Electrical cable facts for kids
An electrical cable is like a special pathway for electricity. It's made of one or more wires bundled together. These wires carry electric current from one place to another.
Sometimes, several electrical cables and their connectors are put together to form a "cable assembly." This can be a part of a bigger product, like something that gets soldered onto a printed circuit board. Cable assemblies can also look like a "cable tree" or "cable harness," which connects many different points.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The word cable first meant very strong submarine telegraph cables. These cables were laid under the sea to send messages. They needed to be covered in iron or steel wires to protect them. This protective layer was called "armouring." Without it, the cables would break too easily.
The companies that made this armouring were experts in making wire rope, like the kind used on ships. So, the protected electrical wires also became known as "cables." Later, the term was used for any group of electrical wires (or even a single wire) covered in an outer layer. Today, it even includes telecommunications cables that use fibre-optic threads instead of copper wires.
How Cables Are Used

Electrical cables are super important! They connect different devices, letting them share electrical signals or power. For example, your TV cable brings signals to your screen, and the power cord for your computer brings electricity.
Very long-distance communication often happens through undersea communication cables that cross oceans. Power cables are used to send large amounts of electricity, especially high-voltage power, over long distances.
Cables are also used a lot in building wiring. They help bring electricity for lights, power outlets, and control systems inside buildings. Since all the wires for a circuit can be put into one cable at once, it saves time when installing them.
Inside an Electrical Cable
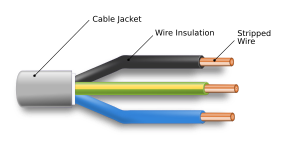
An electrical cable is made up of one or more conductors (the parts that carry electricity). Each conductor has its own insulation, which is a protective layer that stops electricity from escaping. Cables can also have extra screens or coverings.
To make cables more flexible, the wires inside are often "stranded." This means many smaller wires are twisted or braided together. This makes a larger wire that bends more easily than a single solid wire of the same size.
The copper wires inside a cable can be bare, or they might be coated with a thin layer of another metal. This is often tin, but sometimes gold or silver. These metals don't rust as easily as copper, which can make the wire last longer and makes it easier to solder (join with melted metal).
Cable Insulation
In the past, electrical cables were often insulated with cloth, rubber, or paper. Today, most cables use plastic materials. One of the first plastics used for underwater cables in the 1800s was gutta-percha, which comes from a tree.
A very common man-made plastic used for cable insulation is polyethylene. It was invented in 1930. During World War 2, a special telegraph cable using this plastic was laid across the English Channel to help soldiers.
Cables can be kept neat and secure using things like cable trays, cable ties, or special clips. For cables that move a lot, like those in robots, special devices help prevent them from breaking.
Cable Features
Any wire that carries electricity, including a cable, creates an electromagnetic field around it. Also, any wire can pick up energy from other electromagnetic fields nearby. These effects can be a problem. For example, a cable might send out unwanted energy that affects other equipment. Or, it might pick up unwanted "noise" that messes with the signal it's carrying.
To solve these problems, engineers use special cable designs. Here are three main ways:
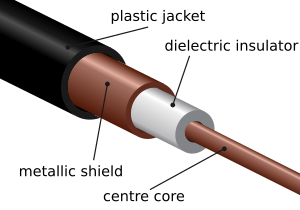
- Shielding: This is like putting a protective cage around the cable. The cable is covered along its whole length with foil or a wire mesh. This "shield" helps block outside electrical fields, especially if it's connected to the ground.
- Coaxial Design: In this design, the shield is circular, and the main wire is exactly in the center. This helps reduce magnetic interference, making the cable work better for signals like those used in cable television.
- Twisted Pair: This design has two wires twisted around each other. This twisting helps cancel out interference. If an unwanted signal tries to affect the wires, the twisting makes sure that the interference affects both wires in opposite ways, so they cancel each other out. This is common in Ethernet cables for computer networks.
Fire Safety
The plastic material that covers electrical cables can burn. If many cables are grouped together, a fire can spread quickly. To prevent this, cable coverings can be made from special materials that stop fire from spreading. Another way is to put fire-resistant coatings directly on the cables or to enclose them in special boxes made of materials that don't burn.
Types of Cables
There are many different kinds of electrical cables, each designed for a specific job:
- Coaxial cable – Used for radio signals, like for cable television.
- Direct-buried cable – Designed to be buried directly in the ground.
- Flexible cables – Easy to bend and move.
- Multicore cable – Has more than one wire inside, all covered by one outer jacket.
- Paired cable – Two insulated wires twisted together, often used for low-frequency signals.
- Portable cord – Flexible cable for power in things you can move, like lamps.
- Ribbon cable – A flat cable with many wires side-by-side, often used inside computers.
- Shielded cable – Has a protective layer to block interference, good for sensitive electronics.
- Twin and earth – A common type of cable used in home wiring.
- Twin-lead – A flat, two-wire cable often used for TV antennas.
- Twisted pair – Two insulated wires twisted together, common in network cables.
Hybrid Cables
Some cables are "hybrid," meaning they combine different types of wires. For example, a hybrid cable might have both fibre-optic threads and electrical wires. The optical fibers carry information, while the electrical wires transmit power. These are often used for things like connecting antennas on poles or towers.
See also
 In Spanish: Cable para niños
In Spanish: Cable para niños
- Wire gauge
- Cable management
- Cable gland
- Cable reel
- Circuit integrity
- Over/under cable coiling