Davao City facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Davao City
Dakbayan sa Dabaw
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Highly urbanized city
|
|||||
|
Poblacion District skyline
People's Park
Davao Cathedral
Davao City Hall
|
|||||
|
|||||
Nickname(s):
|
|||||
| Motto(s):
"Life is Here"
|
|||||
| Anthem: "Tayo'y Dabawenyo" ("We are Davaoeño") | |||||
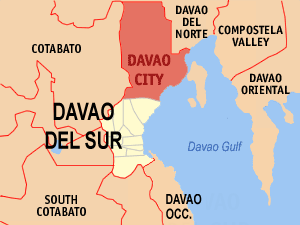
Map of Davao Region particularly Davao del Sur with Davao City highlighted
|
|||||
|
OpenStreetMap
|
|||||
| Country | Philippines | ||||
| Region | Davao Region | ||||
| Province | Davao del Sur (geographically only) | ||||
| District | [[{{#property:P7938}} | — Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1804: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).]] | ||||
| Founded |
|
||||
| Chartered | October 16, 1936 | ||||
| Cityhood | March 16, 1937 | ||||
| Highly urbanized city | December 22, 1979 | ||||
| Founded by |
|
||||
| Barangays | 182 (see Barangays) | ||||
| Government
|
|||||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Highly urbanized city | 2,443.61 km2 (943.48 sq mi) | ||||
| • Urban | 293.78 km2 (113.43 sq mi) | ||||
| • Metro | 3,964.95 km2 (1,530.88 sq mi) | ||||
| Area rank | 1st | ||||
| Elevation | 13 m (43 ft) | ||||
| Highest elevation | 2,909 m (9,544 ft) | ||||
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||||
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|||||
| • Highly urbanized city | 1,776,949 | ||||
| • Rank | 3rd | ||||
| • Density | 727.1819/km2 (1,883.393/sq mi) | ||||
| • Urban | 1,232,958 | ||||
| • Metro | 1,991,457 | ||||
| • Metro density | 502.2654/km2 (1,300.8613/sq mi) | ||||
| • Households | 476,278 | ||||
| Demonyms |
|
||||
| Economy | |||||
| • Gross domestic product (GDP) | ₱595.7 billion (2023) $10.7 billion (2024) |
||||
| • Income class | 1st city income class | ||||
| • HDI | |||||
| • Poverty incidence |
|
||||
| • Revenue | ₱ 17,169 million (2022) | ||||
| • Assets | ₱ 29,701 million (2022) | ||||
| • Expenditure | ₱ 11,029 million (2022) | ||||
| • Liabilities | ₱ 8,462 million (2022) | ||||
| Service provider | |||||
| • Electricity | Davao Light and Power Company (DLPC) | ||||
| • Water | Davao City Water District | ||||
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) | ||||
| ZIP code |
8000 (Davao City), 8016 (Ateneo), 8017 (Bunawan), 8018 (Calinan), 8019 (Davao International Airport), 8020 (Mandug), 8021 (Matina), 8022 (Mintal), 8023 (Talomo), 8024 (Tibungco), 8025 (Toril), 8026 (University of Mindanao)
|
||||
| PSGC |
[https://psa.gov.ph/classification/psgc/?q=psgc/barangays/{{#pro000®code={{&provcode=
|
||||
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)82 | ||||
| Spoken languages | Cebuano Filipino English Hiligaynon |
||||
| Website | www |
||||
Davao City, officially known as the City of Davao, is a very important city in the Davao Region of the Philippines. It covers a huge area of 2,443.61 km2 (943.48 sq mi), making it the largest city in the Philippines by land area. It is also the third-most populated city in the Philippines, after Quezon City and Manila. Davao City is the most populated city in Mindanao and outside of Metro Manila. In 2020, about 1,776,949 people lived there.
Davao City is the main center for trade, business, and industry in Mindanao. It is also the regional center of the Davao Region. The famous Mount Apo, the tallest mountain in the Philippines, can be seen from many parts of Davao City. The city is also known as the "Durian Capital of the Philippines" because of the many durian fruits grown there.
Contents
- What's in a Name?
- A Look Back: Davao City's History
- Exploring Davao City's Geography
- People and Culture of Davao
- Davao's Economy
- Culture and Traditions
- Fun Things to Do: Tourism
- City Government
- Getting Around: Transportation
- City Services: Utilities and Healthcare
- Safety and Rules
- Sports and Recreation
- Learning in Davao: Education
- News and Media
- Davao's Global Connections
- Sister Cities
- Famous People from Davao
- See also
What's in a Name?
The name Davao comes from the local Bagobo people who lived in the area. They had three different names for the Davao River, which flows into Davao Gulf.
- The Obos called it Davah.
- The Clatta (or Giangan/Diangan) called it Dawaw.
- The Tagabawas called it Dabo.
These names blended together to form "Davao." For the Obos, davah also meant "a place beyond the high grounds."
A Look Back: Davao City's History
Early Days
Long ago, the area where Davao City now stands was a thick forest. It was home to different groups of Lumad people, like the Bagobos and Matigsalugs. Other groups like the Aeta and Maguindanaon also lived there. The Davao River was known as Tagloc River.
Spanish explorers first came to Mindanao in 1543. However, they avoided the Davao Gulf area for a long time. This was because of the many Moro warships in the area.
Maguindanao Influence
In the late 1700s, a Maguindanaon leader named Datu Bago was given land around Davao Gulf. He moved there in 1800 and united with local groups. He then took control of the entire Davao Gulf area.
In 1830, Datu Bago built a fort called Pinagurasan. This fort grew into a small city and became a major trading spot. By 1843, Datu Bago was crowned Sultan, making his area independent.
Spanish Arrival and Changes
The Spanish started exploring Davao Gulf in the 16th century, but their real influence began in 1842. The Spanish Governor-General, Narciso Clavería, wanted to colonize the region. This was to gain more resources for Spain.
In 1848, a Spanish expedition led by José Cruz de Oyanguren arrived. They wanted to take over Pinagurasan, Datu Bago's capital. Datu Bago was a strong leader, but he was also disliked by some local tribes. A Mandaya chieftain named Datu Daupan from Samal Island joined forces with the Spanish against Datu Bago.
After a tough three-month battle, the Spanish, with reinforcements, defeated Datu Bago. He and his followers moved further inland. On June 29, 1848, Cruz de Oyanguren founded a new town called Nueva Vergara in honor of his home in Spain. This town later became Davao.
In 1850, the province of Nueva Guipúzcoa was created, with Nueva Vergara as its capital. However, Cruz de Oyanguren's plans for the economy didn't work out, and he was replaced. In 1867, the town was officially renamed Davao.
American Period and Growth
When the Americans took over in 1900, Davao saw many new opportunities. Large areas of land were opened for farming. Foreign business people, especially from Japan, came to Davao. They started big coconut and banana farms.
Davao quickly grew from a small town into a busy economic center. Many people from other parts of the Philippines and Japan moved there. The Port of Davao was opened to help export farm products.
Davao became a part of Moro Province from 1903 to 1914. After that, it became the capital of Davao Province. The current City Hall was built in 1926.
Because of its fast growth, Davao became a charter city on October 16, 1936. This meant it had its own government. It was one of the first two towns in Mindanao to become a city.
World War II
On December 8, 1941, Japanese planes bombed Davao's harbor. Japanese forces landed on December 20 and occupied the city until 1945. Davao was one of the first cities they took over. The city was heavily bombed by American forces before they landed in Leyte in 1944. The Battle of Davao caused a lot of damage to the city.
After the War
After World War II ended in 1945, Davao quickly became an important farming and business center again. Products like wood, coconuts, and bananas were exported. Many Japanese residents stayed and became part of the Filipino community.
In 1967, the Province of Davao was divided into three new provinces. Davao City became part of Davao del Sur. It was no longer a provincial capital but remained a major business hub. In 1967, Elias Lopez, a Bagobo, became the first indigenous mayor of Davao City.
Social Changes and the 1980s
By the late 1960s, Davao became the main city for the Davao Region. However, the late 1960s and 1970s saw some social problems. Many students joined the New People's Army (NPA) due to government issues.
In the 1980s, there was more violence in the city. Some areas became known for conflict. However, many people in Davao wanted peace. Leaders like Archbishop Antonio L. Mabutas spoke out against violence.
Ordinary citizens started to demand change after important events like the assassination of Ninoy Aquino in 1983. People like Soledad Duterte organized groups to protest. This led to the removal of President Marcos in 1986.
Modern Davao
After Marcos was removed, Corazon Aquino appointed Rodrigo Duterte as temporary Vice Mayor. Rodrigo Duterte later became Mayor of Davao City for many years (1988-1998, 2001-2010, 2013-2016). He then became President of the Philippines.
Exploring Davao City's Geography
Davao City is about 946 kilometres (588 mi) southeast of Manila. It is located on the northwestern shore of Davao Gulf, across from Samal Island. You can see Mount Apo and Mount Talomo from the city.
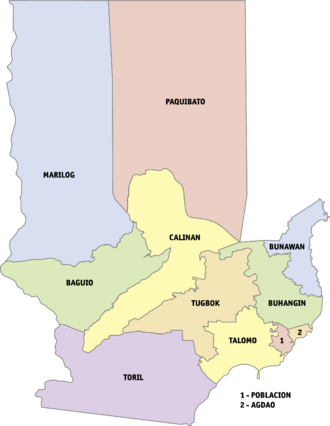
Barangays: City Divisions
Davao City is divided into 11 districts and 182 barangays. Each barangay has smaller areas called puroks or sitios.
Land Features
Davao City's land is hilly in the west (Marilog district) and slopes down to the southeastern coast. Mount Apo, the highest mountain in the Philippines, is at the city's southwestern tip. Mount Apo National Park protects the plants and animals around the mountain.
The Davao River is the city's main river. It is 160-kilometre (99 mi) long and starts in San Fernando, Bukidnon. The river flows into the sea at Barangay Bucana.
Davao's Climate
Davao has a tropical rainforest climate. This means it's warm all year round with lots of rain. The average monthly temperature is always above 26 °C (78.8 °F). It doesn't have a true dry season. The most rain falls during the summer months.
| Climate data for Davao City (1991–2020, extremes 1903–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 35.0 (95.0) |
36.7 (98.1) |
36.7 (98.1) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.3 (99.1) |
35.2 (95.4) |
36.0 (96.8) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.1 (95.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
35.0 (95.0) |
37.3 (99.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.9 (87.6) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.3 (90.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.3 (81.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.4 (83.1) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.2 (82.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.7 (74.7) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
16.1 (61.0) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.1 (66.4) |
16.2 (61.2) |
16.1 (61.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 166.8 (6.57) |
114.4 (4.50) |
106.6 (4.20) |
114.6 (4.51) |
166.2 (6.54) |
192.7 (7.59) |
168.6 (6.64) |
167.4 (6.59) |
162.0 (6.38) |
194.8 (7.67) |
139.7 (5.50) |
141.7 (5.58) |
1,835.5 (72.26) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1 mm) | 11 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 13 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 136 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 80 | 78 | 77 | 80 | 82 | 82 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 81 |
| Source: PAGASA | |||||||||||||
Amazing Plants and Animals
Mount Apo is home to many bird species, with 111 found only in this area. It is also where you can find the critically endangered Philippine eagle, one of the world's largest eagles and the country's national bird. The Philippine Eagle Foundation is located near the city, working to protect these magnificent birds.
Beautiful plants like the waling-waling orchid, known as the "Queen of Philippine Flowers," also grow here. Fruits like mangosteen (the "queen of fruits") and durian (the "king of fruits") are plentiful on Mount Apo.
People and Culture of Davao
In 2020, Davao City had 1,776,949 people. The wider Metro Davao area had about 2.77 million people in 2015. This makes it the third-most populated metropolitan area in the Philippines. Davao City was the first city outside Metro Manila to have over one million people, reaching this number in 1995. The city's population has grown a lot due to people moving there from other parts of the country.
Who Lives in Davao City?
People from Davao City and the Davao Region are called Davaoeños. Most Davaoeños are descendants of settlers from the Visayas region, mainly Cebuanos and Ilonggos. There are also many indigenous people, known as Lumads.
Other groups include Tagalogs, Kapampangans, and Ilocanos from Luzon. Moro groups like the Maguindanaons and Maranaos also live here. Davao City also has communities of Chinese Filipinos and Japanese Filipinos. More recently, people from Indonesia, Malaysia, China, Japan, and Korea have settled in Davao.
Languages Spoken
Cebuano is the most common language in Davao City. Filipino (which is based on Tagalog) is the second most spoken language. English is used in schools and is understood by most people.
Other languages spoken include Chavacano Davaoeño and Hiligaynon. Indigenous languages like Giangan and Tagabawa are also spoken. You might also hear Philippine Hokkien and Japanese in private conversations among Chinese and Japanese Filipinos.
Religion in Davao
Most people in Davao City are Roman Catholic Christians, making up 78% of the population. Islam is the next largest religion, at 4%. Other Christian groups and other faiths like Sikhism, Hinduism, and Buddhism are also present.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Davao is the main Catholic center in southern Mindanao. Saint Peter, known as San Pedro, is the patron saint of the city.
Davao's Economy
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority |
|
Davao is a key part of the East Asian Growth Area, which helps countries in Southeast Asia work together economically. Davao City has one of the largest city economies in Mindanao.
Industries and Products
Farming is the biggest part of Davao's economy. The city has large farms for bananas, pineapples, coffee, and coconuts. It is a top exporter of fruits like mangoes, pomeloes, bananas, and papayas.
The chocolate industry is also growing in Davao. Malagos Chocolate, made here, is a famous artisan chocolate. Seed Core Enterprises is a major exporter of cacao beans. Durian is also a notable export. Big local and international companies like Dole and Del Monte have offices here.
The Davao Gulf provides a living for many fishers. They catch yellowfin tuna, milkfish, shrimp, and crab. These are sold in markets around the city.
Davao City is also a major center for trade and industry in Mindanao. Phoenix Petroleum, a large oil company, is based here. Many industrial plants, like those for soft drinks and steel, are located in the city. The SteelAsia plant is the largest and most modern steel mill in the country.
Shopping and Business Centers
BDO Network Bank is based in Davao City and is the largest rural bank in the Philippines. Many shopping centers are found throughout the city.
- Gaisano Mall of Davao opened in 1997.
- Abreeza opened in 2011 and is the first and largest Ayala Mall in Mindanao.
- SM Lanang Premier is the first SM Premier Mall in Mindanao.
- SM City Ecoland was the first SM Mall in the city.
- NCCC Mall VP (formerly Victoria Plaza Mall) is the oldest mall, opened in 1992.
New malls are also being built, showing the city's growth.
Culture and Traditions
Different Influences
Like many cities in the Philippines, Christianity is widely practiced due to Spanish influence. You can find many churches and chapels. There are also temples and mosques for other religions.
A Spanish tradition still celebrated is the fiesta, a festival for each village's patron saint. These celebrations include singing and dancing.
The biggest local celebration is the Kadayawan Festival in August. It used to be a harvest festival. Today, it celebrates the cultures of the indigenous tribes around Davao City. During this time, many tribal people visit the city. The festival features native dances and art exhibits.

Davao Chinatown is where most of the Chinese community lives. It has its own seaport, Santa Ana Wharf.
Japanese culture also has a strong presence, especially in Barangay Mintal. There's a Japanese cemetery and shrine there. Many Japanese-owned businesses operate in the city. The Philippine Nikkei Jin Kai International School is a Japanese-run school in Davao City.
Local Food
Davao City's food often includes grilled meats. A popular dish is kinilaw, which is raw fish (like tuna) marinated in vinegar with cucumber and chili. Sinuglaw mixes grilled pork belly with kinilaw.
Fruit dishes and desserts are also very popular, especially those made from durian and bananas.
Fun Things to Do: Tourism
Davao is a great place to visit! You can see the Philippine eagle at the Philippine Eagle Foundation. The beautiful waling-waling orchid and delicious fruits like durians and mangosteens are also popular.
Tourist spots include:
- Philippine Eagle Foundation and Nature Center
- Mount Apo
- Gap Farming Resort
- Davao Crocodile Park
- Malagos Garden Resort
- Eden Nature Park
- People's Park in the city center, known for its sculptures and dancing fountain.
Samal Island, just off the coast, is famous for its beautiful beaches.
Davao City has several annual festivals:
- Araw ng Dabaw (Day of Davao) on March 1, celebrating the city's founding.
- Kadayawan Festival in August.
- Pasko Fiesta sa Davao throughout December, with Christmas lights and performances.
- Torotot Festival on New Year's Eve, where people blow party horns. This started in 2013 to make up for the city's firecracker ban.
- Duaw Davao (Visit Davao) in June, showcasing the city's attractions and music.
In 2011, over 1 million tourists visited Davao City.
City Government
Davao City has 182 barangays and three legislative districts. The city government is planning to add another district as the population grows.
As of June 30, 2025, the Mayor of Davao City is Rodrigo R. Duterte, and the Vice Mayor is Sebastian "Baste" Z. Duterte.
City Districts
The 182 barangays of Davao City are organized into 3 legislative districts and 11 administrative districts.
Getting Around: Transportation
By Land
You can get around Davao City using multicabs, jeepneys, tricycles, buses, and taxis. Multicabs and jeepneys follow many routes all day and night. Tricycles are used on smaller streets. Taxis in Davao were the first in the Philippines to accept ATM and debit card payments.
Buses connect Davao City to other cities and provinces in Mindanao. You can even take a bus from Davao to places as far as Pasay in Luzon or Tagbilaran in the Visayas.
Road and bridge improvements are ongoing. The Buhangin Underpass was finished in 2003. The city also has a modern traffic management system.
A 28-kilometre (17 mi) monorail project, called the Davao People Mover, is being planned. The Davao City Bypass road project, which aims to reduce travel time, is expected to be completed by 2028. The Davao City Coastal Road is also being built to offer another route and protect the coast.
Mindanao Railway
The first part of the Mindanao Railway is a 100 km (62 mi) railway line. It will connect Tagum, Davao City, and Digos. This project will have 8 stations and is expected to serve 130,000 riders daily.
Davao Public Transport Modernization Project
This project aims to improve public transport in Davao City. It will introduce a city-wide bus system with modern buses and bus stops. This includes 1,000 buses, with some being electric. The goal is to make public transport more comfortable and efficient.
By Sea
Davao is connected to other major cities by ferries. The city has domestic passenger ferries at Sasa International Seaport and Santa Ana Wharf. These are part of the Port of Davao, which is the busiest port in Mindanao. The port handles both local and international shipments.
A new sea route from Davao City and General Santos to Bitung, Indonesia, started recently. This route helps traders from Mindanao export goods like food, electronics, and farm products to Indonesia.
By Air

Francisco Bangoy International Airport, north of the city center, is the main airport for Davao City and the region. It is also the main international airport in Mindanao. Since 2024, the airport has flights to international places like Quanzhou, Singapore, and Doha.
City Services: Utilities and Healthcare
Davao Light and Power Company provides electricity to the city. It is the third-largest electric company in the Philippines. Davao City Water District supplies water, getting it from mountain springs and underground sources.
Healthcare Services
Davao City has 31 hospitals and medical centers. Some of these include Davao Doctors Hospital and Southern Philippines Medical Center. CURE International also runs the Tebow CURE Hospital in Davao City. This hospital provides orthopedic surgeries for children and adults, helping kids with conditions like clubfoot and bone deformities.
Davao City is known for its smoke-free policy since 2002, which was the first in the Philippines.
Safety and Rules
Law and order in Davao City are kept by the Philippine National Police and Task Force (TF) Davao. TF Davao is a special military group that protects the city from threats.
There is a curfew for minors. Businesses must stop selling alcoholic drinks at 1:00 am. Motorcyclists must wear helmets, and vehicles must have working lights. Speed limits are also enforced in the city.
The Public Safety and Security Command Center (PSSCC) is located in Sandawa, Matina. It is the headquarters for 911 and controls 170 CCTV cameras around the city. These cameras monitor roads, downtown areas, and even water levels in rivers.
Davao City has been recognized as a "Most Child-Friendly City" multiple times, including in 2013, 2014, and 2017. The city also won "Best Disaster Risk Reduction and Management" in 2017.
The city has an anti-smoking ordinance and a firecracker ban. From 2015 to 2017, Davao City received a "Seal of Good Local Governance" award.
Sports and Recreation

Davao City has many sports facilities, including the Davao City Recreation Center and the Davao City–UP Sports Complex. The Davao City Sports Complex is the largest and hosted the 2019 National Games.
Local sports teams represent the city in national events, especially in football and basketball.
Learning in Davao: Education
The city government provides free education for primary (grade school) and secondary (high school) levels in public schools. All schools in the city use the K-12 system. Davao City is home to six universities.
News and Media
Major national TV networks like GMA Network and TV5 have local stations in Davao City. There are also local media networks based in the city, such as Davao Christian Broadcasting Channel and Sonshine Media Network International.
Davao City has many local daily newspapers, including the SunStar Davao and the Mindanao Times.
Radio Stations
TV Stations
- TV5 Channel 2 (TV5 Network, Inc.) (also on DTT Channel 18)
- GMA Channel 5 (GMA Network, Inc.) (also on DTT Channel 37)
- Solar Learning Channel 7 (Southern Broadcasting Network) (also on DTT Channel 21)
- RPN Channel 9 (Radio Philippines Network) (also on DTT Channel 24)
- PTV Channel 11 (People's Television Network) (also on DTT Channel 45)
- IBC Channel 13 (Intercontinental Broadcasting Corporation) (also on DTT Channel 17)
- RPN/CNN Philippines Channel-19 (Nine Media Corporation) (also on DTT Channel 25)
- A2Z Channel 20 (ZOE Broadcasting Network and ABS-CBN Corporation) (DTT Channel 20)
- RJTV Channel 23 (Rajah Broadcasting Network)
- Hope Channel Philippines Channel 25 (Hope Channel Philippines) (soon on DTT)
- GTV Channel 27 (GMA Network, Inc.)
- One Sports Channel 29 (TV5 Network, Inc./Nation Broadcasting Corporation)
- BEAM TV-33 (Broadcast Enterprises and Affiliated Media) (also on DTT Channel 31)
- DZRH News Television Channel 33 (Manila Broadcasting Company) (also on DTT Channel 33)
- Net 25 Channel 39 (Eagle Broadcasting Corporation) (also on DTT Channel 39)
- GNN Channel 41 (Golden Nation Network) (also on DTT Channel 41)
- Sonshine TV-43 (Sonshine Media Network International) (also on DTT Channel 19)
Cable TV Providers
- Sky Cable Davao
- Davao Cableworld Network
- Bongao Cable TV
- Cignal TV
- G Sat Direct TV
Davao's Global Connections
Many foreign visitors and people from other countries live in Davao City. Because of this, Japan, China, Malaysia, and Indonesia have opened Consulates-General in the city. Palau and the United States also have consular offices. Other countries like the Czech Republic, Mexico, Austria, Spain, Timor Leste, Denmark, and South Korea have honorary consulates.
Sister Cities
Davao City has "sister city" relationships with other cities around the world. This helps them share culture and ideas.
 Bitung, North Sulawesi, Indonesia
Bitung, North Sulawesi, Indonesia Jinjiang, Fujian, China
Jinjiang, Fujian, China Kauai County, Hawaii, United States
Kauai County, Hawaii, United States Manado, North Sulawesi, Indonesia
Manado, North Sulawesi, Indonesia Nanning, Guangxi, China
Nanning, Guangxi, China Tacoma, Washington, United States
Tacoma, Washington, United States Sennan, Osaka Prefecture, Japan
Sennan, Osaka Prefecture, Japan Hamamatsu, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan
Hamamatsu, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan
Cooperation and Friendship
 Uijeongbu, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea
Uijeongbu, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea Incheon, South Korea
Incheon, South Korea Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan ("environmental sister city")
Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan ("environmental sister city")
Domestic Cooperation
Within the Philippines, Davao City also works with other cities:
- Angeles City
- Basud
- Cabanatuan
- Cebu City
- City of Mati
- Mandaue
- Lapu-Lapu City
- Dapitan
- Iloilo City
- Liloan
- Marikina
- Quezon City
- San Jose del Monte
- San Juan
- Zamboanga City
Famous People from Davao
- Sara Duterte – current Vice President of the Philippines.
- Dennis Uy – a successful business person and diplomat.
- Sebastian Duterte – the 33rd Mayor of Davao City.
- Rodrigo Duterte – the 16th President of the Philippines.
- Bong Go – a senator and politician.
- Claudine Bautista-Lim – a member of the House of Representatives of the Philippines.
- Isidro Ungab – a congressman.
- Mans Carpio – a lawyer and the Second Gentleman of the Philippines.
- Karlo Nograles – a lawyer.
- Migs Nograles – a congresswoman.
- Antonio Carpio – a former associate justice.
- Gladys Reyes – an actress.
- Erich Gonzales – an actress.
- Sharmaine Arnaiz – an actress.
- Chokoleit – an actor and comedian.
- Jona Soquite – a singer and champion of The Voice Teens season 1.
- Apollo Quiboloy – a religious leader.
- Alfredo E. Evangelista – an archeologist.
See also
 In Spanish: Dávao para niños
In Spanish: Dávao para niños
- KJC King Dome
- Francisco Bangoy International Airport
- Tallest buildings in Davao City
- Zarate v. Aquino III