Human skin colour facts for kids
Human skin color is one of the most noticeable things about people. It can be very dark brown, light pinkish-white, and many shades in between. Your skin color is something you get from your parents, like your eye color. It developed over a very long time through a process called natural selection.
Skin color mainly helps control how much ultraviolet (UV) light gets into your skin. This protects your body from the sun's harmful rays. The most important thing that decides your skin color is a substance called melanin. Melanin is a pigment produced in your skin by special cells called melanocytes.
Contents
Why Skin Color Varies
Melanin and UV Light
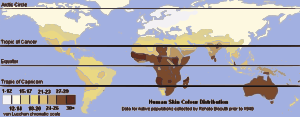
The amount of melanin in your skin determines its color. More melanin means darker skin. Less melanin means lighter skin. There is a clear connection between the amount of UV radiation (UVR) in an area and the skin color of people who have lived there for a long time.
Places with a lot of UVR, like areas near the tropics, usually have people with darker skin. Places far from the tropics, closer to the Earth's poles, have less UVR. People from these areas tend to have lighter skin.
How Skin Color Changed Over Time
Scientists believe that early humans, who lived in Africa, had dark skin. As groups of people moved out of Africa about 100,000 years ago and settled in areas with less sunlight, their skin became lighter. This change helped them adapt to their new environments. Some groups later moved back to areas with high UV levels, and their skin became darker again.
Your natural skin color can also get darker if you spend time in the sun. This is called tanning. Tanning happens because your skin makes more melanin to protect itself. This protection helps against UV rays, which can damage the DNA in your skin cells. Damaged DNA can lead to problems like skin cancer.
Skin Color and Vitamin D
It is easy to see why dark skin is helpful in sunny places. It offers good protection against skin cancer. But why is lighter skin helpful in colder, less sunny places? Researchers have a few ideas.
One idea is that lighter skin helps the body make enough vitamin D. Your body makes vitamin D when sunlight touches your skin. Vitamin D is very important for strong bones and overall health. In places with weaker sunlight, lighter skin can absorb more sunlight. This helps the body produce the vitamin D it needs. This change to lighter skin likely started when people moved north from Africa.
Differences Between Genders
Did you know that adult females often have slightly lighter skin than males? This difference might also be linked to vitamin D. Females need more calcium during pregnancy and when they are feeding babies. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. So, females may have developed lighter skin to help their bodies absorb more calcium from sunlight.
Social Importance of Skin Color
Differences in skin color have been seen differently by various cultures throughout history. Sometimes, skin color has been linked to social status or has led to discrimination. It is important to remember that skin color is just one of many human features.
Images for kids
-
Former Chief Justice of India, P. Sathasivam, has vitiligo
See also
 In Spanish: Color de la piel humana para niños
In Spanish: Color de la piel humana para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |