeg and mace are both used in cooking, but nutmeg is a bit sweeter, and mace has a more delicate flavor. Mace is often chosen for lighter dishes because it can give them a bright orange color, similar to saffron. Nutmeg is used to flavor many different dishes. You can usually buy it already ground or grate a whole nutmeg at home using a special grater.
- In Indonesian cuisine, nutmeg is used in many spicy soups, like soto and oxtail soup. It's also used in gravies for meat dishes, such as semur beef stew.
- In Indian cuisine, nutmeg is found in both sweet and savory dishes, especially in Mughlai cuisine. In some parts of India, grated nutmeg is added to meat dishes and desserts. It can also be a small part of garam masala spice mix.
- In traditional European cuisine, nutmeg and mace are often used in potato dishes and processed meats. They are also common in soups, sauces, and baked goods. Nutmeg is a classic ingredient in rice pudding. In Dutch cooking, nutmeg is added to vegetables like Brussels sprouts and cauliflower. It's also a traditional spice in mulled cider, mulled wine, and eggnog.
- In the Caribbean, nutmeg is often sprinkled on top of drinks like rum punch.
As a Fruit
The outer part of the nutmeg fruit (pericarp) can also be used! People make jam from it, or slice it thinly, cook it with sugar, and crystallize it to make a sweet candy. In Indonesia, this candy is called manisan pala. In Malaysia, dried, shredded nutmeg rind with sugar is used as a topping on a dessert called ais kacang. The nutmeg rind can also be blended or boiled to make iced nutmeg juice. In India, it's used for juice, pickles, and chutney.
Nutmeg Oil and Butter
Essential Oil
An essential oil can be taken from ground nutmeg using steam. This oil is used in perfumes and medicines. It is clear or light yellow and smells and tastes like nutmeg. It's used as a natural food flavoring in baked goods, syrups, drinks, and sweets. It's also used in making toothpaste and cough syrups.
Nutmeg Butter
Nutmeg butter is a semi-solid, reddish-brown substance made from the nut. It tastes and smells like nutmeg. This butter is mostly made of a fat called trimyristin. Trimyristin can be turned into myristic acid, which is a type of fatty acid. This can be used as a replacement for cocoa butter or mixed with other fats.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Nuez moscada para niños
In Spanish: Nuez moscada para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |