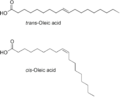Fatty acid facts for kids
A fatty acid is a special kind of carboxylic acid. Think of it as a long chain made mostly of carbon and hydrogen atoms. This long chain is called a hydrocarbon tail. At one end, it has a special group called a carboxyl group. Scientists study fatty acids in organic chemistry and biochemistry.
Fatty acids are very important for your body. They are a big source of energy or "fuel." When your body uses them, they create a lot of ATP. ATP is like the tiny power packets that make your cells work. Many parts of your body, like your heart and muscles, prefer to use fatty acids for energy.
Contents
Types of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids can be divided into two main types. These are saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. The difference between them is in their chemical structure.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids do not have any double bonds between their carbon atoms. This means they are "saturated" with hydrogen atoms. They tend to be solid at room temperature. An example is the fat found in butter.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds in their carbon chain. These double bonds make the chain bend or "kink." They are usually liquid at room temperature. Examples include oils from plants, like olive oil.
How Double Bonds Affect Shape
The double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids can be arranged in different ways.
- A cis arrangement makes the fatty acid chain bend sharply. Most natural unsaturated fatty acids have this shape.
- A trans arrangement makes the chain straighter, similar to a saturated fatty acid. These are less common in nature.
Where Fatty Acids Come From
Natural fatty acids are found in many places. They come from animal or vegetable fat, oil, or wax. They usually have a chain of 4 to 28 carbon atoms. These chains are often straight and have an even number of carbon atoms.
Fatty Acids and Animal Identification
The mix of fatty acids on the skin of mammals is unique. Along with other substances like lactic acid, this mix creates a special scent. Animals with a strong sense of smell can use these scents. This helps them identify other individual animals.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Three-dimensional representations of several fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids have perfectly straight chain structure. Unsaturated ones are typically bent, unless they have a trans configuration.
-
Numbering of carbon atoms. The systematic (IUPAC) C-x numbers are in blue. The omega-minus "ω−x" labels are in red. The Greek letter labels are in green. Note that unsaturated fatty acids with a cis configuration are actually "kinked" rather than straight as shown here.
See also
 In Spanish: Ácido graso para niños
In Spanish: Ácido graso para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |