Candlestick Tower facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Candlestick Tower |
|
|---|---|

Candlestick Tower from the southeast
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 5,867 ft (1,788 m) |
| Prominence | 707 ft (215 m) |
| Isolation | 0.93 mi (1.50 km) |
| Parent peak | Shaft Benchmark (6,329 ft) |
| Geography | |
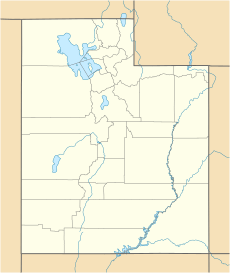
| Location | Canyonlands National Park San Juan County, Utah, U.S. |
| Parent range | Colorado Plateau |
| Topo map | USGS Upheaval Dome |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Late Triassic |
| Type of rock | Wingate Sandstone |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1974 |
| Easiest route | class 5.10 Climbing |
Candlestick Tower is a tall, narrow rock formation in Canyonlands National Park, Utah. It stands about 450 feet (137 meters) high. People call it "Candlestick Tower" because it looks like a giant candlestick.
This amazing tower is made of a type of rock called Wingate Sandstone. This sandstone formed from ancient sand dunes. These dunes were blown by the wind about 200 million years ago. That was during a time called the Late Triassic period.
Candlestick Tower is located in the "Island in the Sky" part of the park. It is in San Juan County, Utah. You can reach it by driving on the four-wheel drive White Rim Road. The tower rises about 1,400 feet (427 meters) above this road. Water from the tower flows into the nearby Green River.
| Top - 0-9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
Exploring Candlestick Tower's Location
Candlestick Tower is surrounded by other interesting places.
- The nearest higher rock formation is Shaft Benchmark. It is about 2 miles (3.2 km) to the east.
- Upheaval Dome is about 3 miles (4.8 km) to the north.
- The Green River Overlook is about 2.5 miles (4 km) to the east.
The tower sits between two large natural bowls. These are called Soda Springs Basin and Holeman Spring Basin.
Climbing Candlestick Tower
Candlestick Tower is a popular spot for rock climbers.
- The first people to climb Candlestick Tower were Jimmy Dunn, Larry Hamilton, Doug Snively, and John Byrd. They made their climb in March 1974.
- The first "free ascent" happened in 1982. This means climbers used ropes only for safety, not to help them go up. Glenn Randall and Kent Lugbill did this climb.
There are several climbing paths on the tower. Some of the well-known routes include:
- The Southwest Corner (rated 5.10)
- The East Face (rated 5.10)
- The Two Worlds Route (an aid climb, where climbers use gear to help them move up)
Weather at Candlestick Tower
The best times to visit Candlestick Tower are spring and fall. The weather is usually mild then.
- The area has a Cold semi-arid climate. This means it's a desert climate.
- It gets less than 10 inches (254 mm) of rain each year.
- Snowfall in winter is usually light.
- The coldest month has an average temperature below 32°F (0°C).
- Most of the rain and snow falls during spring and summer.
Images for kids
-
Candlestick Tower (right), Buttes of the Cross to left in the distance