Cordova Bay facts for kids
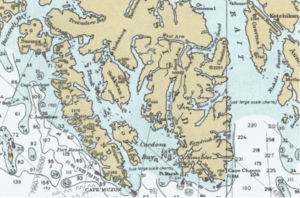
Cordova Bay is a large bay located in the Alexander Archipelago in southeast Alaska. It opens up to the Dixon Entrance in the south. This entrance is found between Cape Muzon on Dall Island and Point Marsh, which is a group of small islands near Prince of Wales Island.
Contents
How Cordova Bay Got Its Name
The name "Puerto Cordova y Cordova" was first given to the bay in 1792. It was named by a Spanish explorer, Lieutenant Don Jacinto Caamaño. He chose the name to honor Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova. The name was later officially published by George Vancouver in 1798.
Where is Cordova Bay?
Cordova Bay has Dall Island, Long Island, Tlevak Strait, and Sukkwan Island on its western side. To the east, it is bordered by Prince of Wales Island. The bay stretches north and west from its mouth all the way to Lime Point. At Lime Point, it connects with Hetta Inlet.
Size and Shape of the Bay
The Coast Survey, which maps coastlines, says Cordova Bay is about 19 nautical miles (35 kilometers) long. This measurement is taken from a spot between the southeast corner of Long Island and Dewey Rocks to Lime Point. The bay is usually about 3 nautical miles (5.6 kilometers) wide.
Hetta Inlet, which connects to Cordova Bay, goes another 15 nautical miles (28 kilometers) north. Then it turns east for about 3 nautical miles (5.6 kilometers). Gould Island almost blocks the inlet where it turns east. After this point, only small boats can get through. The part of the inlet past Gould Island is called Portage Bay. A road called Sulzer Portage connects Portage Bay to Cholmondelay Sound.
Who Controls the Waters?
The Coast Survey does not consider Tlevak Strait, Hetta Inlet, or Kaigani Strait to be part of Cordova Bay. However, an old book called the Geographic Dictionary of Alaska (from 1906) did include Hetta Inlet and Kaigani Strait as parts of the bay. It also included Sukkwan Strait.
In 2006, the US Supreme Court made a decision about these waters. Alaska had asked the court to say that all these waters, including Tlevak Strait, were legally part of Cordova Bay. If Alaska had won, all these waters would have been controlled by the state. But the court ruled against Alaska. So, now, some parts of these waters are controlled by the state, and other parts are controlled by the federal government.
Why is Cordova Bay Important for Boats?
Cordova Bay and Tlevak Strait offer a safe path for boats. This route leads to Bucareli Bay and other places on the west coast of Prince of Wales Island. The Coast Guard has estimated that about 150 commercial fishing boats use this route every week during the summer months.

Land Around Cordova Bay
The land around Cordova Bay is a mix of different types of ownership. Much of it is federal land, meaning it belongs to the government. This land is part of the Tongass National Forest. There is also private land, mostly owned by Alaska Native Corporations. A small amount of land is owned by the state of Alaska.
Natural Features of the Shoreline
A large part of the eastern shore of the bay is within the South Prince of Wales Wilderness. This is a protected area inside the National Forest. The shoreline in the northeast part of the bay, around Hetta and Klakas inlets, is very steep and rocky.
South of Hunter Bay, the Prince of Wales shoreline is not as steep. It rises into low, rolling hills that have many lakes. The other three large islands (Dall, Long, and Sukkwan) have a mix of mountains and hills. They also have some low-lying land right along the shore.
Hydaburg: A City on the Bay
The small city of Hydaburg is located on the north shore of Sukkwan Strait. It is connected to the road system on Prince of Wales Island. This means it's the only place with public road access to the bay. Hydaburg has a harbor for boats and a base for seaplanes.
History of Hydaburg and Old Villages
Hydaburg was created in 1911. It was formed when three Haida villages on Cordova Bay joined together. These villages were Howkan, located on the west coast of Long Island; Sukkwan, at the northern end of Sukkwan Island; and Klinkwan, on Prince of Wales Island near Hunter Bay.
There were also other villages around Hetta Inlet that are now abandoned. These were mining, saltery (where fish were salted), and cannery (where fish were canned) villages. Their names were Copper City, Hetta, Coppermount, and Sulzer. There were also canneries on Hunter Bay and on Rose Inlet, which is off Tlevak Strait.
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |