Eastern Bloc facts for kids
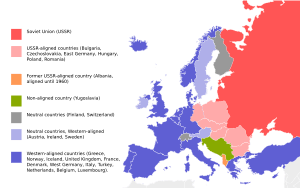
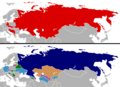
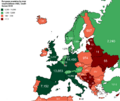
The Eastern Bloc was a group of countries in Eastern and Central Europe that were linked to the Soviet Union after World War II. Most of these countries had Communist governments. The main members were part of the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance, and the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON), which helped them work together on economic matters.
Some countries, like Yugoslavia and Albania, were also part of the Eastern Bloc in a broader sense, even though they later chose to be more independent from the Soviet Union.
Contents
What Was the Eastern Bloc?
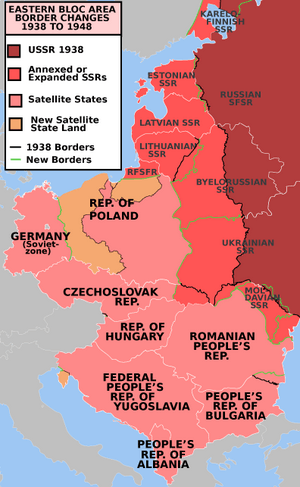
After World War II, the Soviet Union helped set up Communist governments in many countries in Eastern Europe. These new governments had strong control over politics and the media. They also made it very difficult for people to leave their countries.
Why Was the Bloc Formed?
The Soviet Union wanted to create a group of friendly countries around its borders. This was partly because of the Cold War, a long period of tension between the Soviet Union and its allies (the Eastern Bloc) and the United States and its allies (the Western Bloc). The Soviet Union wanted to make sure these countries followed its ideas and policies.
Key Events and Challenges
Even with strong control, there were times when people in the Eastern Bloc tried to change things.
- In 1948, Josip Broz Tito, the leader of Yugoslavia, decided to follow his own path, separate from the Soviet Union.
- The Berlin Blockade in 1948-1949 was another big event. The Soviet Union tried to block all roads and railways into West Berlin, but the Western allies brought supplies by air.
- In 1956, there was a big uprising in Hungary, but Soviet forces stopped it.
- In 1968, the Warsaw Pact countries invaded Czechoslovakia to stop reforms happening there.
Life in the Eastern Bloc
Life in the Eastern Bloc was different from life in Western countries. The governments controlled the economy, which meant they decided what was produced and how goods were shared. This system was called a command economy.
Economy and Daily Life
- Planned Economy: The government planned everything, from how many shoes to make to how much food to grow. Sometimes, this led to shortages of goods or long lines for basic items.
- Housing: Many people lived in apartment blocks built by the state, like the khrushchyovka apartments.
- Propaganda: Governments used posters and media to promote their ideas and show how well the country was doing.
- Limited Choices: People had fewer choices in goods, travel, and even information compared to Western countries.
Urban Design and Architecture
Cities in the Eastern Bloc often had a specific look. Many new buildings were built quickly after World War II, especially in cities like Warsaw that were heavily damaged. Large housing estates, like the Marszałkowska Housing Estate (MDM) in Warsaw, were common.
The End of the Eastern Bloc
By the late 1980s, the command economies in the Eastern Bloc were struggling. There were many problems like not enough goods, outdated technology, and a lack of new ideas.
Revolutions of 1989
In 1989, a series of peaceful protests and changes, sometimes called "counterrevolutions," swept across Eastern Europe.
- The Berlin Wall, which had divided East and West Berlin since 1961, was opened in November 1989. This was a huge moment that showed the beginning of the end for the Eastern Bloc.
- One important event was the "Pan-European Picnic" in August 1989, where the border between Austria and Hungary was briefly opened, allowing many East Germans to escape to the West. Otto von Habsburg played a role in this.
- One by one, the Communist governments in these countries fell.
After the Bloc Dissolved
The Eastern Bloc officially dissolved around 1991, when the Soviet Union itself broke apart. The countries that were once part of the bloc became independent and began to develop their own economies and political systems, often moving towards democracy and market economies. This led to big changes in national borders and how Europe was organized.
Images for kids
-
The "Big Three" leaders (Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and Joseph Stalin) at the Yalta Conference in February 1945, where they discussed the future of Europe.
-
Germans watching planes bring supplies to West Berlin during the Berlin Airlift in 1948.
-
The Russian Orthodox Alexander Nevsky Cathedral in Baku, which was torn down in the 1930s under Stalin's rule.
-
The Berlin Wall in 1975, a symbol of the division between East and West.
-
The Marszałkowska Housing Estate (MDM) in Warsaw, an example of urban design in the Eastern Bloc.
-
Warsaw was heavily damaged during World War II; 85% of its buildings were destroyed by German troops.
-
A recreated living room of a typical working class flat from the khrushchyovka era.
-
A Propaganda poster from East Germany showing increased farm production.
-
A Robotron KC 87 home computer made in East Germany between 1987 and 1989.
-
Plattenbau apartment blocks in East Germany, a common type of housing.
-
Otto von Habsburg, who helped open the "Iron Curtain" border between East and West.
See also
 In Spanish: Bloque del Este para niños
In Spanish: Bloque del Este para niños