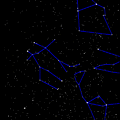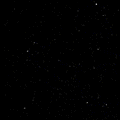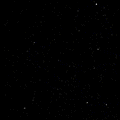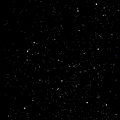
Gemini (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Gemini
|
|
| Abbreviation | Gem |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Geminorum |
| Pronunciation | jem-IH-ny genitive JEM-ih-NOR-əm |
| Symbolism | the Twins, Castor and Pollux |
| Right ascension | 7h |
| Declination | +20° |
| Quadrant | NQ2 |
| Area | 514 sq. deg. (30th) |
| Main stars | 8, 17 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
80 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 4 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 4 |
| Brightest star | Pollux (β Gem) (1.15m) |
| Messier objects | 1 |
| Meteor showers | Geminids Rho Geminids |
| Bordering constellations |
Lynx Auriga Taurus Orion Monoceros Canis Minor Cancer |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −55°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of February. |
|
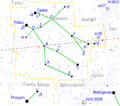
Gemini is a famous group of stars called a constellation. It is part of the zodiac, which is a special path of stars in the sky. Its name comes from the Latin word for twins. People have looked at these stars for thousands of years. The ancient astronomer Ptolemy wrote about it nearly 2,000 years ago. Today, it is still one of the 88 official constellations used by scientists. Its symbol looks like the Roman numeral two (♊︎).
Gemini: The Famous Twins of the Night Sky
Where to find Gemini in the stars
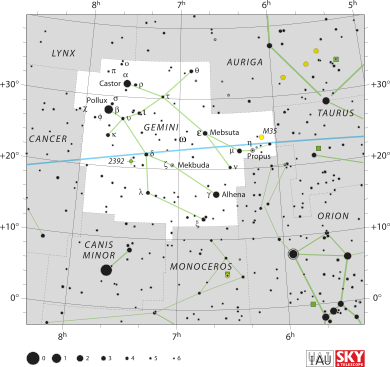
Gemini is located in the northern half of the sky. It sits between Taurus to the west and Cancer to the east. You can see it best during the winter months. In December and January, it stays up all night long.
The easiest way to find Gemini is to look for its two brightest stars, Castor and Pollux. You can find them by looking east from the famous Orion's Belt. If you draw an imaginary line from the Pleiades star cluster through the middle of the sky, you will run right into Gemini. When the Moon passes through this area, you can watch it move past the "twins" in just one night!
The brightest stars in the constellation
There are about 85 stars in Gemini that you can see without a telescope. Even though the constellation represents twins, the stars themselves are very different from each other.
The heads of the twins: Castor and Pollux
- Pollux (Beta Geminorum) is the brightest star in the constellation. It is an orange-colored giant star about 34 light-years away from Earth. Scientists have even discovered a planet orbiting around it!
- Castor (Alpha Geminorum) is the second brightest star. While it looks like one star to us, it is actually a complex system of six stars orbiting each other. It is about 52 light-years away.
Other interesting stars
- Alhena (Gamma Geminorum) is a bright blue-white star. Its name means "the brand" in Arabic.
- Wasat (Delta Geminorum) is a white star. In 1930, the dwarf planet Pluto was discovered very close to this star.
- Mebsuta (Epsilon Geminorum) is a massive yellow supergiant star. It is much larger and brighter than our Sun but is very far away.
- Mekbuda (Zeta Geminorum) is a special kind of star that pulses, getting brighter and dimmer over 10 days.
Amazing objects in deep space
Gemini contains several "deep-sky objects" that you can see with binoculars or a telescope.
- Messier 35 (M35) is a large cluster of about 200 stars. It is so big that it looks about the same size as a full moon in the sky. It is located 2,800 light-years away.
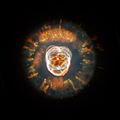
- NGC 2392 is a planetary nebula. This is a glowing cloud of gas created by a dying star. It is often called the "Parka Nebula" because it looks like a person wearing a fuzzy hood.
- The Medusa Nebula is another cloud of gas from a star that ended its life long ago. It is shaped like the snakes on the head of the mythical Medusa.
The Geminid meteor shower
Every year in mid-December, Gemini is the center of one of the best meteor showers. This is called the Geminids. At its peak, you can see up to 100 "shooting stars" every hour. These meteors happen when Earth passes through a trail of dust left behind by an object called 3200 Phaethon.
Myths and legends from around the world
Many different cultures have stories about these stars.
- Ancient Babylon: They called the stars the "Great Twins." They were seen as minor gods who protected people.
- Greek Mythology: This is the most famous story. Castor and Pollux were brothers. Pollux was the son of the king of the gods, Zeus, which made him immortal. Castor was a regular human. They were so close that when Castor died, Pollux asked Zeus to let them stay together forever. Zeus placed them both in the sky as stars.
- Chinese Astronomy: The stars of Gemini are part of two different groups called the White Tiger of the West and the Vermillion Bird of the South.
Famous discoveries made in Gemini
Gemini has been the site of some very important moments in science history:
- In 337 BC, the philosopher Aristotle watched the planet Jupiter move in front of a star in Gemini.
- In 1781, the astronomer William Herschel discovered the planet Uranus while looking at stars in this constellation.
- In 1930, Clyde Tombaugh discovered Pluto by looking at photographs of the stars near Wasat in Gemini.
Images for kids
-
A close-up of the Medusa Nebula taken by a powerful telescope.
See also
 In Spanish: Géminis (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Géminis (constelación) para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |