Grignard reaction facts for kids
The Grignard reaction is a special chemical reaction that helps chemists build new molecules. It's like using LEGOs to build something bigger and more complex! This reaction uses a special ingredient called a Grignard reagent. These reagents are made from a metal called magnesium and other chemical parts.
Grignard reagents are very good at finding and attaching to certain parts of other molecules. When they attach, they create a new connection between carbon atoms. This is super important because carbon atoms are the building blocks of almost all living things and many materials we use every day.
The Grignard reaction was discovered by a French chemist named François Auguste Victor Grignard. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1912 for his amazing work!
One tricky thing about Grignard reagents is that they don't like water. Water can make them stop working. So, chemists have to be very careful to keep water away when they are doing a Grignard reaction.
Contents
How the Reaction Works
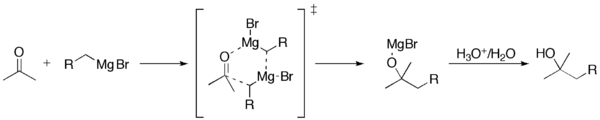
When a Grignard reagent meets a molecule with a special part called a carbonyl group (which has a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom), the Grignard reagent acts like a magnet. It pulls the carbon atom from the carbonyl group and forms a new bond with it.
This reaction usually happens in special liquids called solvents, like diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (often called THF). These solvents help keep the magnesium part of the Grignard reagent stable and happy. It's also important to keep air (especially oxygen) away, because oxygen can also mess up the reaction. Sometimes, chemists do these reactions in a special gas like nitrogen or argon to keep oxygen out.
Making a Grignard Reagent
To make a Grignard reagent, you start with small pieces of magnesium metal and mix them with a chemical called an alkyl halide or aryl halide. This usually happens in a solvent like diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran.
The reaction to make a Grignard reagent can sometimes start slowly. It's like trying to light a campfire – sometimes you need a little help to get it going! Chemists might use special tricks, like stirring very fast, using ultrasound (sound waves), or adding a tiny bit of another chemical like iodine to help the reaction begin.
Once it starts, the reaction can get quite warm. This is because it releases energy, which is called an exothermic reaction.
Many Grignard reagents are so useful that companies make them and sell them already mixed in solvents.
What Grignard Reagents Can Do
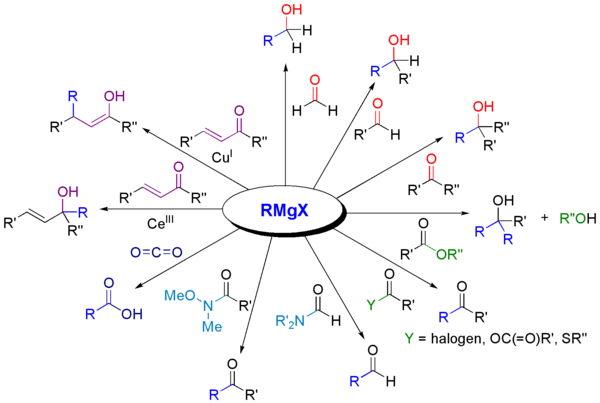
Grignard reagents are super versatile! They can react with many different types of molecules to create new ones.
Reacting with Carbonyl Compounds
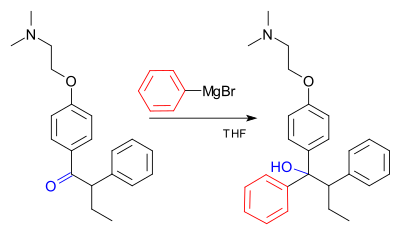
One of the most common things Grignard reagents do is react with molecules that have a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen). This is how they help make alcohols.
For example, they can add to aldehydes and ketones to make new, larger alcohol molecules.
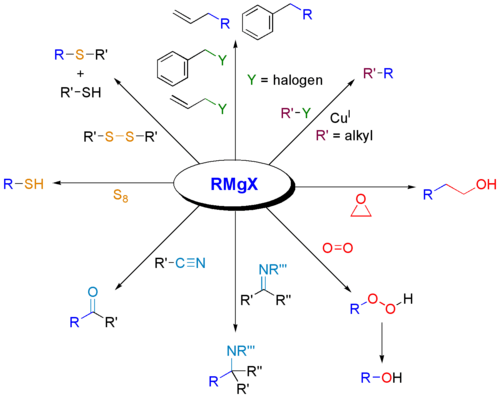
Reacting with Other Chemicals
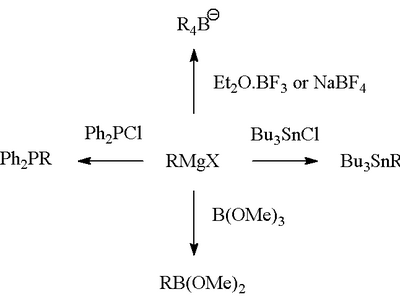
Grignard reagents can also react with other types of chemicals, not just carbonyls. They are great for connecting carbon atoms to other elements like boron, silicon, phosphorus, or tin. This helps chemists build even more kinds of molecules.
Making Carbon-Carbon Bonds
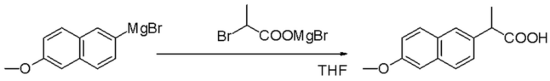
Grignard reagents are especially good at making new carbon-carbon bonds. This is like adding new sections to a carbon chain. For example, they can be used to make complex molecules like Naproxen, which is a medicine.
They are also used in making Tamoxifen, a medicine used to treat breast cancer.
Industrial Uses
Because Grignard reactions are so useful, they are used a lot in factories to make important chemicals and medicines. When making them on a large scale, chemists have to be very careful because the reactions can produce a lot of heat.
Images for kids
Related pages
- Wittig reaction
- Barbier reaction
- Organolithium reagents
See also
 In Spanish: Reacción de Grignard para niños
In Spanish: Reacción de Grignard para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |