Great Recession in the United States facts for kids
The Great Recession was a very serious economic problem in the United States. It was a time when the country faced a big financial crisis and a deep recession. A recession means the economy shrinks for a while, and people lose jobs. Even though the official recession lasted from December 2007 to June 2009, it took many years for the economy to get back to normal. This was because families and banks had to pay off a lot of money they had borrowed. Also, the government didn't spend as much after some early efforts to help. This crisis happened after a "housing bubble" burst, meaning house prices that were too high suddenly dropped.
During this time, about 8.7 million jobs were lost between 2008 and 2010. This was about 7% of all jobs. The country's total economic output, called GDP, also shrank by 4.2%. This made the Great Recession the worst economic downturn since the Great Depression in the 1930s. The economy started growing again in mid-2009, but it didn't reach its old size until 2011. Unemployment went from 4.7% to a high of 10% in 2009. It took until 2016 for unemployment to return to 4.7%. Many jobs didn't come back until 2014.
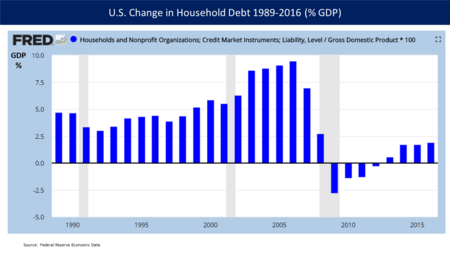
Families and non-profit groups borrowed about $8 trillion between 2000 and 2008. This helped create the housing bubble. Then, they started paying off this debt from 2008 to 2012. This was the first time this kind of debt had gone down since the 1950s. However, the government's debt grew a lot. It went from 35% of GDP in 2007 to 77% by 2016. This happened because the government spent more money to help the economy. Meanwhile, people and businesses paid off their own debts. President Barack Obama said in 2014 that the government's efforts to help the economy, which started under President Bush, were finished and had mostly made a profit.
Contents
How the Economy Changed
After the Great Depression in the 1930s, the American economy grew strongly. There were smaller recessions sometimes. The government had strict rules for financial markets.
In the early 1980s, the government started to loosen these rules. This led to a big expansion of the financial sector. Investment banks grew much larger. From 1978 to 2008, the average salary for investment bankers grew much faster than for other workers. Looser rules also led to more financial fraud, often linked to real estate. Many Americans lost their life savings because of this. Large investment banks started merging, forming giant companies like Goldman Sachs.
Early Signs of Trouble
In early 2008, many experts thought a U.S. recession had begun. When a big investment bank called Bear Stearns collapsed, it showed the crisis would be serious.
Alan Greenspan, a former head of the Federal Reserve, said in March 2008 that this crisis would likely be the worst since World War II. Some economists predicted a mild recession. They thought it would end when government stimulus checks were spent. However, others believed it would be much more severe.
It takes time for official groups to declare a recession. Even if GDP numbers looked positive, some analysts argued that if you considered inflation, the economy was actually shrinking. By summer 2008, some states, like New York and Florida, officially declared they were in a recession.
What Caused the Great Recession?
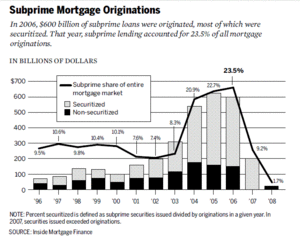
Federal Reserve Chair Ben Bernanke explained the causes of the crisis. He said there were "triggers" that started it and "vulnerabilities" that made it worse. Triggers included big losses on risky home loans called "subprime mortgages." Also, a "run" on the "shadow banking system" began. This meant people tried to pull their money out of certain financial companies all at once.
Vulnerabilities in the private sector (businesses) included banks relying too much on unstable short-term loans. They also took on too much debt to invest, which is called "leverage." They used complex financial tools in risky ways. Vulnerabilities in the public sector (government) included unclear rules for banks and not enough power for regulators to stop problems.
The U.S. Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission looked into the causes. They concluded that the crisis could have been avoided. They found problems like:
- Widespread failures in how financial companies were regulated.
- Banks acting carelessly and taking too many risks.
- Too much borrowing by families and Wall Street.
- Key leaders not being ready for the crisis.
- Problems with responsibility and ethics at all levels.
Important reasons for the crisis included a lot of money flowing into the housing market. Banks got involved in the mortgage bond market. Government policies aimed to expand homeownership. Many home buyers also speculated, hoping to make quick money. Risky lending practices by mortgage companies, like adjustable-rate mortgages, also played a role.
