Hoya of Guadix facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hoya of Guadix |
|
|---|---|
| Guadix Basin | |
 |
|
| Geography | |
| Country | Spain |
| State | Andalusia |
| Region | Granada |
| Population center | Guadix |

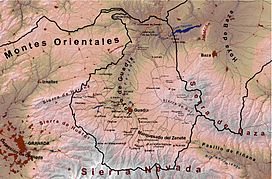
The Hoya of Guadix (pronounced "OY-ah day GWAH-deesh") is a large, flat area of land in southern Spain. It's like a big bowl or basin, surrounded by tall mountains. This special place is found in the northern part of the Granada province in Andalusia.
The Hoya of Guadix covers about 500 square kilometers (193 square miles). It was formed by the basins of two rivers, the Fardes and the Guadix. High mountains surround it: the Sierra Nevada to the south, the Sierra de Baza to the east, the Sierra Mágina to the north, and the Sierra Harana to the west.
The word Hoya means a low-lying plain or basin in this context.
Contents
How the Hoya of Guadix Formed
This area's unique landscape was created over millions of years. Imagine a deep dip in the land that slowly filled up.
Ancient Seas and Sediments
About 20 million years ago, during a time called the early Miocene period, the Hoya of Guadix was part of the sea. Materials like calcarenites (a type of rock made from shells) were laid down. These are typical of coastal areas.
After these rocks, marine marl (a soft, muddy rock) was deposited. For about 7 million years, the basin was connected to the sea.
From Sea to Land
Eventually, the land began to rise, and the basin became completely cut off from the sea. From then on, only materials from the land were deposited. Rivers carried clays, silts, sands, and gravel from the surrounding mountains. They also brought rocks like gypsum, which forms in dry, lake-like environments. This shows how the area changed from a marine (sea) environment to a continental (land) one.
Shaping the Landscape
Around 500,000 years ago, the Hoya of Guadix started to look much like it does today. Small rivers flowing from the nearby mountains began to carve out the land. This process, called erosion, created the unique gullies and badlands that you can see there now.
Climate and Farming
The Hoya of Guadix has a continental climate. This means it has hot summers and cold winters. The surrounding mountain ranges protect it from the sea's influence. Most of the rain falls during the winter months.
Today, the rivers Fardes and Guadix make this area very fertile. Farmers use the water to irrigate their crops. You can find many fruit orchards, especially melons. People also grow poplar trees for wood, along with cereals, legumes, and different vegetables.
Towns and Cities
The largest city in this basin is Guadix, which gives the area its name. Other important towns include Fonelas, Benalúa, Purullena, and Alcudia de Guadix.
See also
 In Spanish: Hoya de Guadix para niños
In Spanish: Hoya de Guadix para niños


