Horneophyton facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Horneophyton |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
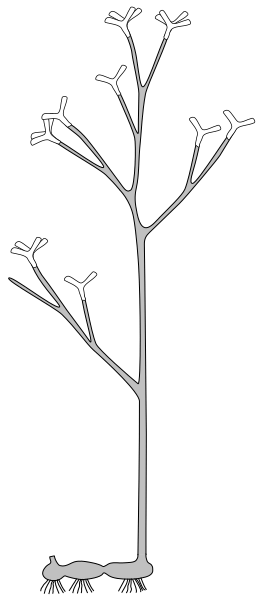
| Schematic reconstruction of Horneophyton lignieri to show its growth habit | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Division: | †Horneophyta |
| Class: | †Horneophytopsida |
| Order: | †Horneophytales |
| Family: | †Horneophytaceae Kenrick & Crane (1997) |
| Genus: | †Horneophyton Bargh. & Darrah (1938) |
| Species | |
|
†H. lignieri (Kidst. & W.H.Lang) Bargh. & Darrah (1938) |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Hornea Kidst. & W.H.Lang (1920) non Baker |
|
Horneophyton was a very old type of plant that lived on land. Its fossils are often found in a special kind of rock called the Rhynie chert. This plant lived during the Devonian period, which was a long, long time ago.
Scientists have found fossils of both the sporophyte and the female gametophyte parts of Horneophyton. These are different stages in a plant's life cycle. The sporophyte part of the plant grew to be about 20 centimeters (about 8 inches) tall. The gametophyte part was smaller, only about 6 centimeters (about 2.4 inches) tall.
About Horneophyton
Horneophyton was not a true vascular plant. Vascular plants have strong tubes inside them to carry water and nutrients. Horneophyton had some tubes, but their walls were thin. This means they were not as strong as the tubes in modern vascular plants.
What it Looked Like
The way Horneophyton was built inside was similar to hornworts. Hornworts are a type of simple plant, like mosses. Horneophyton also looked a bit like another ancient plant called Rhynia, which lived at the same time.

Its Importance
Because Horneophyton shared features with both simple plants (like hornworts) and more complex vascular plants (like Rhynia), it might be a missing link. This means it could show us how plants changed and evolved over millions of years. It helps scientists understand how the first plants moved from water to land and developed special features.
See also
 In Spanish: Horneophyton lignieri para niños
In Spanish: Horneophyton lignieri para niños

