Great Barrier Reef Marine Park facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Great Barrier Reef Marine ParkQueensland |
|
|---|---|

Boardwalk through a mangrove forest featured in Estuarine Conservation Zone as part of The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park
|
|
| Established | 1975 |
| Area | 343,966 km2 (132,806.0 sq mi) |
| Managing authorities |
|
| Website | Great Barrier Reef Marine Park |
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park helps protect a huge part of Australia's Great Barrier Reef from harm. It is a massive marine park used for many different activities. These include tourism, fishing, shipping, and scientific research. Indigenous people also use the park in traditional ways.
Fishing and taking things like coral or seashells are carefully controlled. Big ships must follow special paths. These paths avoid the most delicate parts of the park. The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest and most famous coral reef system. It has almost 3,000 reefs. This is about 10% of all coral reef areas globally. The park is home to thousands of different plants and animals. These include corals, fish, sharks, rays, marine mammals, sea turtles, and sea snakes.
Contents
Protecting the Reef: Who's in Charge?
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (GBRMPA) looks after the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. They use many tools to manage the park. These include special laws and rules. They also create zoning plans and work with traditional owners. Education, research, and monitoring help them protect the reef.
GBRMPA gives out permits for different activities in the park. They also watch how the park is used. This makes sure everyone follows the rules. GBRMPA gets money from the Australian government. They also get money from a small fee. This fee is paid by passengers visiting the park.
In May 2022, the Darumbal people were officially recognized. They became the traditional custodians of a large ocean area. This area is off the Central Queensland Coast. It covers about 36,606 square kilometers. This was the largest Traditional Use of Marine Resources Agreement (TUMRA) on the reef. This agreement created a partnership with GBRMPA. It also involved Queensland's Department of Environment and Science. A special ceremony took place on the beach to celebrate.
What the Park Looks Like
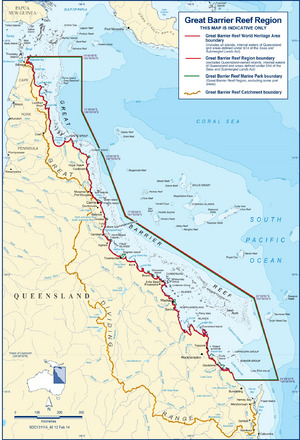
Where the Park Is Located
The marine park is east of Queensland, Australia. It starts in the north near Cape York. Its northern border includes some small, uninhabited Torres Strait Islands. These islands are east of Cape York.
The park's southern border is south of Gladstone. It is north of Bundaberg. This area includes Lady Elliot Island.
How Areas Are Protected
The marine park has different zones. Each zone has a special protection level. These levels are set by the IUCN protected area categories.
- Some areas are Strict Nature Reserves. These are very highly protected.
- Other areas are like National Parks. They protect large ecosystems.
- Some zones are for managing specific habitats or species.
- Other zones allow for sustainable use of natural resources. This means people can use them carefully.
History of the Park
In 1975, the Government of Australia passed a law. It was called the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975. This law created the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. It also listed what activities were not allowed on the reef.
The Australian Government knows how important this park is. It is part of the nation's Biodiversity Action Plan. The government works with the Government of Queensland. They want to make sure the reef is understood and used in a way that protects it for the future. They use zoning, management plans, and education. They also encourage eco-tourism.
Many animals on the Great Barrier Reef travel long distances. So, different laws and agreements must be considered. These include international agreements. For example, the park follows rules from the Ramsar Convention and CITES. It also follows agreements with Japan and China about migratory birds.
The park also follows many Australian national laws. These include the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975. It also follows state laws from Queensland. For example, Queensland has plans to manage fishing. The East Coast Trawl Management Plan 1999 limits trawling. It controls when and how trawling can happen. The Fisheries (Coral Reef Fin Fish Fishery) Management Plan 2003 aims to reduce fishing. It also stops fishing when fish are spawning.
The Great Barrier Reef became a World Heritage Site in 1981.
Before 1999, the park had four main zones. These zones were created between 1983 and 1987. A new plan, the Great Barrier Marine Park Zoning Plan 2003, started in 2004. This new plan replaced all the old ones.
In July 2004, a new zoning plan began. It was praised as a great way to protect marine ecosystems. This plan used special computer software called MARXAN. On July 1, 2004, the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park became the world's largest protected sea area. The Australian Government greatly increased the areas protected from fishing. This went from 4.6% to 33.3% of the park.
The current way of zoning is called the "Representative Areas Program." It protects "typical" areas of the reef. These are called "Green Zones" where nothing can be taken. The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area is divided into 70 natural regions.
In 2006, the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975 was reviewed. It was suggested that no more zoning changes happen until 2013. Also, a report on the reef's health should be published every five years.
In 2007, GBRMPA was nominated for an award. It was for their work in sustainable tourism.
On April 3, 2010, a ship called the Shen Neng 1 ran aground. It caused an oil spill.
In 2012, a new law made developers pay money into the Reef Trust. Some experts say this made it easier to approve new buildings in the area.
Threats to the Reef
The Great Barrier Reef faces several challenges.
Crown-of-Thorns Starfish
The crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci) lives on the reef naturally. But when too many of them appear, they can harm the reef. They eat coral. People are working to control these outbreaks. Robots like COTSBot help find and remove them.
These outbreaks have made more people aware of the reef's problems. Industries and conservation groups are working together. They want to control the starfish and protect the reef. You can learn more about this threat here.
Future of the Reef
The Great Barrier Reef Outlook Report is published every five years. It looks at the reef's health and future. This report is required by law. It helps everyone understand how the reef is doing.
The report says the biggest dangers to the reef are climate change. Also, pollution from land and coastal development are threats. Some fishing impacts and illegal fishing also cause problems.
Other Protected Areas Nearby
The Great Barrier Reef Coast Marine Park is next to the Great Barrier Reef. It is in Queensland waters. It was created in 2004. This park helps the main Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. It has similar rules and goals. The Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service manages it.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Parque marino de la Gran Barrera de Coral para niños
In Spanish: Parque marino de la Gran Barrera de Coral para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |