Human musculoskeletal system facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Musculoskeletal system |
|---|
The human musculoskeletal system is your body's amazing team that helps you move! It's also called the locomotor system. This system includes your bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and joints. It gives your body its shape, helps you stand tall, keeps you stable, and lets you move around.
Think of it as the framework and engine of your body. Your skeleton provides the main support. Your muscles pull on your bones to create movement. Other important parts like cartilage, tendons, and ligaments connect everything and help it work smoothly.
This system does many important jobs. It supports your whole body, allows you to walk, run, jump, and lift things. It also protects your important internal organs, like your brain and heart. Plus, your bones store important minerals like calcium and phosphorus. They also help make blood cells!
Sometimes, things can go wrong with this system. Injuries or diseases can make it hard to move. Doctors who specialize in these problems are called physiatrists or orthopaedic surgeons. They help people get back to moving well.
Contents
Parts of Your Movement System
Your Amazing Skeleton
Your skeleton is like the strong frame of a building. It gives your body its shape and protects your vital organs. It also helps you move and even makes blood!
When you were born, you had over 300 bones. But as you grow, some of these bones join together. An average adult has 206 bones. These bones come in different shapes and sizes. There are five main types:
- Long bones: Like the ones in your arms and legs.
- Short bones: Found in your wrists and ankles.
- Flat bones: Such as your skull and shoulder blades.
- Irregular bones: Like the bones in your spine.
- Sesamoid bones: Small bones, like your kneecap.
Your skeleton has two main parts:
- The axial skeleton is the central part. It includes your skull, spine, and rib cage.
- The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of your arms, legs, shoulders, and hips.
How Your Bones Help You
Your skeletal system does many important jobs:
- Support and Shape: It's the framework that holds your body up and gives it its form.
- Protection: Your skull protects your brain. Your rib cage protects your lungs and heart.
- Movement: Muscles attach to bones and pull on them to create movement.
- Blood Production: Inside some of your bones, there's a special substance called bone marrow. Red marrow makes all your red blood cells, platelets, and most white blood cells.
- Mineral Storage: Bones store important minerals like calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are released into your blood when your body needs them.
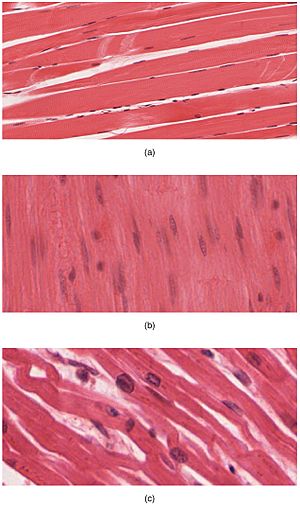
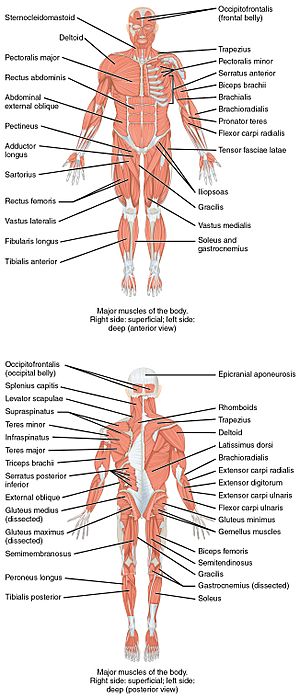
Your Powerful Muscles
Your body has three types of muscles, but only two are part of your musculoskeletal system:
- Skeletal muscles: These are the muscles you can control. They are attached to your bones and help you move your body.
- Smooth muscles: These muscles work automatically. You can't control them. They are found in the walls of your internal organs, like your stomach or intestines. They help move food or other substances through your body.
- Cardiac muscle: This special muscle is only found in your heart. It pumps blood around your body and also works automatically.
Skeletal muscles are arranged in groups around your joints. When you want to move, your brain sends a signal through your nerves to these muscles. This signal makes the muscles contract, or shorten, which pulls on your bones and creates movement.
How Muscles Contract
When you decide to move a muscle, your brain sends an electrical message. This message travels along a nerve to the muscle. At the point where the nerve meets the muscle, special chemicals are released. These chemicals tell the muscle to start contracting. This process makes the muscle fibers shorten, pulling on the bone it's attached to.
Strong Tendons
A tendon is a tough, rope-like band of tissue. It connects your muscles to your bones. When your muscle contracts, the tendon pulls on the bone, causing it to move. Tendons are strong but also a little stretchy. This helps them act like springs, saving energy when you move.
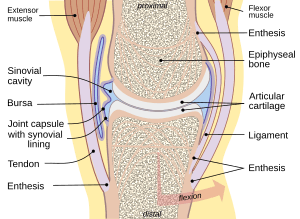
Joints, Ligaments, and Bursae
Joints are places where two or more bones meet. They allow your bones to move against each other. There are different types of joints:
- Movable joints: These allow a lot of movement, like your knee or shoulder.
- Slightly movable joints: These allow some movement, like the joints between your vertebrae in your spine.
- Immovable joints: These allow little to no movement, like the joints in your skull.
Many of your movable joints are called synovial joints. They have a special fluid called synovial fluid inside them. This fluid acts like oil, reducing friction between the bones and helping them slide smoothly. The joint is enclosed in a strong capsule that holds the fluid in.
Flexible Ligaments
A ligament is a strong, flexible band of tissue. It connects bones to other bones, holding your joints together. Ligaments help keep your bones in place and prevent them from moving too far or dislocating. They are a bit elastic, but if they stretch too much, they can get injured, making the joint unstable. Ligaments also stop certain movements, like bending a joint too far backward or forward.
Cushiony Bursae
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac. It acts like a cushion between your bones, tendons, and muscles around a joint. Bursae are filled with synovial fluid and are found near almost every major joint in your body. They help reduce friction and pressure when you move.
Keeping Your System Healthy
Your musculoskeletal system works closely with other body systems, like your blood system and nervous system. Because they are so connected, problems in one system can sometimes affect the musculoskeletal system.
Many issues with this system involve problems with movement. The seriousness of the problem depends on what it is and how bad it is. Common reasons people go to the hospital for musculoskeletal issues include knee or hip replacements, and spine surgeries.
Problems can include issues with your joints, muscles, or nerves. They can also be caused by infections, certain medical conditions, or even not getting enough nutrients. Sometimes, a problem with your muscles can affect how your eyes move, how you breathe, or even how your bladder works.
One common issue, especially for pregnant people, is pelvic girdle pain. This pain can be complex and has many possible causes, including changes in muscles or ligaments.
See also
 In Spanish: Aparato locomotor para niños
In Spanish: Aparato locomotor para niños
- Skeletal muscles of the human body
- Skeletal muscle
- Muscular system
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |