Fraser Canyon Gold Rush facts for kids
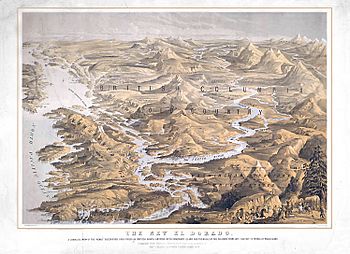
The New Eldorado: "A Complete View of the Newly Discovered Goldfields"
|
|
| Duration | 1858 – c. 1927 |
|---|---|
| Location | Fraser Canyon, British Columbia |
| Type | Gold rush |
The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush began in 1858. This happened after gold was found on the Thompson River in British Columbia. Many people quickly rushed to the area around Fraser Canyon.
The main gold rush was mostly over by 1927. However, miners kept exploring and found other gold fields. These were located throughout the British Columbia Interior and North. The most famous new gold area was in the Cariboo. The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush led to new European settlements on the mainland of British Columbia. Settlers built roads and created the Colony of British Columbia. They also founded many towns within it.
Contents
The Gold Rush Begins
People had mined for gold in the area for a few years. But the big news spread when James Douglas, the governor of Vancouver Island, sent gold ore to a mint in San Francisco. News traveled very fast. Within a month, about 30,000 people rushed to Victoria, British Columbia. They all hoped to find gold.
This sudden rush changed the way things were for the Hudson's Bay Company fur traders. It also changed life for the Indigenous peoples living there. By the fall, many new miners had not found gold. They went home, but other men quickly took their place.
Governor Douglas later said that people had to enter the colony through Victoria. But thousands of miners used other trails illegally. These trails included the Douglas Road, the Okanagan Trail, the Similkameen Trail, Whatcom Trail, and the Skagit Trail. Because of this, it was hard to count how many miners joined the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush.
Richard Clement Moody and British Columbia
When news of the gold rush reached London, England, the Colonial Office chose Richard Clement Moody. His job was to bring British order to the area. Sir Edward Bulwer-Lytton wanted Moody to make British Columbia a strong British area in the far west. He hoped it would become "a second England" on the Pacific Ocean.
Moody arrived in British Columbia in December 1858. He was in charge of the Royal Engineers, Columbia Detachment. He also helped found the new capital city of New Westminster.
Conflicts During the Rush
In the fall of 1858, problems grew between the miners and the Nlaka'pamux people. The Nlaka'pamux are the First Nations people of the Canyon. This led to a fight known as the Fraser Canyon War. Governor Douglas arranged for the Douglas Road to be built. He went to Yale to accept apologies from Americans who had fought against the Indigenous people. He also appointed British judges and changed mining rules. He tried to keep order, but it was hard without many soldiers.
Tensions also rose between European American miners and non-white miners. On Christmas Eve 1858, Isaac Dixon was beaten. He was a freed American black man and the town barber. Later, he became a popular journalist. Dixon was beaten by two men from Hill's Bar, another main town in the goldfields. This event led to a series of problems called McGowan's War.
After the Gold Rush
By 1860, most of the gold in the area was gone. Miners either went home or traveled deeper into the British Columbia wilderness. They were searching for new riches. Other gold rushes happened later in the area. These new rushes drew people away from British Columbian cities.
Interesting Facts About the Gold Rush
- The Indigenous communities traded with the new arrivals. They gave them food and supplies needed for travel and gold-mining.
- They also worked as trusted guides and translators.
- James Douglas of New Caledonia did not want to lose more land to Americans. So, he asked Queen Victoria to create a colonial government there.
- The queen renamed the territory British Columbia. She made Douglas its first governor.
- If Douglas had not asked for the queen's help, America might have taken New Caledonia.
- The gold rush disturbed the Nlaka'pamux salmon fishery. This was a very important way for the people to get food and make a living.
- A smallpox sickness spread in 1862. It caused the deaths of many Indigenous people.
- On August 22, 1858, the Nlaka’pamux agreed to let miners use their resources and lands.
See also
In Spanish: Fiebre del oro del cañón del Fraser para niños


