Coaxial cable facts for kids
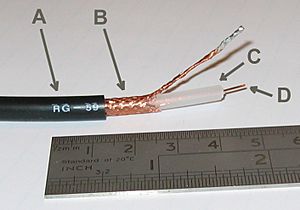
Coaxial cable, often called coax, is a special type of electrical cable. It has an inner wire surrounded by an insulating layer, which is then covered by a tube-shaped metal shield. This design helps it carry electrical signals. The cable is quite stiff because of its special insulation.
Coaxial cables are used to send high-frequency signals, like those for Cable TV. They are also used for computer networks, though less often now. The special design of coax cable means the signal stays inside, so it doesn't get messed up by outside electrical signals.
Contents
What are Coaxial Cables Used For?
Coaxial cables are used to send radio signals. You can find them connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. They also carry digital audio and cable television signals.
There are many kinds of coaxial cables, each made for different uses and standards. Common uses include video and CATV (Cable TV) systems, radio frequency (RF) and microwave signals, and connecting computers or other devices.
How Coaxial Cable is Built
A coaxial cable carries an electrical signal using an inner wire. This wire is usually made of solid copper, braided copper, or copper-coated steel. It's surrounded by a layer of insulation. Around that, there's a shield, which is often made of one to four layers of braided metal or metallic tape. Finally, an outer plastic jacket protects the whole cable.
Different Types of Coaxial Cables
- Hard line
- Radiating cable
- RG-6 (a common type for home use)
- Triaxial cable (has an extra shield)
- Twin-axial cable (has two inner conductors)
- Semi-rigid cable
- Rigid line
Connectors for Coaxial Cables
The ends of coaxial cables usually have special connectors. These connectors are designed to keep the cable's special shape and have the same electrical properties as the cable itself. This helps the signal travel smoothly.
Connectors are often coated with metals that conduct electricity well, like silver or gold. However, silver can tarnish quickly, which means it gets a dark coating that doesn't conduct electricity well. This can make the connector work poorly.
Where You See Coaxial Cables in Use
Short coaxial cables are often used to connect home video equipment, in ham radio setups, and in measurement devices. While they used to be common for computer networks like Ethernet, most networks now use other types of cables. However, they are still widely used for cable modems to provide broadband Internet.
In the past, long coaxial cables were used to connect radio networks, television networks, and long-distance telephone systems. Today, newer technologies have mostly replaced them for these very long distances.
Shorter coaxial cables still deliver cable television signals to most TVs. This is one of the biggest uses for coaxial cable production today. In the 1980s and early 1990s, coaxial cable was also used a lot in computer networking.
Tiny coaxial cables, called micro coaxial cables, are used in many everyday devices, military equipment, and even in ultrasound scanning machines.
Coax cable is often used to carry data or signals from an antenna to a receiver. For example, from a satellite dish to a satellite receiver, from a television antenna to a TV, or from a radio mast to a radio receiver.
Timeline of Coaxial Cable History
- 1880 — Coaxial cable was patented in England by Oliver Heaviside.
- 1884 — Siemens & Halske patented coaxial cable in Germany.
- 1894 — Oliver Lodge showed how signals could travel through a "waveguide" at the Royal Institution.
- 1929 — The first modern coaxial cable was patented by Lloyd Espenschied and Herman Affel from AT&T's Bell Telephone Laboratories.
- 1936 — The first closed circuit transmission of TV pictures on coaxial cable happened. It went from the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin to Leipzig.
- 1936 — The world's first underwater coaxial cable was installed between Apollo Bay, Australia, and Stanley, Tasmania. This 300 km cable could carry one radio channel and seven phone calls.
- 1936 — AT&T installed an experimental coaxial cable for phones and TV between New York and Philadelphia. It had automatic booster stations every ten miles and could carry 240 phone calls at once.
- 1936 — Coaxial cable was laid by the General Post Office (now BT) between London and Birmingham, providing 40 phone channels.
- 1941 — The first commercial use in the USA by AT&T happened between Minneapolis, Minnesota, and Stevens Point, Wisconsin. It could carry one TV channel or 480 phone calls.
- 1956 — The first transatlantic coaxial cable, called TAT-1, was laid across the Atlantic Ocean.
Images for kids
-
High-end coaxial audio cable (S/PDIF)
See also
 In Spanish: Cable coaxial para niños
In Spanish: Cable coaxial para niños