Common ling facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Common ling |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Gadiformes |
| Family: | Lotidae |
| Genus: | Molva |
| Species: |
M. molva
|
| Binomial name | |
| Molva molva (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
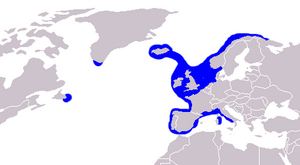
| Molva molva range map. | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The common ling (Molva molva), also called the white ling, is a very large fish. It belongs to the Lotidae family, which is a group of fish similar to cod. The common ling looks a bit like rocklings, but it is much bigger. It has a single whisker-like feeler, called a barbel, on its chin.
This fish is not related to the pink ling, which lives in the Southern Hemisphere. Common ling live in the northern Atlantic Ocean, mostly near Europe. They are also found in parts of the Mediterranean Sea. People catch common ling for food, especially in the northeastern Atlantic. It is eaten fresh, frozen, or dried. Sometimes, it is even prepared using a special process with lye. The eggs of the ling, called roe, are a special food in Spain.
Contents
What Does the Common Ling Look Like?
The common ling is the longest and one of the biggest fish in the cod family. It can grow up to 200 cm (about 6.5 feet) long and weigh up to 30 kg (about 66 pounds). It has a long, thin body with a small head and small eyes. Its mouth is large and has big teeth. The upper jaw sticks out further than the lower jaw. It also has a clear barbel (feeler) on its chin.
The common ling has two dorsal fins (fins on its back). The front dorsal fin is short and rounded. The back dorsal fin is much longer and stays the same height. It is similar in length to the anal fin (fin on its belly). The pelvic fins (fins on its underside) are short and do not reach past its pectoral fins (fins on its sides).
The top of the ling's body is a marbled greenish-brown, sometimes reddish-brown. Its sides and belly are lighter in colour. The anal and dorsal fins have a clear white edge and a dark spot at the back. The spot on the front dorsal fin is easier to see. Young ling are usually lighter in colour than adults. They often have pale, shiny, purplish lines.
A very large common ling, measuring 6 ft (183 cm) long, was caught near Shetland on February 24, 2013. This was the biggest ling ever caught with a rod and line in British waters.
Where Does the Common Ling Live?
The common ling lives in the North Atlantic Ocean. You can find it off the eastern coast of Canada, southern Greenland, and Iceland. It also lives in the northeastern Atlantic, from the Barents Sea to the coasts of the UK. It is less common further south, but can be found down to the Strait of Gibraltar and into the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. It is rare in the Mediterranean and the North Sea.
Common Ling Habitat and Life Cycle
The common ling is a demersal fish, meaning it lives near the bottom of the sea. It prefers rocky areas at depths from 15 to over 600 meters. It is most often found between 100 and 400 meters deep.
Young ling, less than 2 years old, live closer to the coast in shallower waters (15–20 m). They also swim in the open water (pelagic). When they are 3 years old, they move to deeper areas.
Reproduction
Male ling become ready to reproduce at 5 years old, when they are about 80 cm long. Females are ready at 5 or 6 years old, when they are between 90 and 100 cm long. Ling lay their eggs from March to July. The eggs and young larvae float in the open water. A single female can lay between 20 and 60 million eggs!
The main places where ling lay eggs are:
- In the Bay of Biscay to the Norwegian Sea, at depths of 200 m.
- Off southern Iceland, at depths of 100 to 300 m.
- In the Mediterranean Sea, at depths of 50 to 300 m.
Ling grow quickly, adding 8–10 cm to their length each year. A 1-year-old fish is typically 20 cm long, and 2-year-olds are 31–35 cm. Females grow faster than males. The oldest recorded male ling lived for 10 years, and the oldest female lived for 14 years. At that age, they can reach about 200 cm in length.
What Do Common Ling Eat?
Common ling usually live alone and hide among rocks, in cracks, or near shipwrecks in deep water. They are mainly carnivores, meaning they eat other animals. Their diet mostly includes other fish like Trisopterus esmarkii, Atlantic cod, Atlantic herring, and flatfish. They also eat crustaceans (like European lobsters), squid and octopus, and starfish.
How Do People Use Common Ling?
Common ling is a popular fish to eat. It is sold fresh, salted, or dried. It is also used to make fishmeal. The salted eggs (roe) of the ling are a special food in Spain, known as huevas de maruca. Ling can also be made into lutefisk, a traditional Nordic dish.
Commercial fishing boats catch common ling using large nets called trawls. Some fisheries in Europe and the Faroe Islands use long lines with many hooks. Because ling live in deep water, their swim bladder (an organ that helps them float) can be badly damaged when they are brought quickly to the surface. For this reason, sport anglers (people who fish for fun) are advised not to release ling back into the sea if they catch them from a boat. They should stop fishing once they have caught enough for food.
The IUCN says that there isn't enough information about the common ling's population size or how it is changing. So, they have listed its status as "data deficient." This means we don't have enough facts to know if the population is healthy or at risk. The Marine Conservation Society suggests that consumers "avoid" ling caught by trawling. In 1999, about 53,870 tonnes of common ling were caught globally. Norway caught the most (19,215 tonnes), followed by the United Kingdom (11,350 tonnes).
See also
 In Spanish: Maruca para niños
In Spanish: Maruca para niños




