Corbel arch facts for kids
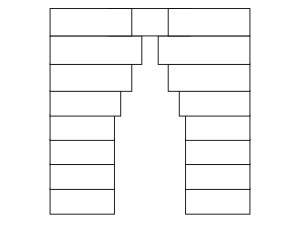
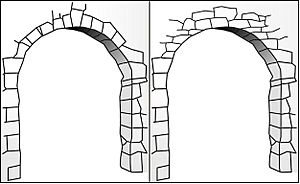
A corbel arch is a special way to build an arch shape without using a "true" arch. Imagine stacking stones or bricks, each one sticking out a little further than the one below it. You keep doing this from both sides of an opening until the stones meet in the middle. This creates a strong, arch-like shape.
This method is called "corbeling." It's used to create openings in walls, like doorways, or to build parts of bridges. When this technique is used to support a roof, it's called a corbel vault.
Corbel arches are sometimes called "false arches." This is because they are built differently from "true" arches. A true arch uses wedge-shaped stones that push against each other and are held together by a central "keystone." Corbel arches, however, use flat stones stacked horizontally. They are strong, but they need thick walls around them to help hold them up.
Ancient Builders and Corbel Arches
Corbeling is a very old building technique. People have been using it for thousands of years!
Ireland's Ancient Structures
In Ireland, you can find amazing examples of corbel arches.
- The Newgrange passage tomb was built a very long time ago, between 3200 and 2500 BC. It has a corbel vault that still supports its roof today.
- The old monastery buildings on Skellig Michael island also used this method.
Ancient Egypt's Pyramids
The ancient Egyptians were masters of building with stone.
- Around 2600 BC, during the time of Pharaoh Sneferu, Egyptian pyramids used corbel vaults in some of their rooms.
- Famous pyramids like the Meidum Pyramid, the Bent Pyramid, and the Red Pyramid all feature corbel vaults.
- The amazing Great Pyramid of Giza also has corbel arches in its Grand Gallery.
- Even though Egyptians knew how to build "true" arches, they often chose to use corbel arches in their temples.
Across the Ancient Mediterranean
Corbel arches and vaults were popular all around the ancient Mediterranean Sea.
- In Syria, the ancient city of Ebla had corbelled burial vaults.
- In Canaan (modern-day Israel and Palestine), sites like Tell el-Ajjul and Tel Megiddo also show corbelled structures.
- The city of Ugarit in Syria also used corbeling.
- On the island of Sardinia, ancient Nuraghe buildings from the 18th century BC used similar corbel techniques.
- "Beehive tombs" found in places like the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) from 3000 BC also show this style.
Hittites in Anatolia
The Hittites were an ancient people in what is now Turkey.
- They built corbelled vaults as early as the 16th century BC.
- Some of their building styles are similar to those of the Mycenaeans in Greece, but the Hittite vaults are much older.
Greece's Mycenaean and Classical Eras

Greece has many examples of corbel arches and vaults.
- The ruins of ancient Mycenae have many corbel arches and vaults. A famous example is the Treasury of Atreus, built around 1250 BC.
- The Arkadiko Bridge is one of four Mycenaean corbel arch bridges. It was part of an old road network for chariots. Built in the 13th century BC, it's one of the oldest arch bridges still in use!
- On the island of Crete, the Eleutherna Bridge from the Hellenistic period has a very wide corbel arch.
Maya Civilization in Mesoamerica
Corbel arches are a very important part of Maya architecture.
- You can see them in many ancient Maya cities and buildings.
- They were used for doorways and vaults, even from the earliest times of the Maya civilization.
- By about 250 CE, corbel vaults were used almost everywhere in Maya buildings in the central lowlands.
India's Historical Architecture

Before "true" arches became common in India, most arches were either flat (trabeated) or corbelled.
- In North India, many temples used corbelled vaulting. The Mukteswar temple, built around 950 AD, is a great example.
- When the Delhi Sultanate began in 1206, they used Indian workers who were used to building with corbel arches. Even though the new rulers came from places where "true" arches were common, they built huge corbel arches in mosques like the Quwwat-ul-Islam Mosque in Delhi and the Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra mosque.
- It took almost 100 years for "true" arches and domes to appear in Indian buildings. The ruined Tomb of Balban (died 1287) might be the earliest example of a true arch in Delhi.
Indonesia's Temples
The ancient temples of Indonesia, called candi, used corbel arch techniques.
- These temples were built between the 8th and 15th centuries.
- A famous example is the Borobudur temple. Its corbel arches are made of interlocking stone blocks that have a special "T" shape at the top.
Cambodia's Angkor Temples
All the temples in Angkor, Cambodia, used the corbel arch. These temples were built between the 9th and 12th centuries AD.
Images for kids
-
Doorway of Indo-Parthian Buddhist monastery at Takht-i-Bahi, Pakistan, c. 3rd century AD
-
Stone corbelled arches at Borobudur (9th century AD) in Java, Indonesia. Note the "T"-shaped central stones.
-
Brickwork corbelled arch at Ubud in Bali, Indonesia
-
A brick corbelled arch disintegrating slowly at Mỹ Sơn (4th-14th c. Hindu temples) in Vietnam
-
The corbel span of Spean Praptos, 12th-century Cambodia
-
Stone corbelled gateway arch to walls of Angkor Thom (12th-17th c. city) in Cambodia
-
Stone corbelled arch in the 13th-century Konark temple, India
-
Screen of the Adhai Din Ka Jhonpra mosque (c. 1229), Ajmer, India; Corbel arches, some cusped.
-
Mausoleum of Iltutmish, Delhi, by 1236, early Indo-Islamic architecture
See also
 In Spanish: Falso arco para niños
In Spanish: Falso arco para niños