Differential geometry facts for kids
Differential geometry is a part of mathematics. It uses special math tools like differential calculus and integral calculus. It also uses linear algebra. These tools help us study shapes and spaces.
This field looks at things like flat surfaces, curves, and 3D shapes. It helps us understand how these shapes behave. Important discoveries in this area happened in the 1700s and 1800s.
A famous mathematician, Carl Friedrich Gauss, was one of the first to think about modern differential geometry. He wondered if the angles of a very large triangle, like one made by ship paths, always added up to exactly 180 degrees. This question led to new ideas about how space can be curved.
Contents
What is Differential Geometry?
Differential geometry studies shapes and spaces using calculus. Calculus is a type of math that deals with change. It helps us understand how things curve or bend.
Imagine you are drawing a line on a balloon. That line looks straight on the balloon. But if you flatten the balloon, the line might look curved. Differential geometry helps us understand these differences.
Studying Curves and Surfaces
This math field helps us understand curves. A curve is a line that is not straight. It can be simple, like a circle, or more complex.
It also studies surfaces. A surface is a 2D shape in 3D space. Think of the surface of a ball or a donut. Differential geometry helps us measure distances and angles on these surfaces.
Euclidean Space and Beyond
Most of the geometry you learn in school is called Euclidean geometry. This is about flat spaces. For example, a triangle on a flat piece of paper has angles that add up to 180 degrees.
But differential geometry goes further. It looks at spaces that are not flat. These are called "curved spaces." On a curved surface, like a sphere, the angles of a triangle might add up to more than 180 degrees.
How We Use Differential Geometry
Differential geometry is used in many different ways today. It helps us solve real-world problems.
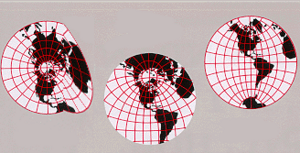
Making Maps
One of the oldest uses of differential geometry was for map projections. This is the process of taking the curved surface of the Earth and showing it on a flat map. It's tricky to do this without stretching or squishing parts of the map.
Differential geometry helps mapmakers create the best possible maps. It helps them understand how to represent a curved world on a flat surface.
Today, differential geometry is very important for satellite navigation. This includes systems like GPS. GPS uses signals from satellites to figure out your exact location on Earth.
To do this accurately, the system needs to account for the Earth's curved shape. It also needs to consider how space and time can be affected by gravity.
Understanding Gravity
Differential geometry is also key to general relativity theory. This is Albert Einstein's theory of gravity. It says that gravity is not just a force. Instead, it's a curve in space and time caused by mass and energy.
This math helps scientists understand how planets move. It also helps them study black holes and the universe.
Solving Big Math Problems
Sometimes, differential geometry helps solve very complex math problems. For example, it was used in the proof of the Poincaré conjecture. This was a famous math problem that took many years to solve.
The mathematician Grigori Perelman used ideas from differential geometry to prove it. This shows how powerful these mathematical tools can be.
See also
 In Spanish: Geometría diferencial para niños
In Spanish: Geometría diferencial para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |

