Muscular system facts for kids
The muscular system is a super important part of your body! Its main job is to help you move. A muscle is a special kind of tissue found in animal bodies. Muscles work with your skeleton to create movement. Together, they form what's called the musculoskeletal system.
Contents
Types of Muscles
You have three main types of muscles in your body. Each type does a different job:
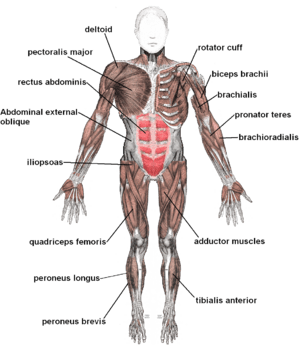
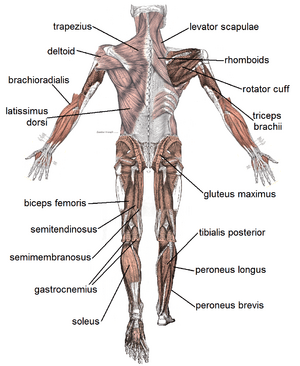
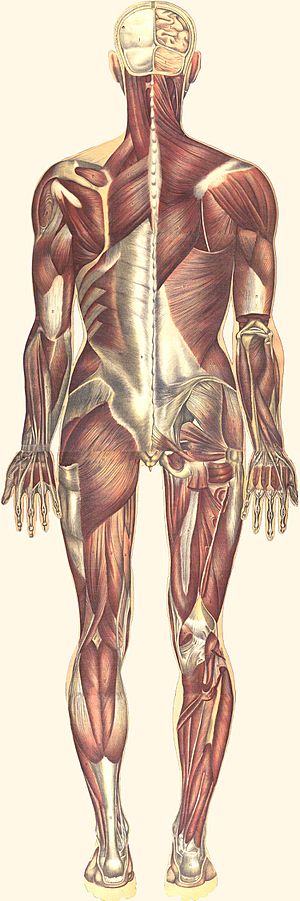
- Skeletal muscles: These are the muscles attached to your bones. They pull on your bones to make you move.
- Smooth muscles: You find these in places like your blood vessels and bladder. You don't control them directly.
- Cardiac muscle: This is the special muscle that makes up your heart.
Muscles can also be described as either voluntary or involuntary.
Voluntary Muscles
Your skeletal muscles are the only ones you can choose to move. This is why they are called voluntary muscles. They help you do things like:
- Move your arms and legs.
- Chew your food by moving your jaw.
- Run, jump, or pick things up.
Involuntary Muscles
The other two types of muscles, cardiac and smooth muscles, are involuntary. This means they work without you even thinking about it!
- Cardiac Muscle: This muscle is only found in your heart. When it squeezes, it pushes blood all through your circulatory system. You don't have to tell your heart to beat; it just does it!
- Smooth Muscles: These muscles are found in many places inside your body. They help with important jobs you don't control:
- Digestive System: Smooth muscles in your stomach and intestines help move food through your body. This allows you to get energy from what you eat.
- Blood Vessels: They can make your blood vessels wider or narrower. This helps control your blood pressure.
- Hair: Tiny smooth muscles attached to your hair follicles can make your hair stand up. This happens when you get scared or cold.
How Muscles Work
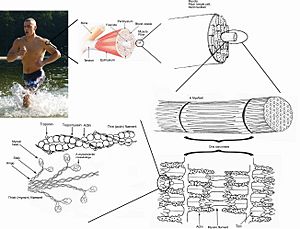
Muscles are made of many tiny muscle cells. When these cells get a signal, they all work together to make the muscle shorter. This is called contracting.
Muscle Signals
Muscle cells get signals from nerves. When a nerve sends a message, it tells some muscle cells to contract. These cells then pass the message to nearby cells. They do this by sending a small electrical current.
Muscle Proteins
Inside muscle cells, there are special proteins called actin and myosin. These are the proteins that actually make the muscle contract and get shorter.
Muscle Contraction
When a nerve tells a muscle to contract, tiny holes open up in the muscle cell's outer layer, called the cell membrane. These holes are like gates for something called calcium ions.
Calcium ions then rush into the cell. More calcium also comes from a special storage area inside the cell. This calcium sticks to the actin and myosin proteins. This action makes the proteins slide past each other, causing the muscle to contract.
Muscles also need a lot of ATP to work. ATP is like the energy currency your cells use. It's made from glucose (sugar) in your cells. It takes energy not only to contract muscles but also to relax them!
Exercise and Muscles
When you do exercise, your muscles get bigger and stronger. This is called hypertrophy. If a person doesn't exercise, their muscles can get smaller and weaker. This is known as atrophy. So, staying active helps keep your muscles healthy!
Muscle Problems
There are different kinds of muscle diseases that can affect how your muscles work. Here are some main groups:
- Neuromuscular Diseases: These problems affect how nerves tell muscles to move. Examples include Strokes and cerebral palsy.
- Motor Endplate Diseases: These are issues at the exact spot where a nerve connects to a muscle. Tetanus is an example of this type of disease.
- Myopathies: These are problems with the muscle structure itself. Muscular dystrophy and some cancers like Ewing's sarcoma are myopathies.
Related Pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema muscular para niños
In Spanish: Sistema muscular para niños
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |