Department of the Pacific facts for kids
The Department of the Pacific was a major command of the United States Army that existed from 1853 to 1858. It was created to replace an older command called the Pacific Division. Later, it was replaced by two new commands: the Department of California and the Department of Oregon. This department was very important for managing military activities in the growing western United States.
Contents
How the Department of the Pacific Started
The Department of the Pacific was officially created on October 31, 1853. Its main office was in San Francisco, California. It took over from the earlier Pacific Division, which had been around since 1848. This new department combined two smaller military areas, the 10th (California) and 11th (Oregon) Departments, into one big command.
This department reported directly to the main Army headquarters in Washington, D.C.. It was in charge of all military activities in the country west of the Rocky Mountains. This huge area included what is now California, Oregon Territory, and Washington Territory. However, it did not include the Utah Territory or most of the New Mexico Territory.
On September 2, 1854, the department's main office moved to Benicia Barracks in Benicia, California. A few years later, from 1855 to 1857, a special area called the Puget Sound District was set up within the department. In January 1857, the main office moved back to San Francisco.
In January 1858, the Utah Territory was briefly added to the Department of the Pacific. But it was soon moved to its own command, the Department of Utah, which lasted until 1861.
Leaders of the Department
Here are the main commanders who led the Department of the Pacific during its first period:
- Ethan A. Hitchcock: 1853–1854
- John E. Wool: 1854–1857
- Newman S. Clarke: 1857–1858
Important Military Posts
The Department of the Pacific oversaw many important military forts and camps across the western United States. These posts helped the Army keep peace and protect settlers in the expanding territories. Some of these locations include:
- Fort Alcatraz, California
- Fort Bellingham, Washington Territory
- Benicia Barracks, California
- Fort Bragg, California
- Fort Dalles, Oregon
- Fort Humboldt, California
- Fort Jones, California
- Fort Mohave, Arizona Territory
- Fort Point, San Francisco, California
- Fort Steilacoom, Washington Territory
- Fort Yuma, California
- Fort Vancouver, Washington Territory
- Fort Tejon, California
- Fort Yamhill, Oregon
- Fort Simcoe, Washington Territory
- Fort Walla Walla, Washington Territory
- Fort Crook, California
- Fort Hoskins, Oregon
The Department is Divided
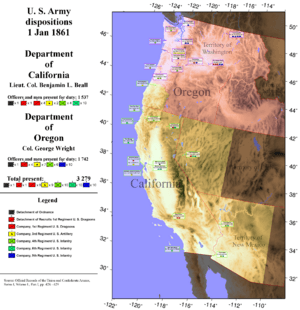
On September 13, 1858, the Department of the Pacific was officially closed down. In its place, the Army created two new, smaller departments: the Department of California and the Department of Oregon.
The Department of California covered the area west of the Rockies, including parts of Oregon, Utah, and New Mexico. The Department of Oregon was in charge of the Oregon and Washington Territories. This change helped the Army manage its forces more closely in these growing regions.
Reformed During the Civil War
The Department of the Pacific was brought back during the American Civil War. On January 15, 1861, the Army combined the Departments of California and Oregon to create a new, independent Pacific Department.
The first commander of this new department was Colonel Albert Sidney Johnston. He later became a very important general for the Confederate States Army. The department played a key role in keeping peace and order in the western states during the war, even though most of the fighting happened in the eastern United States.
Civil War Leaders
Here are the commanders who led the Department of the Pacific during the Civil War:
- Albert Sidney Johnston: 1861 (He left to join the Confederate Army.)
- Edwin Vose Sumner: 1861
- George Wright: 1861–1864
- Irvin McDowell: 1864–1865
Military Districts During the War
During the Civil War, the Department of the Pacific was divided into several smaller military districts to help manage its vast area. These districts included:
- District of Oregon (main office at Vancouver Barracks)
- District of California (main office in San Francisco)
- District of Southern California (main office at Drum Barracks)
- District of Humboldt (main office at Fort Humboldt)
- District of Utah (main office at Fort Douglas)
- District of Arizona (main office at Prescott)
Final Reorganization
On July 27, 1865, after the Civil War ended, the Department of the Pacific was reorganized again. It was replaced by the Military Division of the Pacific, led by Henry W. Halleck. This new division included the Department of the Columbia (covering Oregon, Washington, and Idaho) and an expanded Department of California (covering California, Nevada, New Mexico, and Arizona).
The Philippine Expedition
Much later, in 1898, during the Spanish–American War, a new "Department of the Pacific" was briefly created. General Wesley Merritt set up its headquarters in San Francisco. This department was in charge of sending American forces to help Admiral Dewey in the Philippines.
By March 1900, the job of dealing with local fighters and governing the islands became very complex. So, this temporary Department of the Pacific was changed into the Philippine Department. This new department was divided into four smaller geographical areas, each with its own military districts. This change also marked the end of the Eighth Corps.