Government Policies and Rules
A federal investigation found that some government policies, or a lack of them, were largely responsible for the recession.
- The "shadow banking" system was not regulated like regular banks. The top 5 investment banks involved in the crisis had borrowed huge amounts of money. When the value of their assets dropped, they became very unstable. They also relied on short-term loans, which dried up during the crisis.
- Companies like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac could borrow money cheaply because they were government-sponsored. They used this to buy many mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. They didn't have to keep as much money in reserve as other banks. This led to them losing a lot of money on risky loans. Eventually, the government had to take them over.
The Role of Alan Greenspan
Alan Greenspan was the head of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006. Some people blamed him for the housing bubble. He later said he didn't fully understand the problem until late 2005 or 2006. Greenspan admitted he was "partially wrong" in his hands-off approach to banks. He thought banks would protect themselves, but they didn't. However, the Federal Reserve didn't have all the power to regulate the banking sector at that time.
The Recession is Official
On December 1, 2008, the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) officially announced that the United States had entered a recession in December 2007. They looked at job numbers and economic production. On that day, the stock market, measured by the Dow Jones Industrial Average, dropped a lot. Some economists, like Paul Krugman, even worried it looked like the start of a "second Great Depression."
Rise in Unemployment
The Great Recession caused millions of jobs to be lost. High unemployment lasted for years after the recession officially ended in June 2009. To help, Congress passed and President Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) in 2009. This was an $800 billion plan, known as "The Stimulus." It included tax cuts and spending programs.
The total number of jobs in the U.S. peaked in January 2008. It then fell by nearly 8.8 million jobs. It took until May 2014 for the number of jobs to return to the January 2008 level. The unemployment rate went from 4.7% in November 2008 to a high of 10.0% in October 2009. It then slowly fell back to 4.7% by May 2016.
Banks Running Out of Money
The major investment banks got a lot of their money from short-term loans. These loans were disrupted during the crisis. It was like a "bank run" on the unregulated "shadow banking" system. This system had grown larger than the regulated banking system.
Because they couldn't get money, some banks had to merge (like Bear Stearns and Merrill Lynch). Some went bankrupt (Lehman Brothers). Others got federal bank charters and private loans (Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley). A huge insurance company called AIG also needed a massive government bailout. AIG had insured many of the risks of these banks. The bailout of AIG essentially helped banks around the world.
Here are some key events during the crisis from 2007 to 2008:
- From late 2007 through September 2008, there were many smaller bank rescues.
- In summer 2007, Countrywide Financial, a big mortgage lender, needed a lot of credit.
- In July 2008, IndyMac Bank was taken over by federal regulators. This happened after people rushed to withdraw their money.
- In September 2008, Lehman Brothers declared bankruptcy. This was a huge event. At the same time, Bank of America bought Merrill Lynch. The insurance giant AIG sought a loan from the Federal Reserve.
- On September 16, 2008, the Federal Reserve announced an $85 billion rescue package for AIG.
- The biggest bank failure in history occurred on September 25. JP Morgan Chase agreed to buy the banking assets of Washington Mutual.
The year 2008 saw a record number of big company bankruptcies in the U.S. The Federal Reserve took steps to help the economy by lowering interest rates.
| Date | Primary discount rate | Secondary discount rate | Fed funds rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apr 30, 2008 | 2.25% | 2.75% | 2.00% |
| Mar 18, 2008 | 2.50% | 3.00% | 2.25% |
| Mar 16, 2008 | 3.25% | 3.75% | 2.25% |
| Jan 30, 2008 | 3.50% | 4.00% | 3.00% |
| Jan 22, 2008 | 4.00% | 4.50% | 3.50% |
Government Help for Banks
On September 17, 2008, Federal Reserve chairman Ben Bernanke advised the Treasury Secretary that a large amount of public money was needed to stabilize the financial system. The government temporarily banned "short selling" of financial stocks to stop prices from falling further. The Treasury also announced a new $50 billion program to insure money funds. This was similar to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) program.
President George W. Bush asked Congress for as much as $700 billion to buy troubled mortgage assets. The House of Representatives first rejected the bill, causing the stock market to drop sharply. A revised version of the bill was later passed by Congress.
By mid-November 2008, the total amount of loans, purchases, and guarantees by the Federal Reserve and Treasury to help the financial system was over $5 trillion. However, much of this money was eventually paid back. By March 2018, the bailouts had actually generated an $87 billion profit for the government.
How the U.S. Responded
The Federal Reserve, Treasury, and Securities and Exchange Commission took several steps to intervene in the crisis. They made it easier for financial groups to share funds. They also temporarily stopped certain types of stock trading. These actions were part of their reaction to the mortgage crisis.
