Elam facts for kids
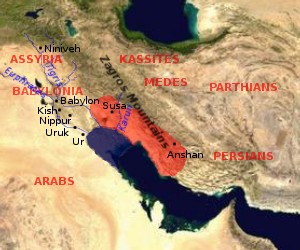
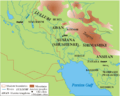
Elam was a very old civilization that lasted a long time. It was located just east of Mesopotamia, in what is now southwest Iran. Elam was mainly in the western and southwestern parts of modern-day Iran. This included the lowlands of Khuzestan and Ilam Province, plus a small part of southern Iraq.
Contents
History of Elam
We don't know everything about Elamite history. Most of what we know comes from records left by their neighbors in Mesopotamia. The history of Elam is divided into four main periods. These periods cover more than two thousand years!
Early Elamite Times
- Proto-Elamite Period: (around 3200 BC – 2700 BC)
- This was the earliest time.
- The city of Susa was founded around 5000 BC.
- Susa became a very important center for early Elamite culture.
- They used a special writing system called Proto-Elamite script.
- Old Elamite Period: (around 2700 BC – 1600 BC)
- Written records began around 3000 BC.
- This period saw the rise of early Elamite kingdoms.
- Middle Elamite Period: (around 1500 BC – 1100 BC)
- This was a time of powerful Elamite dynasties.
- It ended when the Babylonians invaded Susa.
- Neo-Elamite Period: (around 1100 BC – 539 BC)
- During this time, Elam was influenced by Iranian and Syrian cultures.
- The year 539 BC marks the start of the Achaemenid period.
Elamite Language
The Elamite language is unique. It doesn't seem to be related to any other known language. It's like Sumerian in that way, which is also a "language isolate." Some experts have suggested it might be part of a bigger group called Elamo-Dravidian, but this idea is not widely accepted.
Later, during the Achaemenid Empire, the Elamite language was one of the official languages used.
Elam's Name
The Elamites called their own country Haltamti. However, the Sumerians and Akkadians called it Elam. This is also the name used in the Hebrew Bible.
The End of Elam
The Elamite civilization began around 2700 BC. They were finally conquered by the Achaemenids in 640 BC. A tablet found in 1848 tells us about this conquest. The Assyrian king Ashurbanipal proudly wrote about his victory:
"Susa, the great holy city, home of their Gods, seat of their mysteries, I conquered. I entered its palaces, I opened their treasuries where silver and gold, goods and wealth were gathered...I destroyed the ziggurat of Susa. I smashed its shining copper horns. I reduced the temples of Elam to nothing; their gods and goddesses I scattered to the winds. The tombs of their ancient and recent kings I destroyed, I exposed to the sun, and I carried away their bones to the land of Ashur. I destroyed the provinces of Elam and on their lands I sowed salt."
Even after this disaster, the Elamites managed to stay independent for some time. The destruction was not as complete as Ashurbanipal claimed. Elamite rule continued, though it was broken up, until 540 BC. That's when the Achaemenid Empire took over Susa.
Later, during the Parthian period, a kingdom called Elymais existed. This kingdom was in the heartland of ancient Elam. It survived until the Sassanids invaded in the early third century AD.
Images for kids
-
Proto-Elamite (Susa III) cylinder seal, 3150–2800 BC. From the Louvre Museum.
-
Seal impression of King Ebarat, who founded the Sukkalmah Dynasty. From the Louvre Museum.
-
The Chogha Zanbil ziggurat site, built around 1250 BC.
-
An Elamite archer fighting against Neo-Assyrian troops of Ashurbanipal. He protects the wounded king Teumman at the Battle of Ulai, 653 BC.
-
Elamite soldier in the Achaemenid army around 470 BC, from a Xerxes I tomb relief.
-
Golden statuette of a man (likely a king) carrying a goat. From Susa, Iran, around 1500–1200 BC (Middle Elamite period).
-
A 4.5-inch long lapis lazuli dove with gold pegs. Dated 1200 BC from Susa.
-
Elamite reliefs at Eshkaft-e Salman. The picture of a woman shows the importance of women in the Elamite era.
See also
 In Spanish: Elam (reino) para niños
In Spanish: Elam (reino) para niños