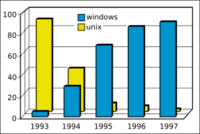History of the web browser facts for kids
A web browser is a special computer program that lets you find and look at information on the World Wide Web. Think of it as a window to the internet! It helps you see web pages, pictures, videos, and other cool stuff online. When you type an address, like a website name, into your browser, it finds that information for you.
Browsers also let you click on links to jump to other related pages. This makes it super easy to explore the internet.
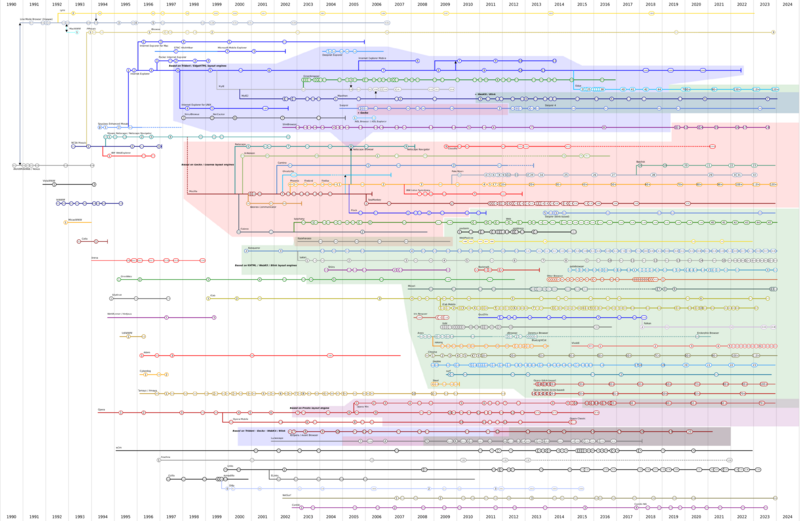
The very first web browser was created in 1990 by Tim Berners-Lee, who also invented the World Wide Web itself. His browser was called WorldWideWeb (later renamed Nexus). Soon after, many other browsers appeared. One of the most important was Mosaic, made by Marc Andreessen in 1993. Mosaic was easy to use and helped make the internet popular for everyone.
Today, you probably use browsers like Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Opera, or Edge.
Contents
How Browsers Started
Even before the internet as we know it, people were thinking about ways to link information together.
- In the 1980s, programs like MaxThink and Houdini allowed users to jump between different text files using special links. Imagine having notes on your computer, and clicking a word in one note would instantly take you to another related note!
- Another early program called Silversmith, created in 1986, used special tags to organize documents. It even allowed links between images, text, and sound.
- In 1990, a program called HyTelnet helped people connect to online libraries around the world. It was a quick way to access information, but it needed a better way to organize all the links. This problem was later solved by the invention of the web server.
- Around the same time, in 1990, an idea for a "PageLink" device was proposed. It was like an early vision of a tablet, with a touch screen for browsing pages, storing shopping lists, and even getting updated newspapers! But this idea was too advanced for its time.
The World Wide Web Arrives
The real start of web browsers came with the WorldWideWeb browser, created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990. He made it for the NeXT Computer, which was also the first web server.
- In 1991, a simpler browser called the Line Mode Browser was released. It could show web pages on older computer terminals, just using text.
- Other early browsers included MidasWWW and ViolaWWW.
- The Lynx browser, also from 1992, is still used today! It's a text-only browser, popular for people who prefer text or have visual impairments.
- Erwise was the first browser with a graphical user interface (meaning it had pictures and buttons you could click), but it didn't last long.
- In 1993, Cello was one of the first graphical web browsers that worked on Windows computers.
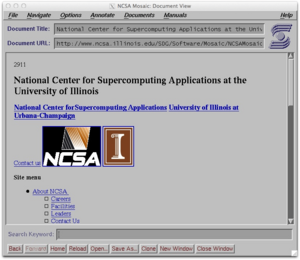
However, the internet really took off because of NCSA Mosaic.
- Released in 1993, Mosaic was a graphical browser that worked on many different computers, including Windows and Apple Macintosh.
- It was called the "killer application" of the internet because it made the web exciting and easy for everyone.
- Mosaic was the first browser to show images directly on the web page, alongside the text. Before Mosaic, you had to click an icon to open images in a separate program. This made web pages much more fun to look at!
- Marc Andreessen, who led the Mosaic team, later left to start a company that created Netscape Navigator.
IBM also released its own browser, IBM WebExplorer, in 1994.
In 1995, UdiWWW was the first browser to support all the features of HTML 3, which is the language used to build web pages.
The Browser Wars: Netscape vs. Microsoft
In 1994, Netscape released its main product, Netscape Navigator. It quickly became very popular. But then, Microsoft entered the scene with its own browser, Internet Explorer, in 1995. This started what became known as the "browser wars."
- At first, Netscape had a huge lead, with about 86% of the browser market in 1996.
- But Microsoft started including Internet Explorer with its Windows operating system. This meant that when people bought a new computer with Windows, Internet Explorer was already there.
- Within four years, Internet Explorer had taken over, reaching 75% of the market, and by 1999, it had almost 99%!
- This competition made it harder for web standards to develop, as both companies added their own special features to HTML.
Netscape couldn't keep up with Microsoft's power. So, they decided to make their browser's code open source, meaning anyone could see and help improve it. This led to the creation of Mozilla. Netscape was later bought by AOL in 1998.
Browsers in the 2000s and Today
The Mozilla project, born from Netscape, eventually led to the creation of Firefox.
- Firefox was released in 2002 and quickly became a popular choice. It was always free to download.
- Firefox makes money by partnering with search engines like Google, directing users to them.
Meanwhile, Microsoft announced in 2003 that Internet Explorer would no longer be a separate product. It would just be part of Windows.
- In 2004, Internet Explorer had its highest market share, over 92%. But then, its popularity slowly started to drop.
- Microsoft later changed its mind and released new standalone versions of Internet Explorer, like IE7, IE8, IE9, IE10, and IE11.
- However, with Windows 10, Microsoft introduced a new default browser called Microsoft Edge.
- Apple's Safari became the main browser for Mac computers. Safari, along with Google Chrome, uses a special engine called WebKit to display web pages.
- Google Chrome was released in 2008 and quickly became the most popular browser in the world.
- Opera, first released in 1996, was very popular on older mobile phones. It's still a choice for computers today.
- Text-based browsers like Lynx and Links are still used by some people, especially those who prefer a simple, fast experience without graphics.
How Browsers Are Related
Many web browsers are built using parts of older browsers or share similar underlying technology. This means they can sometimes be like cousins, sharing common features or ways of working.
See also
- Comparison of web browsers
- History of the Internet
- History of the World Wide Web
- Timeline of web browsers
- List of web browsers
- Usage share of web browsers
 | May Edward Chinn |
 | Rebecca Cole |
 | Alexa Canady |
 | Dorothy Lavinia Brown |