Hatzegopteryx facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hatzegopteryx |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A fossil of the upper arm bone (humerus) from the first discovered Hatzegopteryx | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Suborder: | †Pterodactyloidea |
| Family: | †Azhdarchidae |
| Subfamily: | †Quetzalcoatlinae |
| Genus: | †Hatzegopteryx Buffetaut et al., 2002 |
| Type species | |
| †Hatzegopteryx thambema Buffetaut et al., 2002
|
|
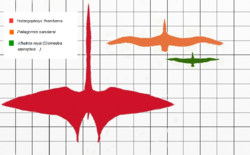
Hatzegopteryx was a giant flying reptile called a pterosaur. This creature was one of the biggest pterosaurs ever to exist. Scientists estimate its wingspan was between 10 to 12 meters (33 to 39 feet), which is as long as a school bus! It lived about 70 million years ago, during the late Cretaceous period, not long before the dinosaurs went extinct.
Unlike other giant pterosaurs, Hatzegopteryx was built differently. It had a very wide and strong skull, and its bones had a spongy texture inside, making them light but tough. It also had a short, thick, and powerful neck.
Hatzegopteryx lived on a place called Hațeg Island. Because there were no large meat-eating dinosaurs on the island, Hatzegopteryx was the top hunter, or apex predator. It could hunt much larger animals than other pterosaurs, including small dinosaurs.
Contents
Discovery and Naming
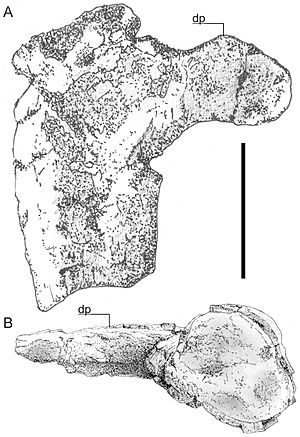
The first fossils of Hatzegopteryx were found in Romania in the late 1970s. One piece of its skull was so large that scientists at first thought it belonged to a meat-eating dinosaur.
In 2002, a team of paleontologists, Eric Buffetaut, Dan Grigorescu, and Zoltan Csiki, realized they had found a new type of giant pterosaur. They named it Hatzegopteryx thambema. The first part of the name comes from the Hatzeg Basin where it was found, and the Greek word pteryx, meaning "wing." The second part, thambema, is Greek for "monster" or "terror," because of its huge size.
Since then, more fossils have been found in other parts of Romania, including a very strong neck bone. These discoveries have helped scientists learn more about this amazing creature.
What Hatzegopteryx Looked Like
As Big as a Giraffe
Hatzegopteryx was enormous. With a wingspan of 10 to 12 meters, it was one of the largest flying animals of all time. When it stood on the ground, it was likely as tall as a modern giraffe.
Even though it was so big, its bones were lightweight, which allowed it to fly. Scientists have compared its size to another giant pterosaur, Quetzalcoatlus, and believe they were similar in wingspan.
A Giant, Lightweight Skull
The skull of Hatzegopteryx was huge, estimated to be about 2.5 meters (8.2 feet) long. That's one of the largest skulls of any land animal ever!
Unlike the thin, delicate skulls of other pterosaurs, the skull of Hatzegopteryx was very wide and strong. The bones were thick and had large ridges where powerful muscles would have attached. Its massive jaw could open very wide, allowing it to catch and eat large prey.
A Short and Powerful Neck
One of the most unusual things about Hatzegopteryx was its neck. While other giant pterosaurs like Arambourgiania had very long and slender necks, the neck of Hatzegopteryx was short and incredibly muscular.
Its neck bones were thick and wide, making the neck about 1.5 meters (5 feet) long. This was only about half the length of what you would expect for a pterosaur of its size. This powerful neck was built to handle strong forces, which would have been useful for hunting large and struggling animals.
Hatzegopteryx Family Tree
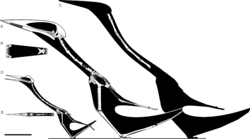
Hatzegopteryx belongs to a family of pterosaurs called Azhdarchidae. This group includes all of the largest known pterosaurs. They are famous for their long legs and necks, and for spending a lot of time walking on the ground to hunt.
Scientists believe Hatzegopteryx is closely related to other giants like Quetzalcoatlus and Arambourgiania. However, its unique features, like its super-strong skull and short neck, make it very different from its relatives. This shows that the azhdarchid family was very diverse, with different members adapted to different lifestyles. Another pterosaur found in the same area, Albadraco, may have been its closest relative.
How It Lived
Built Strong but Light
How could an animal with such a giant head fly? The secret was in its bone structure. The bones in its skull and neck were not hollow tubes like in other pterosaurs. Instead, they were filled with a network of small, thin bony struts, like the inside of a sponge.
This structure made the bones incredibly strong and resistant to bending, but also very light. Scientists have compared it to modern packing material like Styrofoam. This clever design allowed Hatzegopteryx to have a powerful, giant head without being too heavy to get off the ground.
A Top Predator on the Ground
Like other azhdarchids, Hatzegopteryx was probably a predator that hunted on the ground. It would have walked on all fours, using its folded wings like front legs, stalking its prey through the ancient forests and plains.
Its strong build suggests it was a powerful hunter. While other azhdarchids might have eaten small animals they could swallow whole, Hatzegopteryx was built to take on much larger prey. Its strong neck and robust skull would have allowed it to attack and kill animals that were too big to eat in one bite, including young or small dinosaurs.
The World of Hațeg Island

During the Late Cretaceous, much of Europe was an archipelago of islands. Hatzegopteryx lived on one of these, known today as Hațeg Island. This island was a very special place.
Because it was isolated, many of the dinosaurs that lived there were much smaller than their relatives on the mainland. This is a phenomenon called island dwarfism. Some of the animals Hatzegopteryx shared its home with included:
- Dwarf sauropods like Magyarosaurus, a long-necked dinosaur that was only about the size of a cow.
- The dwarf duck-billed dinosaur Telmatosaurus.
- The plant-eating dinosaur Zalmoxes.
- The armored dinosaur Struthiosaurus.
There were no large meat-eating dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus rex on the island. This left the role of top predator open for Hatzegopteryx. It was the king of its ecosystem, a giant hunter in a land of dwarfs.
The climate on Hațeg Island was likely warm and subtropical, with wet and dry seasons. The landscape was a mix of rivers, wetlands, and forests. Today, this area is so important for its fossils that it has been named a UNESCO Global Geopark.
See also
 In Spanish: Hatzegopteryx para niños
In Spanish: Hatzegopteryx para niños
- List of pterosaur genera
- Timeline of pterosaur research
- Pterosaur size