The Recovery Period
The recession officially ended in mid-2009. But the nation's economy was still described as in an "economic malaise" in 2011. Some economists called the recovery the weakest since the Great Depression. It was even called a "Zombie Economy" because it was neither fully dead nor alive. Household incomes kept falling until 2012. Also, long-term unemployment was the highest it had been since World War II. The Federal Reserve kept interest rates very low from 2008 until 2015.
Recoveries from financial crises can take a long time. This is because people and businesses need to reduce their debt. Economist Carmen Reinhart stated in 2011 that debt reduction takes about seven years. She also noted that economic growth is usually slower in the decade after a severe financial crisis.
Then-Fed Chair Ben Bernanke explained several reasons why the recovery was slow:
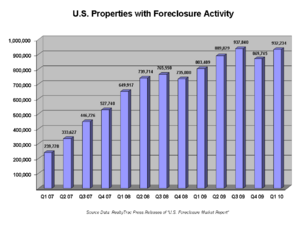
- The housing sector did not bounce back. It was severely damaged during the crisis. Millions of foreclosures created a surplus of properties. Consumers were paying down debts instead of buying homes.
- It was hard for individuals and companies to borrow money. Banks were also paying down their debts.
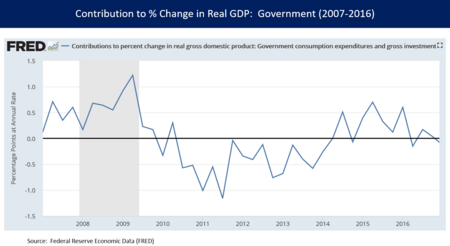
- Government spending was limited after initial efforts. This was not enough to make up for private sector weaknesses.
For example, U.S. federal spending actually decreased in dollar terms from 2009 to 2014. This slowed down economic growth. When both families and the government try to save money at the same time, it can lead to a slow recovery.
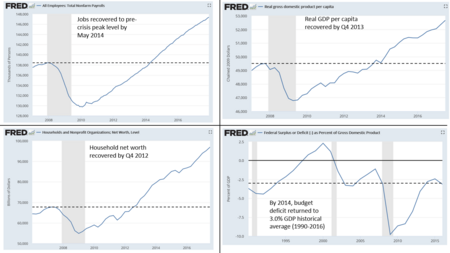
Several key economic measures improved. These included job levels, GDP per person, the stock market, and household net worth. They hit their low points in 2009 or 2010. They then began to turn upward. They recovered to pre-recession levels between late 2012 and May 2014. By May 2014, all the jobs lost during the recession had returned. Real median household income fell to a low in 2012. But it recovered to an all-time high by 2016.
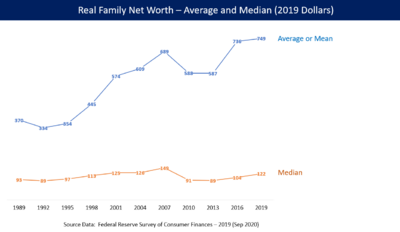
However, the gains during the recovery were not spread evenly. Economist Emmanuel Saez wrote that the wealthiest 1% of families captured 52% of the total income growth from 2009-2015. According to the Federal Reserve, median family net worth peaked in 2007. It fell to a low point in 2013. It only partially recovered by 2016. Middle-class families had much of their wealth in housing. This caused much of their decline when the housing bubble burst.
President Obama declared the bailout measures finished and mostly profitable by December 2014. By January 2018, bailout funds had been fully recovered by the government. This included interest on loans. A total of $626 billion was invested, loaned, or granted. But $390 billion was returned as principal. The Treasury also earned another $323 billion in interest. This resulted in an $87 billion profit.
How Bad Was It?
Most economic historians believe the Great Recession was the second worst economic downturn in U.S. history. It was only less severe than the Great Depression. Some economists, including Ben Bernanke, have argued that the financial crisis that started the Great Recession was arguably more severe than the one before the Great Depression. They believe a depression was only avoided because the Federal Reserve and federal government took strong actions.
See also
- Timeline of the Great Recession
- Causes of the Great Recession
- New Deal
- 1991 Indian economic crisis
- Stock market crashes in India
- Financial crisis of 2007–2008
- 2008–2011 bank failures in the United States
- 2008–09 Keynesian resurgence
- 2010 United States foreclosure crisis
- United States debt-ceiling crisis of 2011
- List of economic crises
- The Big Short
- List of stock market crashes and bear markets
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |