Iligan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Iligan
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Highly urbanized city
|
|||
| City of Iligan | |||
|
Skyline of Iligan from Mount Lelong, pictured in 2023
Andres Bonifacio Avenue
Maria Cristina Falls
Saint Michael's Cathedral
Iligan City Hall
|
|||
|
|||
Nickname(s):
|
|||
| Anthem: Martsa Iliganon (English: Iligan March) |
|||
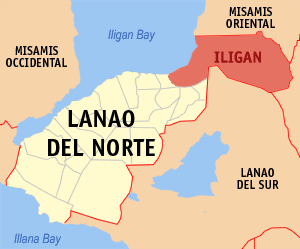
Map of Northern Mindanao with Iligan highlighted
|
|||
|
OpenStreetMap
|
|||
| Country | Philippines | ||
| Region | Northern Mindanao | ||
| Province | Lanao del Norte (geographically only) | ||
| District | [[{{#property:P7938}} | — Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1804: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).]] | ||
| Founded | 1609 | ||
| Chartered | 1914 | ||
| Cityhood | June 16, 1950 | ||
| Highly urbanized city | November 22, 1983 | ||
| Barangays | 44 (see Barangays) | ||
| Government
|
|||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 813.37 km2 (314.04 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 262 m (860 ft) | ||
| Highest elevation | 1,195 m (3,921 ft) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|||
| • Total | 363,115 | ||
| • Density | 446.433/km2 (1,156.255/sq mi) | ||
| • Households | 87,239 | ||
| Demonym(s) | Iliganon | ||
| Economy | |||
| • Gross domestic product | ₱77.015 billion (2022) $1.36 billion (2022) |
||
| • Income class | 1st city income class | ||
| • Poverty incidence |
|
||
| • Revenue | ₱ 3,156 million (2022) | ||
| • Assets | ₱ 13,109 million (2022) | ||
| • Expenditure | ₱ 2,545 million (2022) | ||
| Service provider | |||
| • Electricity | Iligan Light and Power Incorporated (ILPI) | ||
| • Water | Iligan City Waterworks System | ||
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) | ||
| ZIP code |
9200
|
||
| PSGC |
[https://psa.gov.ph/classification/psgc/?q=psgc/barangays/{{#pro000®code={{&provcode=
|
||
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)63 | ||
| Native languages | Maranao Cebuano Binukid Tagalog |
||
| Major religions | Roman Catholicism, Islam | ||
| Website | www |
||
Iligan, officially known as the City of Iligan, is a large and important city in the Northern Mindanao region of the Philippines. In 2020, it had a population of 363,115 people. This makes it the second most populated city in Northern Mindanao, after Cagayan de Oro.
Even though Iligan is located in the province of Lanao del Norte, it is managed separately. It is the largest city in the province by both population and land area. Iligan used to be part of Central Mindanao (Region 12) until 2001, when it moved to Northern Mindanao (Region 10). The city is about 90 kilometers from Tubod, the capital of Lanao del Norte. It is also about 800 kilometers from Manila, the capital of the Philippines.
Iligan covers a total land area of 813.37 square kilometers. This makes it one of the largest cities in the Philippines by land area. Among the big cities in the Philippines, Iligan is not very crowded. It has about 421 people living in each square kilometer.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Iligan comes from the Higaonon word "Ilig." This word means "to go downstream." However, some people believe the name comes from "iligan" or "ilijan." This Higaonon term means "fortress of defense." This name would make sense because the area often faced attacks from pirates and other tribes.
A Look Back in Time
Early Settlements
Iligan was first settled by the Higaonon Manobos. They lived on Bayug island, which is now part of Barangay Hinaplanon. This area is about four kilometers north of the current city center. These early settlers were people who lived by the sea.
In 1565, a local leader named Datu Pagbuaya met with Spanish agents. Later, Pagbuaya's son, Manooc, became a Christian and was named Don Pedro Manuel Manooc. By the end of the 1500s, Manooc took control of the Bayug settlement. He helped it become one of the first Christian communities in the Philippines.
Spanish Influence
Even though Bayug survived attacks from other groups, the early settlers moved. They moved their community to Iligan, which was founded by Augustinian Recollects in 1609. During this time, the Spanish sent soldiers to Iligan for protection.
In 1639, the Jesuits took over from the Recollects. Iligan became a key base for the Spanish. From here, they tried to take control of and spread Christianity around the Lake Lanao area. A stone fort called Fort St. Francis Xavier was built in 1642. People in Iligan used it for safety during raids. However, this fort sank due to floods. Another fort was then built and named Fort Victoria or Cota de Iligan.
In 1850, floods caused problems again. Don Remigio Cabili, who was the leader of Iligan at the time, built a new fort. He also moved the main town area of Iligan to its current location.
Iligan is the oldest town in Northern Mindanao. By 1832, it was already part of the large Misamis Province. However, its church was managed from Misamis, the provincial capital. Iligan was one of the biggest towns in Misamis Province.
The Spanish left Iligan in 1899. Soon after, American forces arrived in 1900.
American Rule
In 1903, the Moro Province was created. Because Iligan had many Moro residents, it was separated from Misamis Province. Iligan then became the capital of the Lanao District. American officials lived and worked there. In 1907, the capital of the Lanao District moved to Dansalan.
In 1914, Iligan became a municipality with eight smaller areas called barrios. This happened after the Moro Province ended. Iligan enjoyed peace for about 40 years. However, Japanese forces invaded the city in 1942 during World War II.
Philippine Commonwealth forces later freed Iligan from Japanese control. This happened between 1944 and 1945, when the war ended. On November 15, 1944, the city celebrated Commonwealth Day. This marked the end of the Japanese occupation.
After World War II
Becoming a City
Iligan officially became a chartered city of Lanao del Norte on June 16, 1950. This was made possible by Republic Act No. 525. The bill was proposed by Mohammad Ali Dimaporo, a congressman from Lanao.
Iligan was declared a first-class city in 1969. It was reclassified as a First Class City "A" in 1977. In 1983, Iligan was again reclassified as a highly urbanized city.
The Iligan Steel Mill
The Iligan Steel Mill was started in 1952. It was a government project by the National Shipyards and Steel Corporation (NASSCO). Later, the company was sold to a private group in 1963.
Challenges and Changes
In the late 1960s, more Christian groups moved to Mindanao. This led to disagreements over land and some violence. The government encouraged local groups to form militias, which were called the Ilaga. This caused lasting tension between different communities.
In 1968, the Jabidah massacre sparked more unrest. Reports of Moro men being killed after joining the army made many feel they were treated unfairly. This led to groups forming to fight for more rights.
In 1972, the Philippines was placed under Martial Law. This period lasted 14 years and brought more challenges. In Iligan, some people who spoke out for human rights faced difficulties. Many brave activists from Iligan worked for change during this time. Some of them were later honored for their efforts to bring back democracy.
Recent History
Economic Recovery
During the 1997 Asian financial crisis, Iligan faced economic problems. Many factories closed, including the National Steel Corporation.
The city's economy started to get better when the National Steel Corporation reopened in 2004. It was renamed Global Steelworks Infrastructures, Inc. (GSII). This was a big step for Iligan. It brought back many jobs and helped the local economy grow again. In 2005, GSII changed its name to Global Steel Philippines (SPV-AMC), Inc. This showed their plan to improve and compete in the steel industry.
A Lone District
On October 20, 2009, Iligan became its own congressional district. This was made possible by Republic Act No. 9724. This change gave Iligan more political independence and a stronger voice. Having its own representative in Congress helps the city address its unique needs. This also helps Iligan get more support and resources for its growth.
Where is Iligan?
Iligan is surrounded by other places. To the north are three towns in Misamis Oriental. To the south are three towns in Lanao del Norte and two towns in Lanao del Sur. To the northeast is the city of Cagayan de Oro. To the east is the town of Talakag, Bukidnon. To the west is Iligan Bay.
Iligan Bay on the west side is used for ferries and cargo ships. East of the city, there are flat farmlands. These lands then rise into steep volcanic hills and mountains. These mountains are where the famous waterfalls and cold springs of the area are found.
Climate and Weather
| Climate data for Iligan, Philippines | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.6 (87.1) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.9 (89.4) |
31.9 (89.4) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.1 (88.0) |
32.8 (91.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.5 (79.7) |
27.1 (80.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 21.7 (71.1) |
21.8 (71.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.6 (72.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 106.1 (4.18) |
90.5 (3.56) |
88.2 (3.47) |
80.2 (3.16) |
145.1 (5.71) |
217.7 (8.57) |
247.9 (9.76) |
342.0 (13.46) |
578.1 (22.76) |
780.0 (30.71) |
299.3 (11.78) |
208.1 (8.19) |
3,183.2 (125.32) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 23.2 | 19.5 | 22.0 | 22.8 | 29.6 | 28.9 | 29.0 | 29.8 | 28.1 | 28.8 | 26.1 | 24.1 | 311.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 390.6 | 370.1 | 545.6 | 573.0 | 378.2 | 225.0 | 229.4 | 254.2 | 246.0 | 294.5 | 360.0 | 421.6 | 4,288.2 |
| Source 1: Average Climate of Iligan City | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Climate of Iligan City | |||||||||||||
Iligan has a climate where the seasons are not very distinct. Rain falls fairly evenly throughout the year. Because it is in a tropical area, the city does not get cold weather. It also avoids strong typhoons because of its location and the mountains around it.
City Divisions: Barangays
Iligan is divided into 44 smaller areas called barangays. Each barangay is further divided into puroks or zones.
- Abuno
- Acmac-Mariano Badelles Sr.
- Bagong Silang
- Bonbonon
- Bunawan
- Buru-un
- Dalipuga
- Del Carmen
- Digkilaan
- Ditucalan
- Dulag
- Hinaplanon
- Hindang
- Kabacsanan
- Kalilangan
- Kiwalan
- Lanipao
- Luinab
- Mahayahay
- Mainit
- Mandulog
- Maria Cristina
- Pala-o
- Panoroganan
- Poblacion
- Puga-an
- Rogongon
- San Miguel
- San Roque
- Santa Elena
- Santa Filomena
- Santiago
- Santo Rosario
- Saray
- Suarez
- Tambacan
- Tibanga
- Tipanoy
- Tomas L. Cabili (Tominobo Proper)
- Upper Tominobo
- Tubod
- Ubaldo Laya
- Upper Hinaplanon
- Villa Verde
People of Iligan
The people of Iligan are called Iliganons. Most of them speak Cebuano. There are also local groups like the Maranaos and Higaonons. Many people from other parts of the Philippines have also moved here. Iligan is known for its mix of different cultures.
Languages Spoken
Cebuano is the most common language. About 92% of people speak it as their first language. Other languages include Maranao, Hiligaynon, and Tagalog. Most people can also speak and understand Tagalog (Filipino) and English. These are the official languages of the country. Tagalog and English are taught in schools in Iligan.
Religions in Iligan
Most people in Iligan are Christians, mainly Roman Catholics. The city is also the center of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Iligan. This diocese covers Iligan City and twelve towns in Lanao del Norte. About 65.5% of the population are Roman Catholics.
Other Christian groups are also present in Iligan. These include Iglesia ni Cristo, Members Church of God International, and Baptist churches. About 24% of residents practice these other Christian faiths.
Muslims are the largest minority group. They make up about 11.48% of the population. Most of them are Sunnites.
Iligan's Economy
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority |
|
Iligan is known as the "Industrial Center of the South." Its economy relies heavily on big industries.
Industries and Factories
Iligan produces hydroelectric power for the Mindanao region. This power comes from plants like Agus V, VI, and VII. These plants are run by the National Power Corporation (NAPOCOR). Holcim Philippines has its largest cement plant in Mindanao here. The city also has factories for steel, tinplate, cement, and flour.
After the Maria Cristina (Agus VI) Hydroelectric Plant was built in 1950, Iligan grew quickly in industry. This growth continued until the late 1980s. The country's largest steel plant, National Steel Corporation (NSC), was also built here in 1962.
Farming and Livestock
Besides big industries, Iligan also grows and exports many plants and crops.
- Banana Plantations: 12,780.40 hectares
- Coconut Plantations: 11,036.95 hectares
- Corn Plantations: 4,193.86 hectares
- Coffee Production: 969.43 hectares
- Livestock: 28,992 heads
- Poultry: 17,728 heads
Fun Things to See and Do
Iligan is often called the "City of Majestic Waterfalls." This is because it has many beautiful waterfalls. There are about 24 waterfalls in the city. The most famous one is Maria Cristina Falls. This waterfall also provides most of the city's electricity.
Other waterfalls to visit include Tinago Falls, which you can reach by climbing 300 steps. There's also Mimbalut Falls, Abaga Falls, and Dodiongan Falls.
Limunsudan Falls is about 50 kilometers from the city center. These are the tallest waterfalls in the Philippines, standing at 265 meters (870 feet) high.
Iligan is also home to the famous San Miguel of Iligan. This is an image of Saint Michael the Archangel. He is often shown wearing a Native American headdress when fighting evil. People from different cultures in Iligan, including Lumad, Moro, and Christians, celebrate a festival for San Miguel. They even have special Eskrima dances dedicated to him. The martial art called San Miguel Eskrima is named after this saint.
How Iligan is Governed
Iligan is a highly urbanized city. This means it is politically separate from the province of Lanao del Norte. People who vote in Iligan do not vote for provincial leaders like the Governor. This is because Iligan became a chartered city in the 1950s.
The city hall, where the local government works, is located at Buhanginan Hills. The local government has one mayor, one vice mayor, and twelve councilors. Each official is elected by the public for a 3-year term. They can be re-elected up to three times in a row. A city administrator handles the daily running of the city.
City Mayors Since 1986
- 1950–1953: Benito S. Ong (Charter Mayor)
- 1954–1955: Benito C. Labao (Appointed)
- 1956–1959: Mariano Ll. Badelles (First Elected Mayor)
- 1960–1984: Camilo P. Cabili
- 1984–1986: Pacificador A. Lluch (by Succession)
- 1986–1987: Alan L. Flores (Appointed OIC-Mayor Designate)
- 1987–1988: Lucio C. Badelles (Appointed)
- 1988 (3 days): Esperidion L. Sagrado (Appointed)
- 1988–1992: Camilo P. Cabili
- 1992–1998: Alejo A. Yañez
- 1998–2004: Franklin M. Quijano
- 2004–2013: Lawrence Ll. Cruz
- 2013–2022: Celso G. Regencia
- 2022–2025; 2025–present: Frederick W. Siao
City Vice Mayors Since 1986
- 1998–2001: Pedro B. Generalao
- 2001–2004: Lawrence Ll. Cruz
- 2004–2013: Henry C. Dy
- 2013–2016: Ruderic C. Marzo
- 2016–2022: Jemar L. Vera Cruz
- 2022–2025: Marianito Dodong D. Alemania
- 2025–present: Wekwek Uy
Getting Around Iligan
Seaports
The Port of Iligan is located on the northern coast of Mindanao, facing Iligan Bay. It serves people and goods coming from Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, parts of Misamis Oriental, and the cities of Iligan and Marawi.
Ships from the Port of Iligan travel to and from Manila, Cebu City, and Ozamiz. There are also about seven private seaports in Iligan. These are run by large industrial companies.
Airports
The main airport for Iligan is Laguindingan Airport. It is located in Laguindingan, Misamis Oriental. This airport opened on June 15, 2013. It replaced Lumbia Airport as the main airport for Northern Mindanao. It has daily flights to and from Manila, Cebu, Davao, Iloilo, and Clark.
Maria Cristina Airport was Iligan's main airport in the late 1980s. However, it closed after an airline stopped its services. Philippine Airlines also used to fly to Iligan but stopped in 1998 due to economic challenges.
Bus Terminals
Iligan has two main bus terminals:
- The Integrated Bus and Jeepney Terminal (IBJT) handles trips going west. These trips go to Cagayan de Oro, Davao, and other parts of Misamis Oriental.
- The Southbound Bus and Jeepney Terminal handles trips going east. These trips go to Dipolog, Pagadian, Cotabato City, Ozamiz, Zamboanga City, and various parts of Lanao del Norte and Marawi.
Bus companies like Rural Transit and Super 5 Land Transport have daily trips to and from Iligan. Vans and jeeps also provide transport to nearby towns.
City Transportation
Within the city, people use jeepneys (both old and new) and pedicabs to get around. Tartanillas (horse-drawn carriages) can be found on main roads in Barangay Pala-o and Barangay Tambacan.
Learning in Iligan
Iligan City has one state university and seven private colleges. These schools offer courses in Engineering, Information Technology, Health Services, Maritime Science, Business, and Education.
With 181 schools, including vocational and technical schools, Iligan has a high literacy rate of 94.71%. This is one of the highest in the Philippines.
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology
The Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology (MSU-IIT) is a top university in the Philippines. It is known for its excellent programs in Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics, and Natural Sciences. Many of its students achieve high scores in national exams.
Colleges in Iligan
- St. Michael's College, Iligan City is the oldest school in the Lanao area. It was founded in 1914. It offers many courses like Business Administration, Nursing, and Engineering.
- St. Peter's College, Iligan City was founded in 1952. It specializes in engineering, accounting, and business.
- Capitol College of Iligan Inc. (ICC) was started in 1963. It is a private school that offers various learning programs.
- Iligan Medical Center College is a private school for Medicine and Health Services. It was founded in 1975.
- Adventist Medical Center College – Iligan focuses on healthcare courses. These include Nursing, Medical Technology, and Pharmacy.
- The Lyceum of Iligan Foundation offers maritime and engineering courses. It also has programs in Hotel and Restaurant Management and Nursing.
- Other notable schools include Iligan Computer Institute (ICI), Santa Monica Institute of Technology (SMIT), and STI College.
Basic Education Schools
- Iligan City National High School is the largest high school in Iligan.
- Lanao Chung Hua School is the first and only Chinese school in Iligan. It was founded in 1938.
- La Salle Academy is a Lasallian school. It was one of the first of its kind founded by the De La Salle Brothers in the country.
- Corpus Christi Parochial School of Iligan is a Catholic private school founded in 1964.
- Iligan City East National High School specializes in research, sciences, and technology. It was founded in 1986.
- The Integrated Developmental School was established in 1946. It became part of MSU-IIT in 1968.
- Del Carmen Integrated School
- Suarez National High School
Famous People from Iligan

- Tomas Cabili – A former Senator and Secretary of National Defense. He was a World War II veteran.
- Salvador T. Lluch (1894–1969) – The first elected Congressman of the Lanao province.
- Gloria Macapagal Arroyo – The 14th President of the Philippines. She also served as Vice President and Speaker of the House.
- Cyrus Baguio – A basketball player in the Philippine Basketball Association.
- Riego Gamalinda – Another basketball player in the Philippine Basketball Association.
- Nikki Bacolod – A singer and TV personality.
- Shamcey Supsup – Miss Universe Philippines 2011 and 3rd runner-up in Miss Universe 2011.
- Kath Arado – A volleyball player for the UE Lady Warriors and PLDT High Speed Hitters.
- Junix Inocian – An international actor and comedian, known as "Kuya Mario" from Batibot.
- Jeson Patrombon – An international tennis player.
- Pia Wurtzbach – Miss Universe 2015. She lived in Iligan briefly as a child.
Sister Cities
Local Connections
 Cagayan de Oro, Misamis Oriental
Cagayan de Oro, Misamis Oriental General Santos, South Cotabato
General Santos, South Cotabato Makati, Metro Manila
Makati, Metro Manila Dipolog, Zamboanga del Norte
Dipolog, Zamboanga del Norte Ozamiz, Misamis Occidental
Ozamiz, Misamis Occidental Butuan, Agusan del Norte
Butuan, Agusan del Norte Tagbilaran, Bohol
Tagbilaran, Bohol
See Also
- List of cities in the Philippines
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Iligan
- Iligan Crusaders
- Iligan Steel Mill
- Mount Agad-Agad
- Timoga Spring