Barents Sea facts for kids
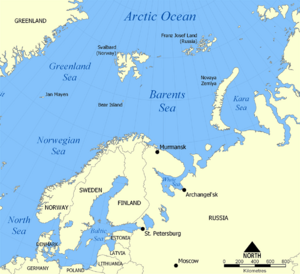
The Barents Sea is a part of the Arctic Ocean. It is located north of Norway and Russia. Long ago, in the Middle Ages, it was known as the Murman Sea. It got its current name from Willem Barents, a Dutch explorer.
This sea is a rather deep shelf sea. This means it's a part of the ocean that covers the edge of a continent. Its average depth is about 230 meters (760 feet), and its deepest point is around 450 meters (1,480 feet). The Barents Sea is surrounded by other waters and land. To the west is the Norwegian Sea. To the northwest are the Svalbard islands, which belong to Norway. To the northeast and east are the islands of Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya. The island of Novaya Zemlya acts like a natural wall, separating the Barents Sea from the Kara Sea. The Barents Sea area is also rich in important natural resources like oil and gas.
Contents
Geography of the Barents Sea
The southern part of the Barents Sea stays free of ice all year round. This is because of warm ocean currents from the North Atlantic. These currents bring warmer water from the south. Because of this, important ports like Murmansk in Russia and Vardø in Norway can be used all year. By September, almost the entire Barents Sea is usually free of ice. For a time, Finland's land reached the Barents Sea. This gave them a port at Petsamo that stayed ice-free in winter.
Animals and Plants of the Barents Sea

The Barents Sea has a lot of different plants and animals. This is unusual for an ocean so far north. The warm currents from the North Atlantic help make it a rich environment.
- Tiny Ocean Plants: In spring, tiny ocean plants called phytoplankton grow very quickly. This "spring bloom" often starts near the edge of the melting ice. The fresh water from the melting ice creates a special layer on top of the salt water.
- Tiny Ocean Animals: These phytoplankton blooms provide food for tiny ocean animals called zooplankton.
- Larger Animals: Many larger animals then eat the zooplankton. These include young cod, capelin, polar cod, whales, and Little Auk birds.
- Important Fish: The capelin is a very important fish. It is a main food source for many animals. These include the North-East Arctic cod, harp seals, and seabirds like the Common Guillemot and Brunnich's Guillemot.
Fishing in the Barents Sea is very important for both Norway and Russia. The cod fisheries, in particular, provide a lot of food and jobs.
Images for kids
-
Dutch whalers near Svalbard in 1690.
-
Honningsvåg is a fishing village in northern Norway.
See also
 In Spanish: Mar de Barents para niños
In Spanish: Mar de Barents para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |