Columba (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
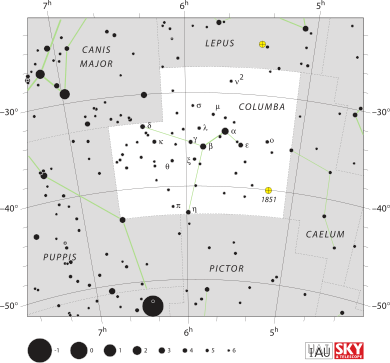
List of stars in Columba
|
|
| Abbreviation | Col |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Columbae |
| Pronunciation | genitive |
| Symbolism | the dove |
| Right ascension | 05h 03m 53.8665s–06h 39m 36.9263s |
| Declination | -27.0772038°–-43.1116486° |
| Area | 270 sq. deg. (54th) |
| Main stars | 5 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
18 |
| Stars with planets | 1 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 1 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 0 |
| Brightest star | α Col (Phact) (2.65m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | None |
| Bordering constellations |
Lepus Caelum Pictor Puppis Canis Major |
| Visible at latitudes between +45° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of February. |
|
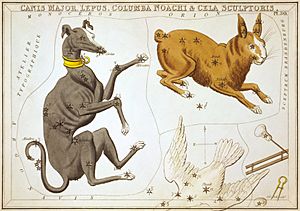
Columba is a small, faint group of stars, also known as a constellation. It was first recognized in the late 1500s. Its name comes from the Latin word for "dove." You can find it in the sky just south of the constellations Canis Major and Lepus.
Discovering the Columba Constellation
The constellation Columba was created by a Dutch astronomer named Petrus Plancius. He made it in 1592. His goal was to give a name to some stars that were part of the much larger constellation Canis Major.
Plancius first called this new constellation Columba Noachi. This means "Noah's Dove." It refers to the story of Noah and the dove that brought back an olive branch. This showed that the great floodwaters were going down. You can see this name on old star maps from the 1600s.
Some people also think Columba might represent the dove from the story of Jason and the Argonauts. This dove helped them sail through a very tricky passage called the Symplegades at the mouth of the Black Sea.
See also
 In Spanish: Columba (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Columba (constelación) para niños
 | Dorothy Vaughan |
 | Charles Henry Turner |
 | Hildrus Poindexter |
 | Henry Cecil McBay |